Back
Purpose: Purpose of this study is to compare film coating compositions dissolution rates. Work is divided in two phases, the first is for free films, second is for films applied on inert cores. Both cases are intended to observe pure film dissolution behavior avoiding influence of pharmaceutical tablet compositions. New filmogen combinations and typical coating compositions are evaluated in this work.
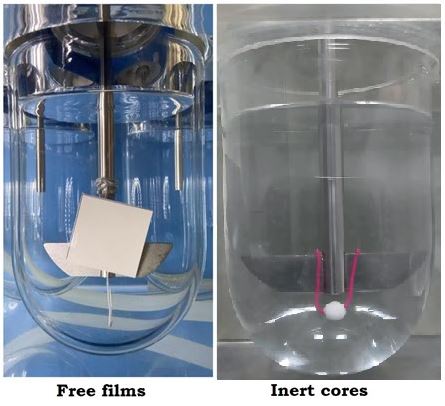
Methods: Free films were obtained spraying coating dispersions on glass surface 25 x 20 cm, letting dry until under 5% moisture content. 4x4 cm 200±20 microns thick film strips were cut and weighted individually and submerged in 900 mL of purified water in dissolution vessels. Time to complete film disintegration was measured. Wire strands were adapted to the paddles to avoid film strips adhesion to vessel wall. 8 mm diameter inert glass spheres were coated using coating product needed for 3% weight gain of equivalent pharmaceutical tablet dimensions. Glass spheres were weighted individually before and after being coated to calculate net film mass adhered. Coated cores were submerged in 900 mL of purified water in dissolution vessels. Wire strands were adapted to the paddles to suspend coated glass spheres for uniform film disintegration. Time to complete film disintegration was measured. >Intrinsic dissolution for free and applied films on inert glass spheres was obtained as follows:
Intrinsic dissolution = film strip weight / [dissolution time x area]
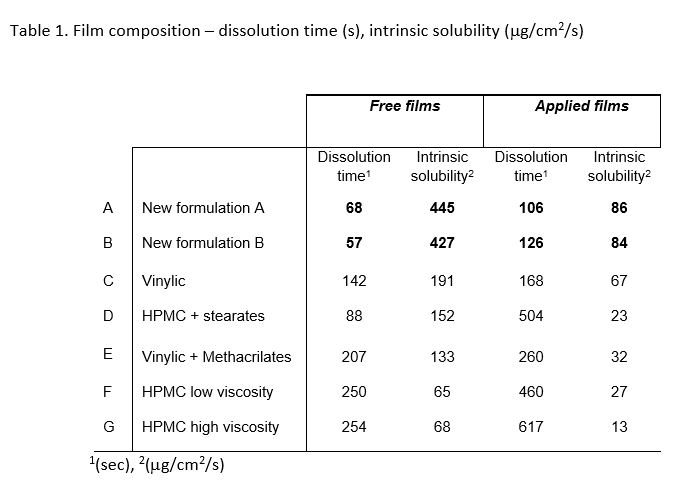
Table 1 shows filmogen components of each tested composition. “A” and “B” are examples of novel formulations, based on proprietary compositions containing combinations of Hypromelose, vinyl alcohol derivate, copovidone and polyols. “C” to “G” formulations are typical coating compositions
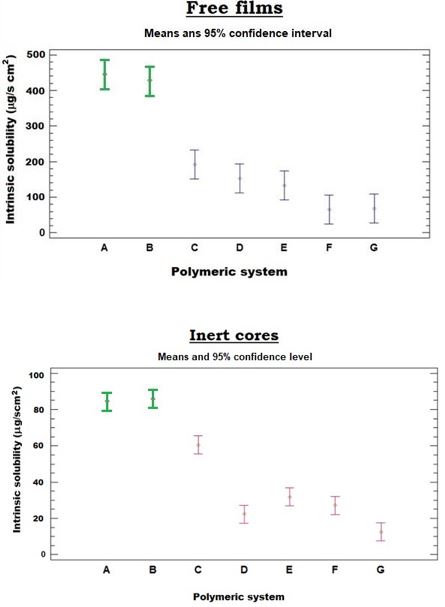
Results: Different groups of intrinsic solubility have been found based on variance analysis. New proprietary compositions “A” and “B” which include polymers combinations and polyol ingredients, show significant faster solubility rates compared to typical coating formulations. Table 1. Film composition – Results dissolution time (s), intrinsic solubility (mg/cm2/s)
Conclusion: New pharmaceutical water dispersible coating products have been formulated. Their composition include filmogen polymers such as Hypromelose, vinyl alcohol derivate, copovidone and polyols. These proprietary compositions show faster dissolution rates compared to classic coating formulations based on Hypromelose or vinyl derivate formulations. Evaluations were carried on free films and applied on inert glass cores in order to avoid influence of typical tablet compositions which usually include disintegrants or agglutinant agents.
Formulation and Delivery - Chemical - Formulation
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(M1030-01-05) Intrinsic Dissolution of New Pharmaceutical Film Coating Systems
Monday, October 17, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:30 AM ET
- FE
Francisco Escorcia Rodriguez, MS
DVA
MEXICO CITY, Distrito Federal, Mexico - FE
Francisco Escorcia Rodriguez, MS
DVA
MEXICO CITY, Distrito Federal, Mexico
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Purpose of this study is to compare film coating compositions dissolution rates. Work is divided in two phases, the first is for free films, second is for films applied on inert cores. Both cases are intended to observe pure film dissolution behavior avoiding influence of pharmaceutical tablet compositions. New filmogen combinations and typical coating compositions are evaluated in this work.
Methods: Free films were obtained spraying coating dispersions on glass surface 25 x 20 cm, letting dry until under 5% moisture content. 4x4 cm 200±20 microns thick film strips were cut and weighted individually and submerged in 900 mL of purified water in dissolution vessels. Time to complete film disintegration was measured. Wire strands were adapted to the paddles to avoid film strips adhesion to vessel wall. 8 mm diameter inert glass spheres were coated using coating product needed for 3% weight gain of equivalent pharmaceutical tablet dimensions. Glass spheres were weighted individually before and after being coated to calculate net film mass adhered. Coated cores were submerged in 900 mL of purified water in dissolution vessels. Wire strands were adapted to the paddles to suspend coated glass spheres for uniform film disintegration. Time to complete film disintegration was measured. >Intrinsic dissolution for free and applied films on inert glass spheres was obtained as follows:
Intrinsic dissolution = film strip weight / [dissolution time x area]
Table 1 shows filmogen components of each tested composition. “A” and “B” are examples of novel formulations, based on proprietary compositions containing combinations of Hypromelose, vinyl alcohol derivate, copovidone and polyols. “C” to “G” formulations are typical coating compositions
Results: Different groups of intrinsic solubility have been found based on variance analysis. New proprietary compositions “A” and “B” which include polymers combinations and polyol ingredients, show significant faster solubility rates compared to typical coating formulations. Table 1. Film composition – Results dissolution time (s), intrinsic solubility (mg/cm2/s)
Conclusion: New pharmaceutical water dispersible coating products have been formulated. Their composition include filmogen polymers such as Hypromelose, vinyl alcohol derivate, copovidone and polyols. These proprietary compositions show faster dissolution rates compared to classic coating formulations based on Hypromelose or vinyl derivate formulations. Evaluations were carried on free films and applied on inert glass cores in order to avoid influence of typical tablet compositions which usually include disintegrants or agglutinant agents.



