Back
Purpose: Direct compression is the simplest method for tablet manufacturing involving blending of the active with suitable excipients to achieve desired powder and tablet properties. When formulating low-dose drugs, achieving good content uniformity (CU) becomes a primary critical quality attribute (CQA) for the tablets. The objective of this work was to study the impact of critical process parameters (CPPs) around tablet compression on selected quality attributes of a low dose model drug, glimepiride, for a directly compressible formulation.
Methods: Glimepiride was used as a model low-dose drug with 1 mg strength. Since glimepiride is poorly water-soluble, lactose monohydrate was selected as a diluent. StarTab®, a novel directly compressible starch was used to provide good flow, compressibility, and disintegration property to the tablet. Tablet manufacturing: Glimepiride, StarTab and lactose monohydrate was passed through ASTM #40 screen, then mixed in a blender for 10 mins at 20 rpm followed by lubrication for 2 min with magnesium stearate after passing through ASTM #60 screen. The powder blend was evaluated for bulk density, tap density, powder flow and drug uniformity (n=10) from different positions within the blender. Tablets were compressed using Cadmach 26 stations compression machine (model- CTX-26D) using 6.00 mm standard concave tooling and tested for weight, hardness, thickness, friability, and disintegration time followed by determination of CU in individual tablets (n=10). Compression Parameters: Twelve trials were conducted to study the impact of compression parameters such as turret speed, feeder speed and compression force (Table 2) on tablet hardness, friability, disintegration time, content uniformity and dissolution (CQAs). Considering operating ranges of 12 to 70 rpm and 10 to 60 rpm for turret and feeder speed, for evaluation 25 and 50 rpm were respectively selected. The main compression forces of 2.5 and 6.5 kN were used.
Results: Powder blend showed satisfactory powder flow properties in comparison with the API alone and the blend uniformity samples taken from 10 different positions of blender such as top, middle, and bottom were found to be within the accepted limit (95-105%) with L1 value of 2.76 and % RSD of 1.14. a. Tablet Physical Properties: All tablets showed good hardness between 2.6 to 6.4 kP based on compression force in each run and low friability of 0.24-0.32% at 100 rotations. The disintegration time was from 20 seconds (compression force 2.5 kN) to 1.8 min (compression force 6.5 kN) and the overall tablet output of 640 to 650 units/ min and 1295 to 1310 units/ min was achieved at 25 and 50 rpm of turret speed, respectively. b. Tablet Content Uniformity: Drug content for 10 individual tablets from the 12 experimental runs was determined, and Acceptance Value (AV) was less than 6 in all compression trials suggesting very good drug uniformity in all tablets (Figure 1). c. Drug Dissolution: No significant difference in the dissolution profile was observed in all compression trials with more than 85% drug release obtained within 20 mins. d. Optimized Trial: The results confirmed that at lower turret to feeder speed ratios, 25:25 and 50:25, the AV is on lower side 1.60 to 3.06 whereas at higher ratios, 25:50 and 50:50, the AV value is on higher side 4.09 to 7.02. Thus, feeder speed had a significant impact whereas turret speed and compression force had a lesser impact on drug content uniformity. An optimized trial was conducted using turret to feeder ratio of 25:25 and 4.5kN compression force with an output of 650 tablets/ min. Tablets were collected at the start, middle and end of tableting process of 4 hours. All the compressed tablets showed robust hardness between 4.0 to 4.5 kP, a DT of less than 1 min and achieved AV of 3.74, 4.64 and 2.97 for content uniformity of the tablets through start, middle and end of the compression cycle, respectively. The tablets were coated with Opadry® QX to achieve elegant, finished appearance.
Conclusion: The impact of turret speed, feeder speed and compression force on product quality attributes (CQAs) of tablet hardness, friability, disintegration time, content uniformity and dissolution for glimepiride tablets (1mg) were studied. All tablets showed good hardness, low friability, and acceptable content uniformity with more than 90% drug release in 20 min. The results indicated that StarTab has a key role as a direct compression excipient for low-dose formulations, enabling good blend homogeneity and content uniformity. The compression study indicated that low feeder speed helped improve content uniformity of the tablets.
.jpg)
Table 1
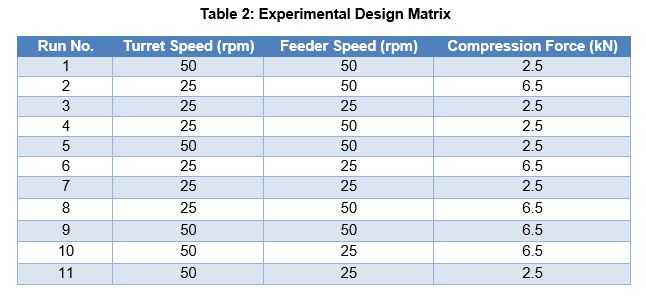
Table 2
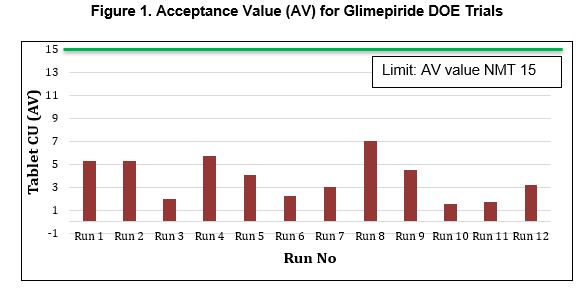
Figure 1
Formulation and Delivery - Chemical - Formulation
Category: Poster Abstract
(T1330-03-14) Study on the Impact of Tablet Compression Parameters for a Directly Compressible Formulation Containing Model Low Dose API
Tuesday, October 18, 2022
1:30 PM – 2:30 PM ET
- MG
Manish Ghimire, Ph.D.
