Back
Clinical Research
(CR-019) Results from a Phase 2 multicenter, prospective, randomized, placebo controlled study performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Bromelain-based enzymatic debridement agent (BBD) in debridement of Venous Leg Ulcers

Co-Author(s):
Cyaandi Dove, DPM
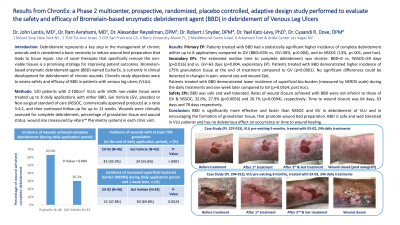
<b>Introduction</b>: <p class="Default"><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">Debridement represents a key step in the management of chronic wounds and is considered a basic necessity to induce wound bed preparation that leads to tissue repair. Use of novel therapies that specifically remove the non-viable tissues, is a promising strategy for improving patient outcomes. Bromelain-based enzymatic debridement agent (BBD) is currently in clinical development for debridement of chronic wounds. Study objectives were to assess safety and efficacy of BBD in patients with venous leg ulcers (VLUs).<span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span></span></p><br/><br/><b>Methods</b>: <p class="Default"><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">120 patients <span class="BodyTextChar1"><span style="mso-ansi-font-size: 11.0pt; mso-bidi-font-size: 11.0pt; mso-bidi-font-style: italic;">with 2-100cm<sup>2</sup> VLUs containing ≥50% non-viable tissue</span></span> were randomized to 3 arms: BBD, </span><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family: 'MS Mincho'; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">Gel Vehicle (GV, placebo) or Non-surgical standard of care (</span><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">NSSOC, commercially approved products) at a </span><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family: 'MS Mincho'; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">ratio 3:3:2. Patients were </span><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">treated with up to 8 daily applications of BBD or GV or with unlimited number of NSSOC treatments (in accordance with its label) and then continued follow-up for up to 12 weeks.</span><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family: 'MS Mincho'; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;"> Wounds were clinically assessed for complete debridement, wound size (measured by Planimetry system) in each clinic visit.</span></p><br/><br/><b>Results</b>: <p class="Default"><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">Patients treated with BBD had a statistically significant higher incidence of complete debridement within up to 8 applications compared to GV (BBD=63% vs. GV=30%, p=0.004), and NSSOC (13%). The estimated median time to complete debridement was shorter: BBD=9 vs. NSSOC=59 days (p=0.016). Patients treated with BBD demonstrated higher incidence of ≥75% granulation tissue at the end of treatment compared to GV (p< 0.0001). A favorable trend was observed in reduction of wound area and pain during follow-up visits. </span></p>
<p class="Default"><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">BBD was safe and well tolerated, without healing impairment (32.6%, 27.9% and 26.7% wound closure achieved for BBD, GV & NSSOC, respectively). </span></p><br/><br/><b>Discussion</b>: <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; border: none; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA;">The data shows that BBD is significantly more effective and faster than NSSOC and GV in debridement of VLU.<span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-family: Calibri; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin; color: black;">BBD is safe and well tolerated in VLU patients (no </span><span style="mso-bidi-font-family: Calibri; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">material differences in systemic and local adverse events<span style="color: black;">), and has no deleterious effect on occurrence or time to wound healing. </span></span></p><br/><br/><b>Trademarked Items</b>: <br/><br/><b>References</b>: <br/><br/>
<p class="Default"><span style="font-size: 11.0pt; font-family: 'Calibri',sans-serif; mso-ascii-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-hansi-theme-font: minor-latin; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">BBD was safe and well tolerated, without healing impairment (32.6%, 27.9% and 26.7% wound closure achieved for BBD, GV & NSSOC, respectively). </span></p><br/><br/><b>Discussion</b>: <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; border: none; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA;">The data shows that BBD is significantly more effective and faster than NSSOC and GV in debridement of VLU.<span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-family: Calibri; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin; color: black;">BBD is safe and well tolerated in VLU patients (no </span><span style="mso-bidi-font-family: Calibri; mso-bidi-theme-font: minor-latin;">material differences in systemic and local adverse events<span style="color: black;">), and has no deleterious effect on occurrence or time to wound healing. </span></span></p><br/><br/><b>Trademarked Items</b>: <br/><br/><b>References</b>: <br/><br/>

.png)
