Formulation and Delivery - Chemical - Biopharmaceutics
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(M1530-03-14) A New Modelling Framework for pH-Sensitive Solid Dispersions Release and Dissolution
- GL
Guillaume Louit, Ph.D.
Siemens Process Systems Engineering
Shin-Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan - GL
Guillaume Louit, Ph.D.
Siemens Process Systems Engineering
Shin-Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) is a polymeric excipient originally developed for enteric formulation that has now become a carrier of choice for solid dispersion, thanks to its ability to allow for an efficient release and extend of dissolution of low solubility synthetics active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) while often avoiding reprecipitation of the stable crystalline form. On the other hand, its pH sensitivity and hydrophobic properties renders its behaviour in solution more complex and choosing the right grade (primarily defined by succinyl and acetyl groups proportions) is arguably more time and API consuming. The purpose of this research was to propose and illustrate a new modelling framework for solid dispersion dissolution depending on polymer and API composition, in order to (1) allow scientists to understand better the interplay of different physical mechanisms and (2) allow for reduced lab experiments to accelerate low solubility drug development.
Methods: We have used the FormulatedProducts software (gPROMS platform) to model in vitro experiments of solid dispersion dissolution experiments in artificial buffers with/without bile salts including the following phenomena (shown as Image 1 scheme):
- Release of the API triggered by polymer carrier dissolution extent (pH dependent) and surface offered
- Primary particles dissolution modelled as solubility/diffusion limited including solid surface equilibria for all species (notably buffers and bile salts), with particle size treated as population balance
- Acid-base equilibria in bulk including effect of buffer strength and effect of polymer acidic groups
- Complex/micelle formation reactions (treated either as fast equilibrium occurring at solid surface or forward/backward reactions in the bulk only)
- supersaturation-based independent nucleation and growth mechanisms, as well as dissolved polymer modulation (EC50-like relationship)
Once the framework was established, the model was tested on published data concerning nifedipine solid dispersions produced from different grades of HPMCAS manufactured by Shin-Etsu [1]. The overall workflow is presented on Image 2. To obtain the necessary parameters for API, polymer and API-polymer interaction, published data was collected regarding polymer dissolution or solubility [1,2], HPMCAS influence on solubility of nifedipine in water [3] and supersaturation properties of pure nifedipine [1,4]. Amorphous solubility and influence of polymer succinyl group proportion on nucleation were estimated from three batches out of the nine documented in the nifedipine solid dispersion publication [1]. The performance of the model to reproduce the results of the 6 other batches was evaluated, and a global system analysis was conducted varying Succinyl group percentage and API loading.
Results: Validation of the model predictive power is presented on Image 3. The behaviour of high solubility LF batches vs low solubility and MF batches was correctly captured quantitatively: For Batch A (highest succinyl group percentage), fast dissolution and short supersaturation (50% reprecipitated in 30min) was predicted and is the most unwanted behaviour. For batches E and F (using MF grade with 10-11% succinyl groups) have an “ideal” behaviour of fast release and dissolution with maintained supersaturation. Using more than 3 batches for parameter estimations did not change very significantly the model accuracy, which indicates that using the framework could potentially avoid several manufacturing and dissolution experiments while allowing an improved mechanistic understanding of the system. The global system analysis allowed to determine that the optimum percentage of succinyl groups for the nifedipine SD should be between 8% and 15%, which corresponds mostly to the range of MF grade.
Conclusion: This work shows that the integration to a modelling framework of a relatively small amount of experimental data - consisting of simple solubility and solution precipitation measurements in absence and presence of polymer as well as a handful of solid dispersion technical batches - can allow to extrapolate effectively to other polymer grades and contributes to explain the drivers of dissolution and precipitation kinetics.
