Back
Poster Session D
Session: (2052–2107) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
2081: COVID-19 Infections, Morbidity, and Seroreactivity in SLE Patients Following Initial Vaccination Series and Additional Dose Through the New York City Omicron BA.1 Wave
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AS
Amit Saxena, MD
NYU School of Medicine
New York, NY, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Amit Saxena1, Alexis Engel2, Brittany Banbury1, Ghadeer Hasan3, Nicola Fraser1, Devyn Zaminski1, Mala Masson4, Rebecca Haberman5, Jose Scher2, Gary Ho6, Jammie Law3, Paula Rackoff1, Chung-E Tseng5, H Michael Belmont1, Robert Clancy1, Jill Buyon7 and Peter Izmirly7, 1NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY, 2New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, 3NYU Langone, New York, NY, 4NYU Langone Medical Center- Division of Rheumatology, New York, NY, 5NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, 6New York University Grossman School of Medicine, VA New York Harbor Health Care System, Brooklyn, NY, 7NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are at high risk for severe disease from COVID-19 and decreased vaccine efficacy, due to inherent immune perturbations and frequent immunosuppressant use. The impact of vaccine responses was “pressure” tested in New York City (NYC) from December 2021-February 2022, due to the highly infectious omicron BA.1 variant which resulted in a significant increase in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations. This study was performed to assess clinical efficacy and seroreactivity in SLE patients with and without an additional vaccination dose after initial vaccine series, particularly during the omicron BA.1 surge in NYC.
Methods: COVID-19 infections after vaccination were evaluated during patient encounters and chart review in subjects from the NYU Lupus Cohort who received an initial SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series with follow-up for at least 6 months or until breakthrough infection. Clinical follow-up was required after February 4, 2022 (when NYC COVID-19 cases returned to their pre-omicron BA.1 baseline), with last patient follow-up recorded April 24, 2022. Positive PCR or antigen-based testing was required, performed at the clinical site or self-reported. Fifty-seven patients receiving additional vaccine doses were evaluated longitudinally for recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain antibodies (#BT10500; R&D Systems). Low post-vaccine antibody response was defined as ≤100 units/ml.
Results: Among the 163 subjects evaluated, 125 (76·7%) received an additional COVID-19 vaccination after the initial series. Demographics and medication usage were similar in patients who did and did not receive the additional vaccination dose, with 50% on at least one immunosuppressant and 16% on more than one at the time of the initial vaccine. Twenty-eight (63·6%) of the 44 patients with a breakthrough infection had received an additional vaccination compared to 97 (81·5%) of the 119 without breakthrough infection (p=0·022) (Table 1). Of the 44 COVID-19 cases, only 2 occurred prior to the omicron wave, both in patients who did not receive the additional dose. There were no COVID-19 related deaths and two patients were hospitalized. Among the 57 patients with serologic evaluation, the median antibody level after initial vaccination series was 397 u/mL (IQR 57-753), and 1036 (IQR 517-1338·5) after the additional dose. After initial vaccination, 21 (37%) had low ELISA responses, but only 4 (7%) continued to have low responses after the additional dose. There was no association between the level of antibody after the additional dose and COVID-19 breakthrough.
Conclusion: SLE patients from a cohort of patients in NYC who received an additional SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose were significantly less likely to have a subsequent COVID-19 infection compared to those who only completed their initial vaccine series. SLE patients demonstrated an improvement in serologic response after an additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. The mild disease in all vaccinated patients is reassuring given the risks inherent and frequent immunosuppressant use in this patient population.
