Case Series/Study
(CS-110) The Use of a Bioresorbable Silver Matrix in Recalcitrant Surgical Wounds of Varying Etiologies
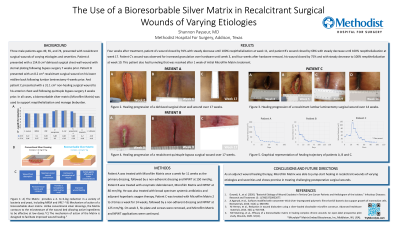
Methods:
Patient A was treated with Microfilm Matrix once a week for 11 weeks as the primary dressing, followed by a non-adherent dressing and NPWT at 150 mm/Hg. Patient B was treated with enzymatic debridement, Microfilm Matrix and NPWT at 80 mm/Hg. He was also treated with broad spectrum systemic antibiotics and adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Patient C was treated with Microfilm Matrix 2 to 3 times a week for 14 weeks, followed by a non-adherent dressing and NPWT at 125 mm/Hg. On week 3, his plate and screws were removed, and Microfilm Matrix and NPWT applications were continued.
Results:
Four weeks after treatment, patient A’s wound closed by 91% with steady decrease until 100% reepithelialization at week 11, and patient B’s wound closed by 68% with steady decrease until 100% reepithelialization at week 17. Patient C’s wound was observed for increased granulation over hardware until week 3, and four weeks after hardware removal, his wound closed by 75% and with steady decrease to 100% reepithelialization at week 10. This patient also had tunneling that was resolved after 1 week of initial Microfilm Matrix treatment.
Discussion:
As an adjunct wound healing therapy, Microfilm Matrix was able to jump-start healing in recalcitrant wounds of varying etiologies and severities and shows promise in treating challenging postoperative surgical wounds.
Trademarked Items:
References: 1) Sarah W. Manning, D. A. H., William R. Shillinglaw, Eric Crawford, Gaurav Pranami, Ankit Agarwal, Michael J. Schurr (2020). "Efficacy of a Bioresorbable Matrix in Healing Complex Chronic Wounds: An Open-Label Prospective Pilot Study." Wounds 32(11).
2) Chatelain, R. (2021). "The Efficacy of a Novel Silver-Containing Bioresorbable Microfilm Matrix in At-Risk Surgical Wounds: A Clinical Case Series." Wounds: a Compendium of Clinical Research and Practice 33(10): 245-252.

.png)