Back
Purpose: Tamoxifen is widely used in transgenic research in mice to induce Cre recombinase activity and achieve conditional gene knockouts1. However administrating tamoxifen to mice is challenging. The commonly used dosing methods are oral gavage or intraperitoneal injection2, which require specialist staff training and can cause pain, distress and adverse effects to the animal. Tamoxifen-containing rodent chow is commercially available; however, the poor palatability of the diet leads to reduced food intake and weight loss of the mice. Current approach to circumvent the problem is the addition of sweeteners to improve palatability but this can affect the metabolic balance of the mice. The aim of this project is to develop a palatable tamoxifen-containing rodent chow by mixing taste masking tamoxifen micropellets with powdered food. Fluidized bed coating is used to produce the micropellets applying a proprietary MicroCoatTM technology.
Methods: Tamoxifen citrate (micronized) was spray layered onto microcrystalline cellulose substrates (MCC, Cellets® 100) to achieve 5% drug loading using an aqueous suspension containing talc and Hypromellose, in a fluidized bed coater (Mini-Glatt®). Mannitol was included in some tamoxifen loading formulations. Tamoxifen citrate-loaded micropellets were coated using an aqueous dispersion of Surelease® (ethyl cellulose) and Hypromellose (METHOCEL® E5) was added to the coating formulation as a pore former at 15-25% w/w. Coating levels of 5-10% were achieved. The MicroCoatTM technology was applied during polymer coating whereby powdered glidant (magnesium stearate) was added into the coating chamber via an external feeding port. Particle size analysis of the coated micropellets was done by sieve analysis. Tamoxifen citrate release from the coated micropellets was measured in 1000 ml pH 3 HCl (mimicking the stomach pH of mice) using USP II apparatus with a paddle speed of 50 rpm at 37°C. Drug concentration was determined using UV spectrophotometer at 275 nm wavelength. The taste masking effectiveness of the coating was determined in water using an “inverting vial” in vitro method whereby the micropellets were dispersed in a small volume (7 ml) of water and tamoxifen citrate release was measured within 30s after 6 inversions of the vial. The tamoxifen citrate-containing rodent feed was obtained by manually (using a spatula) mixing one dose (14mg, 0.04% w/w) of taste masked tamoxifen citrate-loaded micropellets with 35 g of powder rodent feed (400 mg tamoxifen citrate/kg diet) sufficient for feeding 5 mice in one cage) for 2-8 min. The mixture was then divided into five equal weight groups and analysed using HPLC for % recovery and uniformity of mixing.
Results: Tamoxifen Citrate was successfully layered onto MCC cores and coated with a taste masking coating applying the MicroCoatTM technology, with no particle agglomeration and % yield for all coating trials above 99% (proportion of pellets with size < 250 µm). Dissolution of uncoated tamoxifen citrate (micronized and un-micronized particles) was rapid ( >80% release within 45 min) in standard pharmacopeia dissolution test (Figure 1). Micronized tamoxifen citrate dissolution was slower than the un-micronized due to particle agglomeration during the dissolution test. Drug release slowed down after applying the taste masking coating; with increasing pore former concentration or increasing coating thickness, the drug release rate became slower. Figure 1 shows drug release profiles of two formulations: F1: Taste Mask Coated, Coating 5%, Pore former ratio 75:25. F2: Mannitol Loaded, Taste Mask Coated, Coating 10%, Pore former ratio 85:15. After 45 min, F1 showed 95% drug release indicating rapid and complete drug release. Drug release from F2 reached 75% at 45 min. Both formulations would be effective as to achieve immediate tamoxifen citrate release in mice stomach conditions. The in vitro tests for evaluating the taste masking effectiveness of the formulations showed that after 30 s, micropellets with both coating formulations are effective in providing a taste masking barrier with both having a tamoxifen citrate release of less than 0.5% (Table 1). The results of the mixing tests of the micropellets with rodent feed (Table 2) show that the best tamoxifen citrate recovery and mixing uniformity (%RSD) was obtained at 2 min with increasing mixing time reducing the % recovery and uniformity.