Colorcon, Inc.
Harleysville, Pennsylvania, United States - VA
Vaibhav Ambudkar, MS
Colorcon Asia Pvt. Limited
Goa, Goa, India
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Direct compression is the simplest method for tablet manufacturing involving blending of the active with suitable excipients to achieve desired powder and tablet properties. When formulating low-dose drugs, achieving good content uniformity (CU) becomes a primary critical quality attribute (CQA) for the tablets. The objective of this work was to study the impact of critical process parameters (CPPs) around tablet compression on selected quality attributes of a low dose model drug, glimepiride, for a directly compressible formulation.
Methods: Glimepiride was used as a model low-dose drug with 1 mg strength. Since glimepiride is poorly water-soluble, lactose monohydrate was selected as a diluent. StarTab®, a novel directly compressible starch was used to provide good flow, compressibility, and disintegration property to the tablet. Tablet manufacturing: Glimepiride, StarTab and lactose monohydrate was passed through ASTM #40 screen, then mixed in a blender for 10 mins at 20 rpm followed by lubrication for 2 min with magnesium stearate after passing through ASTM #60 screen. The powder blend was evaluated for bulk density, tap density, powder flow and drug uniformity (n=10) from different positions within the blender. Tablets were compressed using Cadmach 26 stations compression machine (model- CTX-26D) using 6.00 mm standard concave tooling and tested for weight, hardness, thickness, friability, and disintegration time followed by determination of CU in individual tablets (n=10). Compression Parameters: Twelve trials were conducted to study the impact of compression parameters such as turret speed, feeder speed and compression force (Table 2) on tablet hardness, friability, disintegration time, content uniformity and dissolution (CQAs). Considering operating ranges of 12 to 70 rpm and 10 to 60 rpm for turret and feeder speed, for evaluation 25 and 50 rpm were respectively selected. The main compression forces of 2.5 and 6.5 kN were used.
Results: Powder blend showed satisfactory powder flow properties in comparison with the API alone and the blend uniformity samples taken from 10 different positions of blender such as top, middle, and bottom were found to be within the accepted limit (95-105%) with L1 value of 2.76 and % RSD of 1.14. a. Tablet Physical Properties: All tablets showed good hardness between 2.6 to 6.4 kP based on compression force in each run and low friability of 0.24-0.32% at 100 rotations. The disintegration time was from 20 seconds (compression force 2.5 kN) to 1.8 min (compression force 6.5 kN) and the overall tablet output of 640 to 650 units/ min and 1295 to 1310 units/ min was achieved at 25 and 50 rpm of turret speed, respectively. b. Tablet Content Uniformity: Drug content for 10 individual tablets from the 12 experimental runs was determined, and Acceptance Value (AV) was less than 6 in all compression trials suggesting very good drug uniformity in all tablets (Figure 1). c. Drug Dissolution: No significant difference in the dissolution profile was observed in all compression trials with more than 85% drug release obtained within 20 mins. d. Optimized Trial: The results confirmed that at lower turret to feeder speed ratios, 25:25 and 50:25, the AV is on lower side 1.60 to 3.06 whereas at higher ratios, 25:50 and 50:50, the AV value is on higher side 4.09 to 7.02. Thus, feeder speed had a significant impact whereas turret speed and compression force had a lesser impact on drug content uniformity. An optimized trial was conducted using turret to feeder ratio of 25:25 and 4.5kN compression force with an output of 650 tablets/ min. Tablets were collected at the start, middle and end of tableting process of 4 hours. All the compressed tablets showed robust hardness between 4.0 to 4.5 kP, a DT of less than 1 min and achieved AV of 3.74, 4.64 and 2.97 for content uniformity of the tablets through start, middle and end of the compression cycle, respectively. The tablets were coated with Opadry® QX to achieve elegant, finished appearance.
Conclusion: The impact of turret speed, feeder speed and compression force on product quality attributes (CQAs) of tablet hardness, friability, disintegration time, content uniformity and dissolution for glimepiride tablets (1mg) were studied. All tablets showed good hardness, low friability, and acceptable content uniformity with more than 90% drug release in 20 min. The results indicated that StarTab has a key role as a direct compression excipient for low-dose formulations, enabling good blend homogeneity and content uniformity. The compression study indicated that low feeder speed helped improve content uniformity of the tablets.
.jpg)
Table 1

Table 2

Figure 1
