Back
Case Series/Study
(CS-072) The Use of Hypochlorous Acid Preserved Wound Cleanser (HAPWOC) as a Wound Bed Preparation and Cleansing Agent for Use with Skin Substitutes

Co-Author(s):
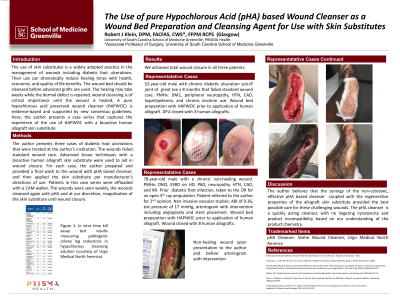
<b>Introduction</b>: <span style="font-family: 'Arial',sans-serif; font-size: 11pt; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-ansi-language: EN-US; mso-fareast-language: EN-US; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA; mso-fareast-theme-font: minor-latin;">The use of skin substitutes is a widely adopted practice in the management of wounds including diabetic foot ulcerations. Their use can dramatically reduce healing times with health, economic, and quality of life benefits. The wound bed should be cleansed before advanced grafts are used. The healing may take weeks while the dermal defect is repaired, wound cleansing is of critical importance until the wound is healed. A hypochlorous acid preserved wound cleanser (HAPWOC) is evidence-based. Here, the author presents a case series that captures the experience of the use of HAPWOC with a bioactive human allograft skin substitute.<br /></span><br/><br/><b>Methods</b>: <span style="font-family: 'Arial',sans-serif; font-size: 11pt; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-ansi-language: EN-US; mso-fareast-language: EN-US; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA; mso-fareast-theme-font: minor-latin;">The author presents three cases of diabetic foot ulcerations that were treated at the author’s institution. The wounds failed standard wound care. Advanced tissue techniques with a bioactive human allograft skin substitute were used to aid in wound closure. For each case, the author prepared and provided a final wash to the wound with HAPWOC, and then applied the skin substitute per manufacturers directions of use. Patients in this case series were offloaded with a CAM walker. The wounds were seen weekly, the wounds cleansed again with HAPWOC and at our discretion, reapplication of the skin substitute until wound closure.</span><br/><br/><b>Results</b>: <p style="margin: 0in; mso-margin-top-alt: auto; mso-margin-bottom-alt: auto;"><span style="font-family: 'Arial',sans-serif; font-size: 11pt; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-fareast-theme-font: minor-latin;">We achieved total wound closure in all three patients. </span></p><br/><br/><b>Discussion</b>: <span style="font-family: 'Arial',sans-serif; font-size: 11pt; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-ansi-language: EN-US; mso-fareast-language: EN-US; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA; mso-fareast-theme-font: minor-latin;">The author believes that the synergy of the non-cytotoxic, effective HAPWOC coupled with the regenerative properties of the allograft skin substitute provided the best possible care for these challenging wounds. HAPWOC is a quickly acting cleanser, with no lingering cytotoxicity and product incompatibility based on our understanding of the product chemistry.</span><br/><br/><b>Trademarked Items</b>: HAPWOC: Vashe Wound Cleanser, Urgo Medical North America<br/><br/><b>References</b>: Harriott MM, Bhindi N, Kassis S, Summitt B, Perdikis G, Wormer BA, Rankin TM, Kaoutzanis C, Samaha M, Stratton C, Schmitz JE. Comparative Antimicrobial Activity of Commercial Wound Care Solutions on Bacterial and Fungal Biofilms. Ann Plast Surg. 2019 Oct;83(4):404-410. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31524733
Robson MC. Treating chronic wounds with hypochlorous acid disrupts biofilm. Wound Prevention and Management 2020;66 (5):9-10.https://www.todayswoundclinic.com/articles/treating-chronic-wounds-hypochlorous-acid-disrupts-biofilm/
Sauer K, Thatcher E, Northey R, Gutierrez AA. Neutral super-oxidised solutions are effective in killing P. aeruginosa biofilms. Biofouling 2009;25(1):45-54. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18846439/
Armstrong DG, Bohn G, Glat P, et al. Expert recommendations for the use of hypochlorous solution: science and clinical
application. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2015;61(5):S2–S19.<br/><br/>
Robson MC. Treating chronic wounds with hypochlorous acid disrupts biofilm. Wound Prevention and Management 2020;66 (5):9-10.https://www.todayswoundclinic.com/articles/treating-chronic-wounds-hypochlorous-acid-disrupts-biofilm/
Sauer K, Thatcher E, Northey R, Gutierrez AA. Neutral super-oxidised solutions are effective in killing P. aeruginosa biofilms. Biofouling 2009;25(1):45-54. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18846439/
Armstrong DG, Bohn G, Glat P, et al. Expert recommendations for the use of hypochlorous solution: science and clinical
application. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2015;61(5):S2–S19.<br/><br/>

.png)