Conclusion: Taste masking coated tamoxifen citrate micropellets were successfully manufactured in a fluidized bed applying the MicroCoatTM technology with > 99% yield and particle size < 250 µm. The coating provided effective protection to prevent tamoxifen citrate release in the mouth but immediate drug release in the stomach pH conditions of the mice. Additionally, the small particle size of the coated micropellets ensured effective mixing with the powder rodent feed with excellent recovery and uniformity. The product is flexible in dose adjustment and improves tamoxifen handling safety in animal units, offering an innovative approach of doing tamoxifen to mice for Cre recombination research via voluntary food intake. The method has the potential to reduce suffering and improve welfare of the mice, promoting 3Rs (replacement, reduction and refinement) in animal research.
References: 1. Kim, H., Kim, M., Im, S. and Fang, S., Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes. Laboratory Animal Research, 34(4), p.147, (2018)
2. Andersson, K., Winer, L., Mørk, H., Molkentin, J. and Jaisser, F., Tamoxifen administration routes and dosage for inducible Cre-mediated gene disruption in mouse hearts. Transgenic Research, 19(4), 715-725, (2009)
Acknowledgments: The project is funded by the United Kingdom National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (the NC3Rs) through the CRACK IT challenge – Tat-Fit (project number NC/C020S02/1).
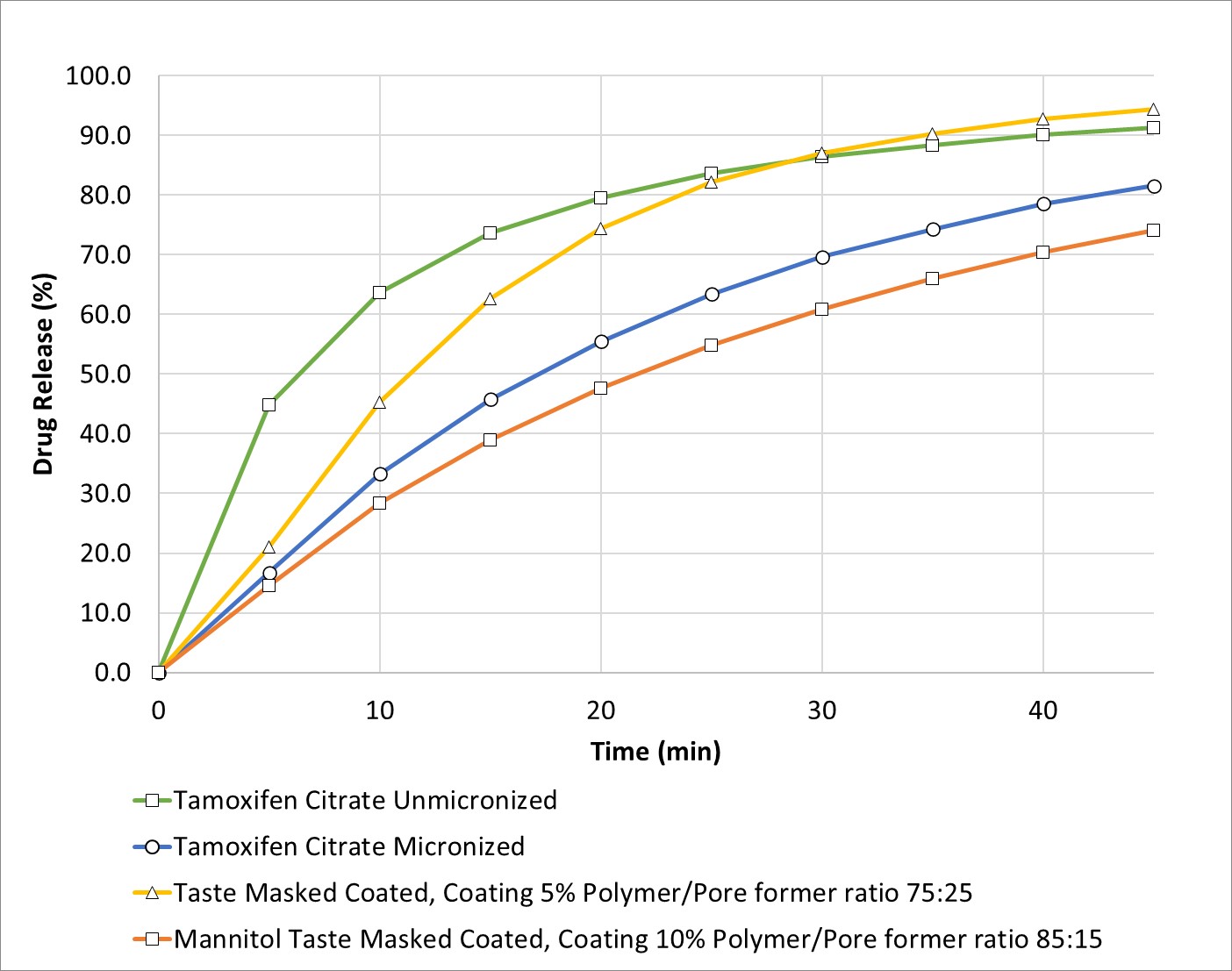
Figure 1: Tamoxifen Citrate Release from taste masking coated micropellets
.jpg)
Table 1: "Inverted Vial" test for Taste Masking Effectiveness Evaluation
.jpg)
Table 2: Mixing Uniformity and % Recovery of micropellets mixed with powder feed at different mixing times
Formulation and Delivery - Chemical - Formulation
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(W1030-03-18) Palatable Tamoxifen Rodent Diet: An Innovative Administration Method in Mice to Achieve Inducible Cre Recombinase
Wednesday, October 19, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:30 AM ET
- AR
Alan Reader, BA
Fluid Pharma
HATFIELD, England, United Kingdom - FL
Fang Liu, Ph.D.
University of Hertfordshire
Hatfield, England, United Kingdom
Main Author(s)
Presenting Author(s)
