Back
Case Series/Study
(CS-004) The use of fish skin graft in patients with periosteum exposed post scalp lesion removal for definitive wound closure

Co-Author(s):
Ryan O'Quinn, MD
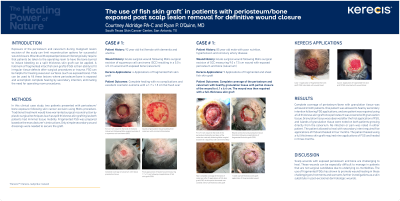
Introduction: Exposure of the periosteum during lesion removal of the scalp can limit reconstruction options for successful wound closure. Wounds with exposed periosteum typically require that patients be taken to the operating room to have the periosteum burred to induce bleeding so a split thickness skin graft can be applied. A hallmark of fragmented intact fish skin grafts (FSG) is their ability to fill up irregular tissue defects after surgical procedures or trauma. FSG can be used to fill these lesions where periosteum is exposed and accomplish complete healing by secondary intention, eliminating the need for operating room procedures.
Methods: In this clinical case study, two patients presented with periosteum exposure following skin cancer excision using Mohs procedure. Traditional treatment would have warranted surgical reconstruction by plastic surgery, as both patients had minimal tissue mobility. Fragmented FSG was prepared based on the manufacturer’s instructions. Only simple secondary wound dressings were needed to secure the graft.
Results: Complete coverage of periosteum with granulation tissue was achieved in both patients. One patient was allowed to heal by secondary intention following FSG applications, and one patient was repaired using a full thickness skin graft once periosteum was covered with granulation tissue. Granulation tissue was observed after the first application of FSG, and islands of granulation tissue were noted on both patients growing directly from the periosteum. No infection or pain was noted in either patient. The patient allowed to heal with secondary intent required five applications of FSG and healed in four months. The patient healed using a full thickness skin graft required nine applications of FSG and healed in three months.
Discussion: Managing scalp wounds with periosteum exposure can be challenging especially in patients that are not healthy enough to undergo sedation in a hospital or ASC setting. The use of fragmented FSG allows granulation tissue to grow covering the periosteum and fill in the loss of volume a split thickness graft cannot fill. Due to the innate properties of the FSG, the 3-D structure, the bacterial barrier, and natural chemical composition, the FSG supports rapid cellular ingrowth and formation of robust granulation tissue. FSGs provide a safe and effective reconstruction alternative for scalp wounds and warrant further investigation as a skin substitute in post-excisional dermatological wounds.
Trademarked Items: *KerecisTM, Kerecis, Isafjordur, Iceland
References:
Methods: In this clinical case study, two patients presented with periosteum exposure following skin cancer excision using Mohs procedure. Traditional treatment would have warranted surgical reconstruction by plastic surgery, as both patients had minimal tissue mobility. Fragmented FSG was prepared based on the manufacturer’s instructions. Only simple secondary wound dressings were needed to secure the graft.
Results: Complete coverage of periosteum with granulation tissue was achieved in both patients. One patient was allowed to heal by secondary intention following FSG applications, and one patient was repaired using a full thickness skin graft once periosteum was covered with granulation tissue. Granulation tissue was observed after the first application of FSG, and islands of granulation tissue were noted on both patients growing directly from the periosteum. No infection or pain was noted in either patient. The patient allowed to heal with secondary intent required five applications of FSG and healed in four months. The patient healed using a full thickness skin graft required nine applications of FSG and healed in three months.
Discussion: Managing scalp wounds with periosteum exposure can be challenging especially in patients that are not healthy enough to undergo sedation in a hospital or ASC setting. The use of fragmented FSG allows granulation tissue to grow covering the periosteum and fill in the loss of volume a split thickness graft cannot fill. Due to the innate properties of the FSG, the 3-D structure, the bacterial barrier, and natural chemical composition, the FSG supports rapid cellular ingrowth and formation of robust granulation tissue. FSGs provide a safe and effective reconstruction alternative for scalp wounds and warrant further investigation as a skin substitute in post-excisional dermatological wounds.
Trademarked Items: *KerecisTM, Kerecis, Isafjordur, Iceland
References:

.png)