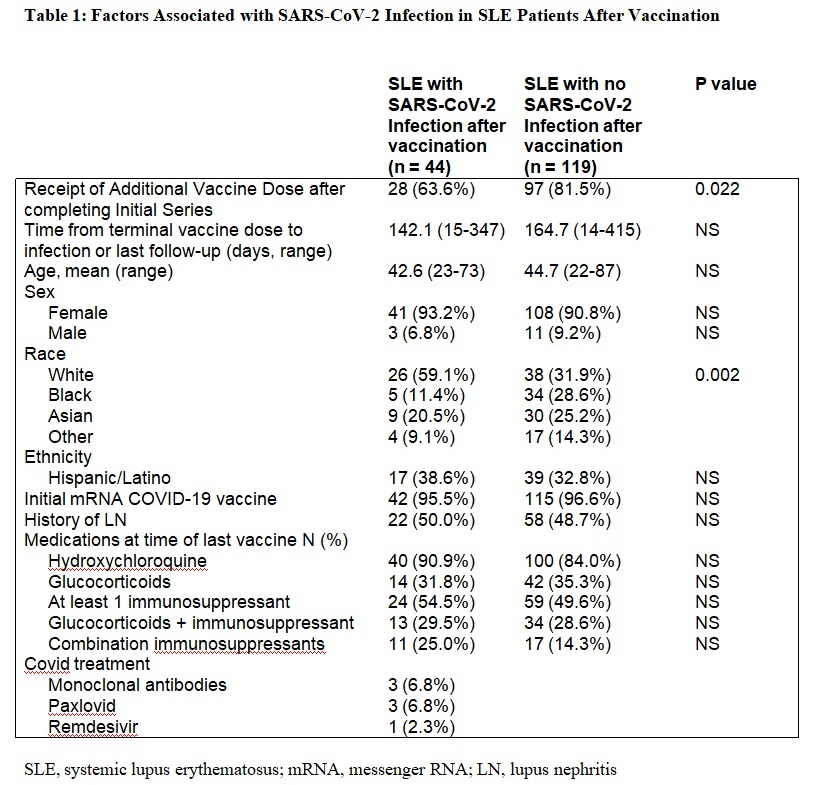 Table 1: Factors Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in SLE Patients After Vaccination
Table 1: Factors Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in SLE Patients After Vaccination
Disclosures: A. Saxena, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kezar Life Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); A. Engel, None; B. Banbury, None; G. Hasan, None; N. Fraser, None; D. Zaminski, None; M. Masson, None; R. Haberman, None; J. Scher, Janssen, Pfizer, AbbVie, Sanofi, Novartis, UCB; G. Ho, None; J. Law, None; P. Rackoff, None; C. Tseng, None; H. Belmont, None; R. Clancy, None; J. Buyon, None; P. Izmirly, Momenta/Janssen.
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are at high risk for severe disease from COVID-19 and decreased vaccine efficacy, due to inherent immune perturbations and frequent immunosuppressant use. The impact of vaccine responses was “pressure” tested in New York City (NYC) from December 2021-February 2022, due to the highly infectious omicron BA.1 variant which resulted in a significant increase in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations. This study was performed to assess clinical efficacy and seroreactivity in SLE patients with and without an additional vaccination dose after initial vaccine series, particularly during the omicron BA.1 surge in NYC.
Methods: COVID-19 infections after vaccination were evaluated during patient encounters and chart review in subjects from the NYU Lupus Cohort who received an initial SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series with follow-up for at least 6 months or until breakthrough infection. Clinical follow-up was required after February 4, 2022 (when NYC COVID-19 cases returned to their pre-omicron BA.1 baseline), with last patient follow-up recorded April 24, 2022. Positive PCR or antigen-based testing was required, performed at the clinical site or self-reported. Fifty-seven patients receiving additional vaccine doses were evaluated longitudinally for recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain antibodies (#BT10500; R&D Systems). Low post-vaccine antibody response was defined as ≤100 units/ml.
Results: Among the 163 subjects evaluated, 125 (76·7%) received an additional COVID-19 vaccination after the initial series. Demographics and medication usage were similar in patients who did and did not receive the additional vaccination dose, with 50% on at least one immunosuppressant and 16% on more than one at the time of the initial vaccine. Twenty-eight (63·6%) of the 44 patients with a breakthrough infection had received an additional vaccination compared to 97 (81·5%) of the 119 without breakthrough infection (p=0·022) (Table 1). Of the 44 COVID-19 cases, only 2 occurred prior to the omicron wave, both in patients who did not receive the additional dose. There were no COVID-19 related deaths and two patients were hospitalized. Among the 57 patients with serologic evaluation, the median antibody level after initial vaccination series was 397 u/mL (IQR 57-753), and 1036 (IQR 517-1338·5) after the additional dose. After initial vaccination, 21 (37%) had low ELISA responses, but only 4 (7%) continued to have low responses after the additional dose. There was no association between the level of antibody after the additional dose and COVID-19 breakthrough.
Conclusion: SLE patients from a cohort of patients in NYC who received an additional SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose were significantly less likely to have a subsequent COVID-19 infection compared to those who only completed their initial vaccine series. SLE patients demonstrated an improvement in serologic response after an additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. The mild disease in all vaccinated patients is reassuring given the risks inherent and frequent immunosuppressant use in this patient population.
 Table 1: Factors Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in SLE Patients After Vaccination
Table 1: Factors Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in SLE Patients After VaccinationDisclosures: A. Saxena, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kezar Life Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); A. Engel, None; B. Banbury, None; G. Hasan, None; N. Fraser, None; D. Zaminski, None; M. Masson, None; R. Haberman, None; J. Scher, Janssen, Pfizer, AbbVie, Sanofi, Novartis, UCB; G. Ho, None; J. Law, None; P. Rackoff, None; C. Tseng, None; H. Belmont, None; R. Clancy, None; J. Buyon, None; P. Izmirly, Momenta/Janssen.