Purpose: Tamoxifen is widely used in transgenic research in mice to induce Cre recombinase activity and achieve conditional gene knockouts1. However administrating tamoxifen to mice is challenging. The commonly used dosing methods are oral gavage or intraperitoneal injection2, which require specialist staff training and can cause pain, distress and adverse effects to the animal. Tamoxifen-containing rodent chow is commercially available; however, the poor palatability of the diet leads to reduced food intake and weight loss of the mice. Current approach to circumvent the problem is the addition of sweeteners to improve palatability but this can affect the metabolic balance of the mice. The aim of this project is to develop a palatable tamoxifen-containing rodent chow by mixing taste masking tamoxifen micropellets with powdered food. Fluidized bed coating is used to produce the micropellets applying a proprietary MicroCoatTM technology.
Methods: Tamoxifen citrate (micronized) was spray layered onto microcrystalline cellulose substrates (MCC, Cellets® 100) to achieve 5% drug loading using an aqueous suspension containing talc and Hypromellose, in a fluidized bed coater (Mini-Glatt®). Mannitol was included in some tamoxifen loading formulations. Tamoxifen citrate-loaded micropellets were coated using an aqueous dispersion of Surelease® (ethyl cellulose) and Hypromellose (METHOCEL® E5) was added to the coating formulation as a pore former at 15-25% w/w. Coating levels of 5-10% were achieved. The MicroCoatTM technology was applied during polymer coating whereby powdered glidant (magnesium stearate) was added into the coating chamber via an external feeding port. Particle size analysis of the coated micropellets was done by sieve analysis. Tamoxifen citrate release from the coated micropellets was measured in 1000 ml pH 3 HCl (mimicking the stomach pH of mice) using USP II apparatus with a paddle speed of 50 rpm at 37°C. Drug concentration was determined using UV spectrophotometer at 275 nm wavelength. The taste masking effectiveness of the coating was determined in water using an “inverting vial” in vitro method whereby the micropellets were dispersed in a small volume (7 ml) of water and tamoxifen citrate release was measured within 30s after 6 inversions of the vial. The tamoxifen citrate-containing rodent feed was obtained by manually (using a spatula) mixing one dose (14mg, 0.04% w/w) of taste masked tamoxifen citrate-loaded micropellets with 35 g of powder rodent feed (400 mg tamoxifen citrate/kg diet) sufficient for feeding 5 mice in one cage) for 2-8 min. The mixture was then divided into five equal weight groups and analysed using HPLC for % recovery and uniformity of mixing.
