Back
Purpose: The purposes of this project are 1) to develop quantitative analysis methods for Kollidon VA-64 (PVPVA) and surfactants in the dissolution medium, 2) to evaluate the release profiles of compound X and Y, polymer, and surfactants from amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) formulations to gain insight of ASD release mechanism1.
Methods: The ASD tablets of compound X and Y were chosen as the pilot cases. Three methods were developed and evaluated for fit-for-purpose to selectively quantify PVPVA, Polysorbate 80 (Tween 80) and D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS) at expected levels in dissolution media in the presence of compound X and Y. The PVPVA method was developed using a Waters Aquity Advanced Polymer Chromatography (APC) system with an UV detector and verified with the presence of both compound X and Y, surfactants, and dissolution media. The Tween 80 method was developed using HPLC with a CAD detector and verified with the presence of compound X and PVPVA. The TPGS method was developed using HPLC with UV detector based on the literature2 and verified in the presence of both compound Y and PVPVA. The dissolution tests of compound X and Y tablets were performed using a two-stage non-sink method with USP apparatus 2 previously developed for compound X and Y. This non-sink method uses 0.1 N HCl as the stage 1 medium and 50 mM pH 6.8 phosphate buffer as the stage 2 medium, and peak vessel with flute disks to enhance hydrodynamics. The non-sink method was used primarily because it has resulted in the similar rank order to in vivo performance of compound X and Y prototype formulations.
Results: The quantitation methods for PVPVA, Tween 80 and TPGS were developed and the release profiles of compounds X and Y, polymer and surfactant for compound X and Y tablets were generated. In all three compound X formulations i.e., 12%, 20%, and 25% drug load (DL), PVPVA reaches complete release at around 2 hours (Figure 1). The preliminary results of compound X 12% and 20% DL formulations indicate that PVPVA is released at a comparable rate to the compound X (Figure 1a and 1b). The release rate of PVPVA is faster than the release of compound X for the 25% DL formulation alone (Figure 1c). Tween 80 release rate is comparable to PVPVA for the 12% drug load formulation, which is as expected since it is a highly soluble surfactant (Figure 1a) (Tween 80 release profiles were not yet generated for the 20% DL and 25% DL formulations). Regarding compound Y, similar release rates were seen between compound Y and both relevant excipients (TPGS and PVPVA, Figure 2).
Conclusion: The preliminary results from three prototype compound X formulations indicated the 25% DL release mechanism is different from the release mechanism for 12% DL and 20% DL formulations. The 25% DL appears be more closely exhibiting behavior of drug-controlled release whereas the 12% and 20% DL formulations have much similar release profiles between PVPVA and compound X, indicating congruent release of compound X and PVPVA1.In the case of compound Y, the release rate of compound Y, PVPVA and TPGS are all comparable, suggesting the release mechanism is most likely dissolution-controlled release, i.e., congruent release. Moving forward, we aim to apply the excipient release tools in the understanding of ASD formulation release mechanisms to improve the drug product development process.
References: 1. Schittny A, et al. Drug Delivery 2020, Vol 27, No 1, 110-127
2. L.Y. Kong, et al. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218 (2011) 8664– 8671
Acknowledgments: Weili Wang, Jessica Hoskins, Matthew Gragg, Tzuchi Ju and Russel Hertzler are employees of AbbVie and may own AbbVie stock. Vivien Ho and Nishal Patel are contract employees of AbbVie and have no other conflicts of interest to report. AbbVie sponsored and funded the study; contributed to the design; participated in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and in writing, reviewing, and approval of the final publication.