References: [1] Shin Etsu “Effect of substitution of Shin-Etsu AQUOT (HPMCAS) on dissolution profile of Nifedipine solid dispersions prepared by melt extrusion” in Cellulose and pharmaceutical excipients (2018) A-032 rev4
[2] B. Li, LA. Wegiel, LS. Taylor, K.J. Edgar “Stability and solution concentration enhancement of resveratrol by solid dispersion in cellulose derivative matrices” Cellulose (2013) p1249-1260 -
[3] K. Ueda, K. Higashi, K. Yamamoto, K. Moribe, “The effect of HPMCAS functional groups on drug crystallization from the supersaturated state and dissolution improvement” International Journal of Pharmaceutics 464 (2014) 205–213
[4] S. Wang, C. Liu, & H. Chen & A. Zhu2 & F. Qian, “Impact of Surfactants on Polymer Maintained Nifedipine Supersaturation in Aqueous Solution”, Pharmaceutical Research (2020) 37:113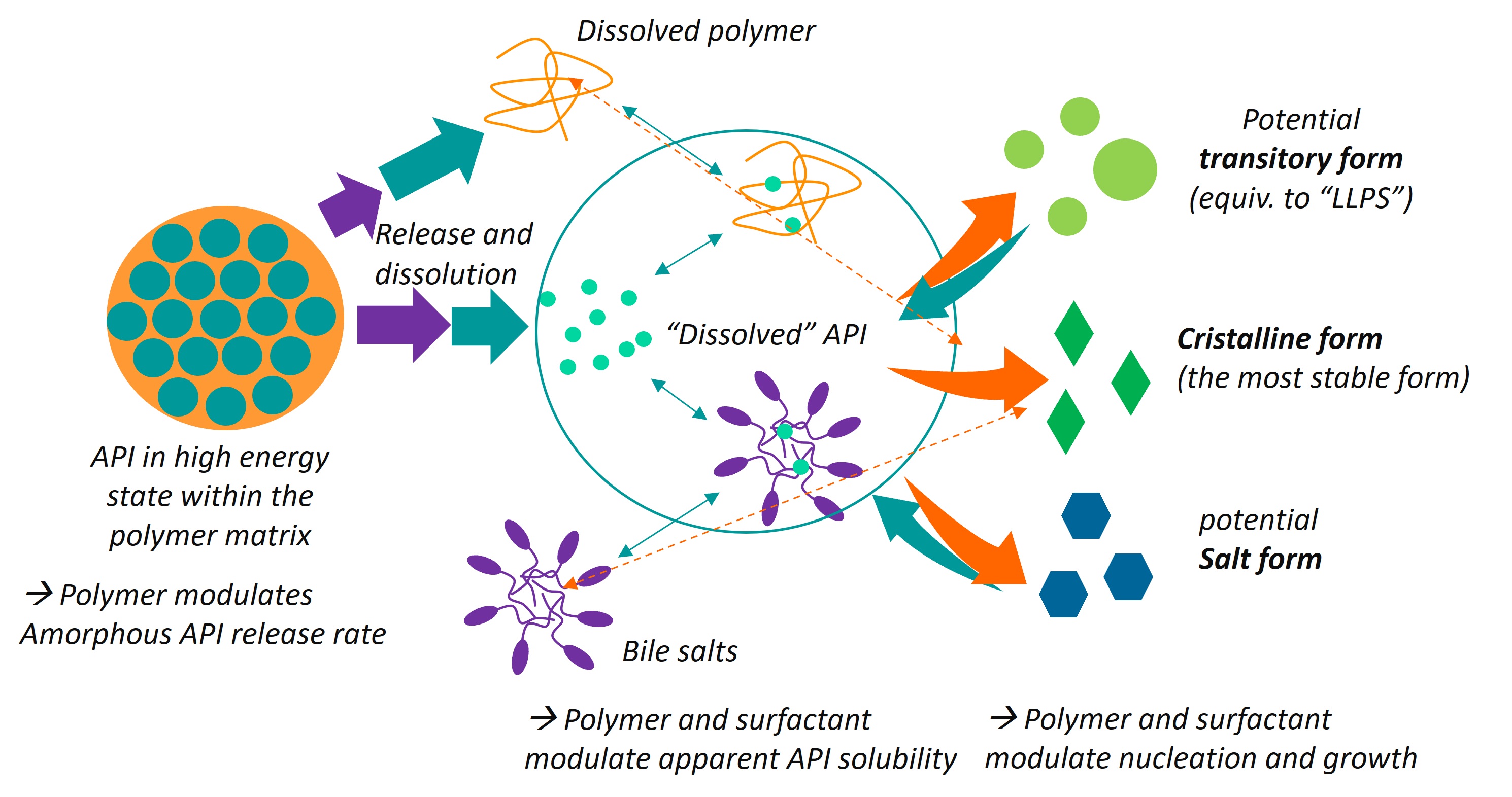
Possible solid forms and interactions part of the modelling framework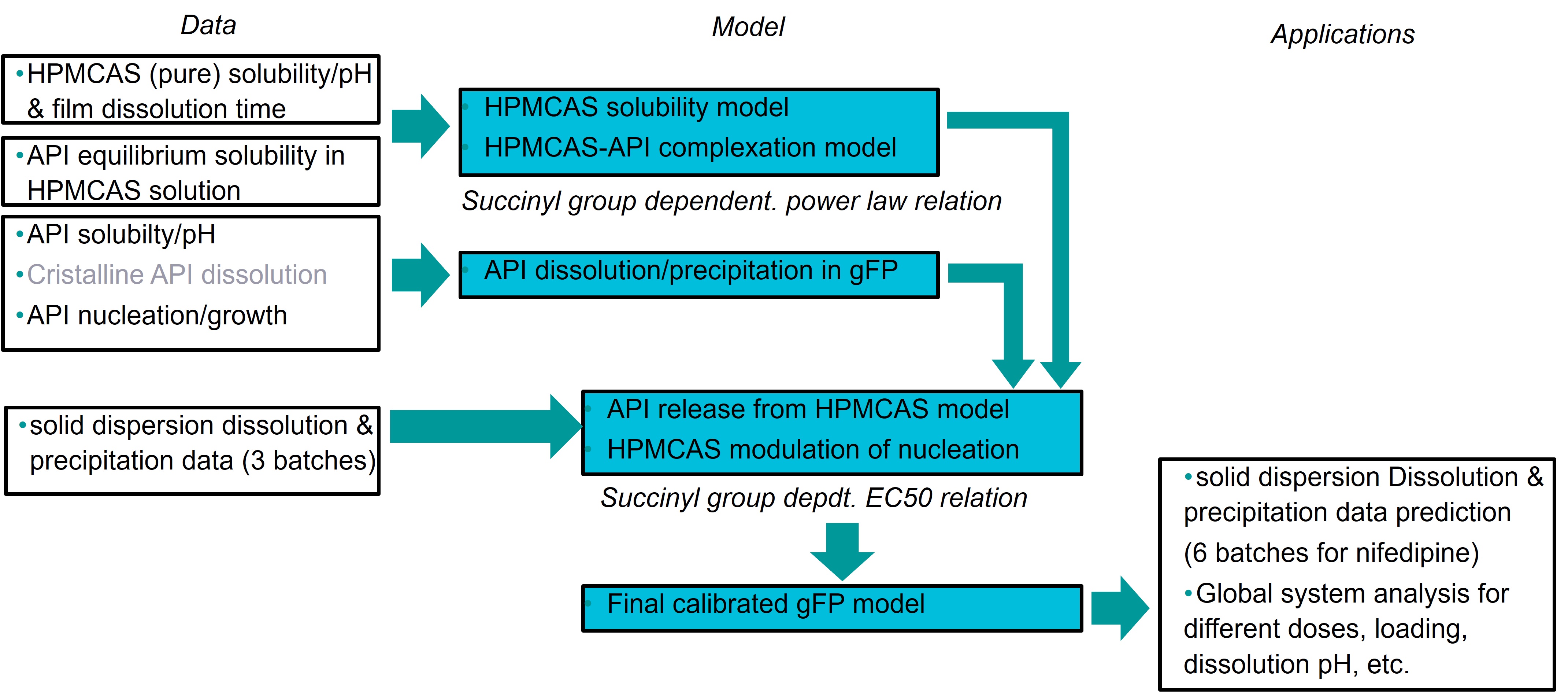
Workflow of data type integration to the model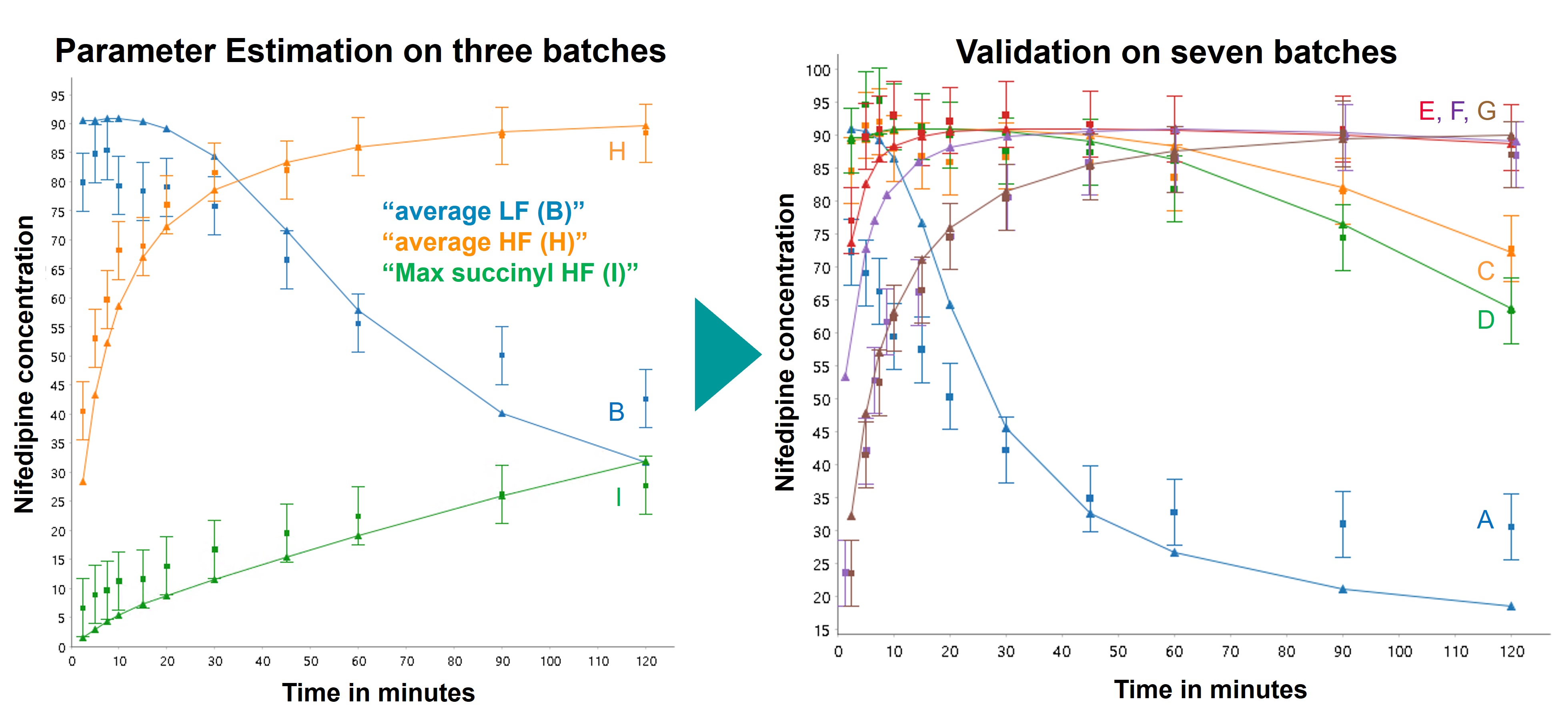
Model results on nifedipine dissolution data