Results: Tamoxifen Citrate was successfully layered onto MCC cores and coated with a taste masking coating applying the MicroCoatTM technology, with no particle agglomeration and % yield for all coating trials above 99% (proportion of pellets with size < 250 µm). Dissolution of uncoated tamoxifen citrate (micronized and un-micronized particles) was rapid ( >80% release within 45 min) in standard pharmacopeia dissolution test (Figure 1). Micronized tamoxifen citrate dissolution was slower than the un-micronized due to particle agglomeration during the dissolution test. Drug release slowed down after applying the taste masking coating; with increasing pore former concentration or increasing coating thickness, the drug release rate became slower. Figure 1 shows drug release profiles of two formulations: F1: Taste Mask Coated, Coating 5%, Pore former ratio 75:25. F2: Mannitol Loaded, Taste Mask Coated, Coating 10%, Pore former ratio 85:15. After 45 min, F1 showed 95% drug release indicating rapid and complete drug release. Drug release from F2 reached 75% at 45 min. Both formulations would be effective as to achieve immediate tamoxifen citrate release in mice stomach conditions. The in vitro tests for evaluating the taste masking effectiveness of the formulations showed that after 30 s, micropellets with both coating formulations are effective in providing a taste masking barrier with both having a tamoxifen citrate release of less than 0.5% (Table 1). The results of the mixing tests of the micropellets with rodent feed (Table 2) show that the best tamoxifen citrate recovery and mixing uniformity (%RSD) was obtained at 2 min with increasing mixing time reducing the % recovery and uniformity.
Conclusion: Taste masking coated tamoxifen citrate micropellets were successfully manufactured in a fluidized bed applying the MicroCoatTM technology with > 99% yield and particle size < 250 µm. The coating provided effective protection to prevent tamoxifen citrate release in the mouth but immediate drug release in the stomach pH conditions of the mice. Additionally, the small particle size of the coated micropellets ensured effective mixing with the powder rodent feed with excellent recovery and uniformity. The product is flexible in dose adjustment and improves tamoxifen handling safety in animal units, offering an innovative approach of doing tamoxifen to mice for Cre recombination research via voluntary food intake. The method has the potential to reduce suffering and improve welfare of the mice, promoting 3Rs (replacement, reduction and refinement) in animal research.
References: 1. Kim, H., Kim, M., Im, S. and Fang, S., Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes. Laboratory Animal Research, 34(4), p.147, (2018)
2. Andersson, K., Winer, L., Mørk, H., Molkentin, J. and Jaisser, F., Tamoxifen administration routes and dosage for inducible Cre-mediated gene disruption in mouse hearts. Transgenic Research, 19(4), 715-725, (2009)
Acknowledgments: The project is funded by the United Kingdom National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (the NC3Rs) through the CRACK IT challenge – Tat-Fit (project number NC/C020S02/1).

Figure 1: Tamoxifen Citrate Release from taste masking coated micropellets
.jpg)
Table 1: "Inverted Vial" test for Taste Masking Effectiveness Evaluation
.jpg)
Table 2: Mixing Uniformity and % Recovery of micropellets mixed with powder feed at different mixing times