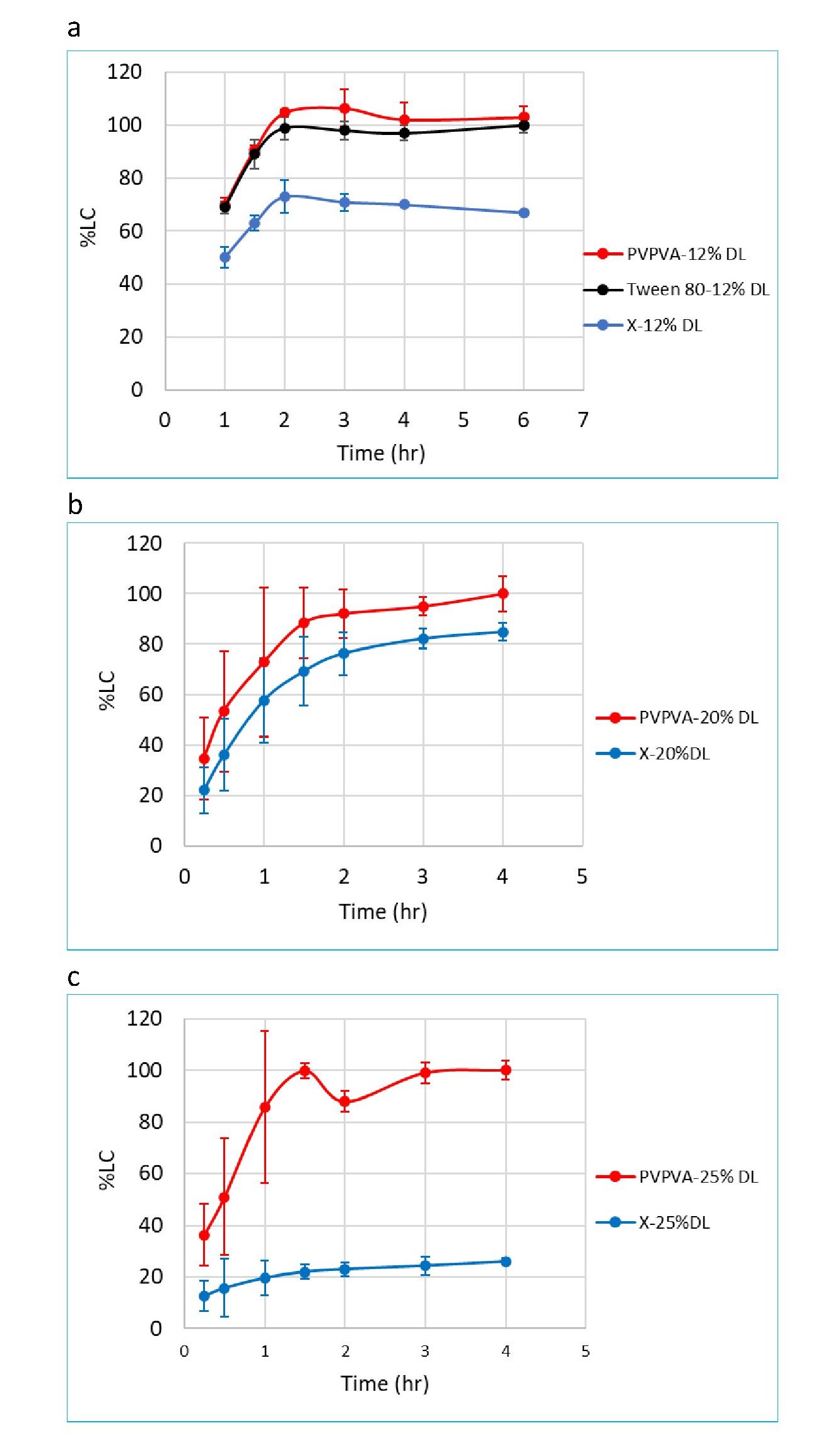
Figure 1. Simultaneous Dissolution Profile of Compound X, PVPVA, and Tween 80 in three Prototype formulations (Mean ± Standard Deviation, N=3). a) 12% DL b) 20% DL c) 25% DL
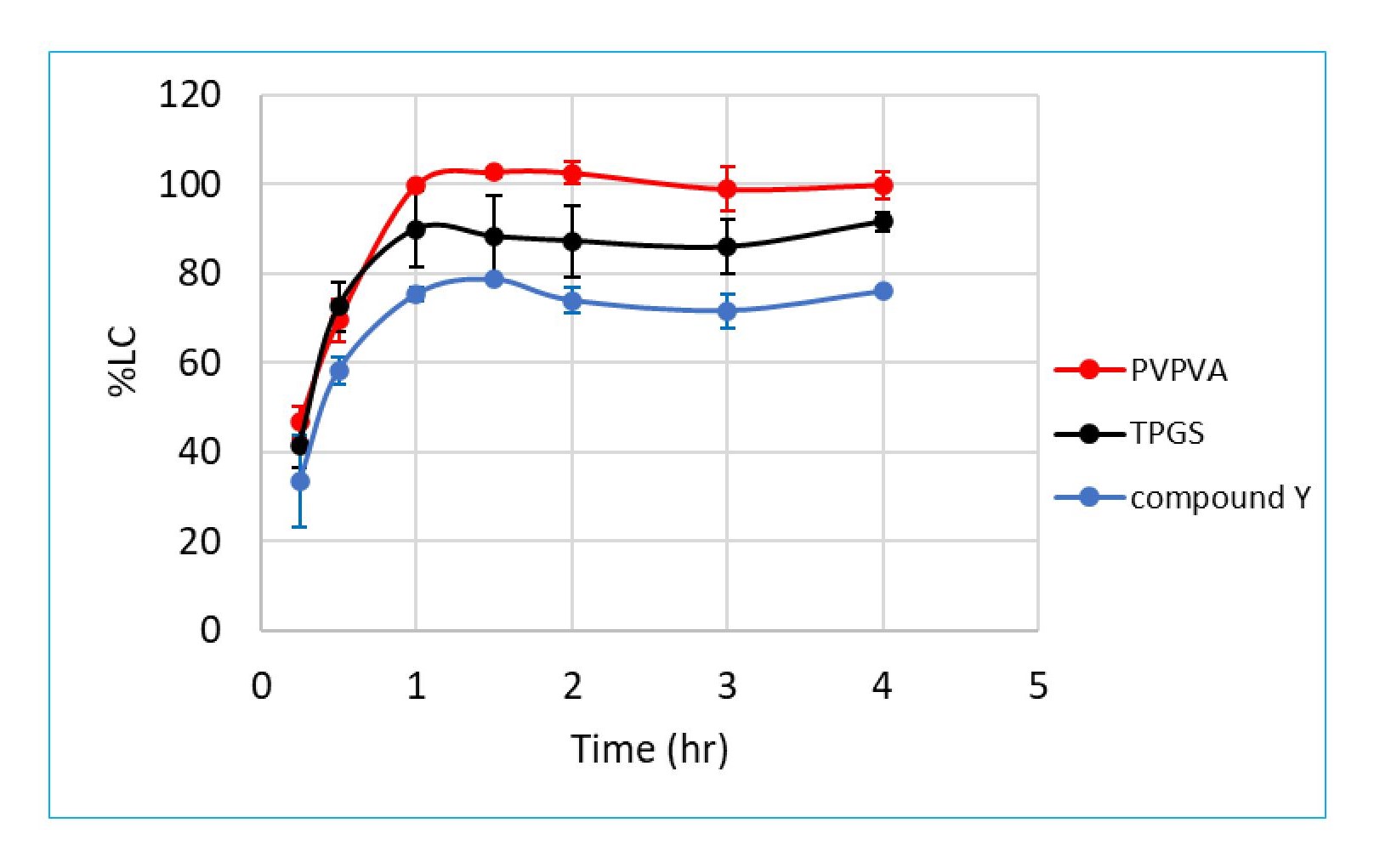
Figure 2. Simultaneous Dissolution Profile of Compound Y, PVPVA and TPGS from Compound Y Tablets (Mean ± Standard Deviation, N=3)
Manufacturing and Analytical Characterization - Chemical - Analytical
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(T1130-08-47) Building Fundamental Understanding of Drug Release Mechanisms via Release of Functional Excipients
Tuesday, October 18, 2022
11:30 AM – 12:30 PM ET
- WW
Weili Wang, MS
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, Illinois, United States - WW
Weili Wang, MS
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, Illinois, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: The purposes of this project are 1) to develop quantitative analysis methods for Kollidon VA-64 (PVPVA) and surfactants in the dissolution medium, 2) to evaluate the release profiles of compound X and Y, polymer, and surfactants from amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) formulations to gain insight of ASD release mechanism1.
Methods: The ASD tablets of compound X and Y were chosen as the pilot cases. Three methods were developed and evaluated for fit-for-purpose to selectively quantify PVPVA, Polysorbate 80 (Tween 80) and D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS) at expected levels in dissolution media in the presence of compound X and Y. The PVPVA method was developed using a Waters Aquity Advanced Polymer Chromatography (APC) system with an UV detector and verified with the presence of both compound X and Y, surfactants, and dissolution media. The Tween 80 method was developed using HPLC with a CAD detector and verified with the presence of compound X and PVPVA. The TPGS method was developed using HPLC with UV detector based on the literature2 and verified in the presence of both compound Y and PVPVA. The dissolution tests of compound X and Y tablets were performed using a two-stage non-sink method with USP apparatus 2 previously developed for compound X and Y. This non-sink method uses 0.1 N HCl as the stage 1 medium and 50 mM pH 6.8 phosphate buffer as the stage 2 medium, and peak vessel with flute disks to enhance hydrodynamics. The non-sink method was used primarily because it has resulted in the similar rank order to in vivo performance of compound X and Y prototype formulations.
Results: The quantitation methods for PVPVA, Tween 80 and TPGS were developed and the release profiles of compounds X and Y, polymer and surfactant for compound X and Y tablets were generated. In all three compound X formulations i.e., 12%, 20%, and 25% drug load (DL), PVPVA reaches complete release at around 2 hours (Figure 1). The preliminary results of compound X 12% and 20% DL formulations indicate that PVPVA is released at a comparable rate to the compound X (Figure 1a and 1b). The release rate of PVPVA is faster than the release of compound X for the 25% DL formulation alone (Figure 1c). Tween 80 release rate is comparable to PVPVA for the 12% drug load formulation, which is as expected since it is a highly soluble surfactant (Figure 1a) (Tween 80 release profiles were not yet generated for the 20% DL and 25% DL formulations). Regarding compound Y, similar release rates were seen between compound Y and both relevant excipients (TPGS and PVPVA, Figure 2).
Conclusion: The preliminary results from three prototype compound X formulations indicated the 25% DL release mechanism is different from the release mechanism for 12% DL and 20% DL formulations. The 25% DL appears be more closely exhibiting behavior of drug-controlled release whereas the 12% and 20% DL formulations have much similar release profiles between PVPVA and compound X, indicating congruent release of compound X and PVPVA1.In the case of compound Y, the release rate of compound Y, PVPVA and TPGS are all comparable, suggesting the release mechanism is most likely dissolution-controlled release, i.e., congruent release. Moving forward, we aim to apply the excipient release tools in the understanding of ASD formulation release mechanisms to improve the drug product development process.
References: 1. Schittny A, et al. Drug Delivery 2020, Vol 27, No 1, 110-127
2. L.Y. Kong, et al. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218 (2011) 8664– 8671
Acknowledgments: Weili Wang, Jessica Hoskins, Matthew Gragg, Tzuchi Ju and Russel Hertzler are employees of AbbVie and may own AbbVie stock. Vivien Ho and Nishal Patel are contract employees of AbbVie and have no other conflicts of interest to report. AbbVie sponsored and funded the study; contributed to the design; participated in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and in writing, reviewing, and approval of the final publication.

Figure 1. Simultaneous Dissolution Profile of Compound X, PVPVA, and Tween 80 in three Prototype formulations (Mean ± Standard Deviation, N=3). a) 12% DL b) 20% DL c) 25% DL

Figure 2. Simultaneous Dissolution Profile of Compound Y, PVPVA and TPGS from Compound Y Tablets (Mean ± Standard Deviation, N=3)
