Back
Purpose: Obesity is a habitus disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the tissues. Continuous fat accumulation has been linked to several serious health problems, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, chronic inflammation, and even cancers. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) surgery is one of the recommended treatments for patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 40 or ≥ 35 with obesity-related disease. The surgery causes changes in the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) of metformin and statins post-surgery. The purpose of the study is to establish a 3D PK/PD correlation for two dosing groups: metformin only treatment and cotreatment of metformin and statins on obese patients post-RYGB surgery, and 3D correlation for these two dosing groups of Css with their pre- and post-surgery time points, and doses, which may offer guidance to individualize treatment regimens post-surgery, against the current practices of either entirely discontinuing or continuing with the same regimen of metformin and/or statins.
Methods: In this study, thirty-one patients had been taking metformin before the surgery (BMI range of 32.7-62.0 kg/m2). Including thirteen patients taking only metformin and eighteen patients taking metformin and statins at the same time. The blood samples were collected, and body weights and hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels were monitored at pre-surgery (baseline), and 3, 6, and 12 months (M) post-surgery. Validated LC-MS/MS assay with LLOQ of 0.25 ng/ml was used to quantify the concentrations of metformin. The 3D PK/PD correlation of % HbA1C change [(HbA1C level at post-RYGB surgery time point- baseline HbA1C)/baseline HbA1C] *100, with weight-loss outcomes BMI, and drug exposure: Css/(dose/BW) of the two groups (metformin treatment only and metformin and statins cotreatment) were analyzed by using Design Expert 9. Furthermore, a 3D correlation of Css with Dose and timeline pre- or post-RYGB of the two treatment groups were also analyzed by using Design Expert 9.
Results: The effects of the RYGB surgery on the PK PD of metformin were analyzed. In the metformin and statin cotreatment group, according to figure 1 (a), there was a clear trend of continuous decrease in metformin concentration on the same dose basis from baseline to 3-, 6-, and 12-months post-surgery. For the metformin-only treatment group compared to baseline, according to figure 1 (b) the trend was less apparent with a slight increase in metformin concentrations in three patients’ post-surgery at the three-month time point but starting decreasing concentrations of metformin at the time points between 3 and 6 months in two patients. The surgery caused bypassing of certain parts of the absorption site for metformin, that might be accounted for the initial concentration decrease of metformin. Further continuous decrease in metformin concentrations may be attributed to the enhancement of cardiac and renal functions thus leading to a higher elimination rate of metformin since metformin is 100% excreted by the renal route. Recent clinical research reports that statins may associate with an escalation of diabetes treatment alert us to take into consideration balancing the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy with the risk of diabetes progression. For the 3D PK/PD correlations of the two dosing groups shown in figure 2 (a) and (b) (data shown in the PK/PD data table), a quadratic model with equation of [% change in HbA1c = 1394.05+2.52*Css/(dose/BW)-91.96*BMI-0.07*Css/(dose/BW)*BMI-0.004*Css/(dose/BW)2+1.48*BMI2] best described the metformin treatment group and a 2FI model with equation of [% change in HbA1c = 4.40-2.02*Css/(dose/BW)- 0.47*BMI+ 0.07*Css/(dose/BW)*BMI] captured the metformin and statins cotreatment group. The 3D correlation of Css with Dose and the timeline pre- or post-RYGB in figure 2. (c) and (d), fitted cubic models with equation of Css= 965.13+1002.76*A-3.52*B-1.14*AB-144.87*A2+0.0038* B2+0.042* A2B+0.00056*AB2+6.33*A2-1.02E-06* B2 (A: Timeline; B: Dose) for the metformin treatment group and Css=638.93-217.48*A+469.54*B+12.96* A2-3100.57* B2-977.47* A3 (A: Timeline; B: Dose) for metformin/statin co-treatment groups.
Conclusion: The clinical 3D correlations of PK/PD in obese patients post-RYGB surgery and clinical 3D correlations of Css with Dose and timeline pre- or post-RYGB are established for both metformin treatment and metformin and statins cotreatment groups, but of obviously different patterns. Showing that statins cotreatment with metformin may affect the PK/PD of metformin. These results indicate possible rational dose modifications of metformin regimens in obese patients post-RYGB surgery depending on the type of treatment: metformin only or cotreatment with statins. These models may guide individualized dose regimen modifications of metformin post-RYGB surgery, pending further validation. Properly modified regimens post-surgery may offer significant benefits to patients, reducing the recurrence of hyperglycemia and thus substantial medical costs.
References: 1. El-Zailik, A., Cheung, L. K., Wang, Y., Sherman, V., & Chow, D. S. (2019). Longitudinal Impacts of Gastric Bypass Surgery on Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of Statins. Obesity surgery, 29(8), 2571–2583.
2. Mansi, I. A., Chansard, M., Lingvay, I., Zhang, S., Halm, E. A., & Alvarez, C. A. (2021). Association of Statin Therapy Initiation With Diabetes Progression: A Retrospective Matched-Cohort Study. JAMA internal medicine, 181(12), 1562–1574.
Acknowledgements: Funding sources: Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI), grant number 5G12MD007605-23
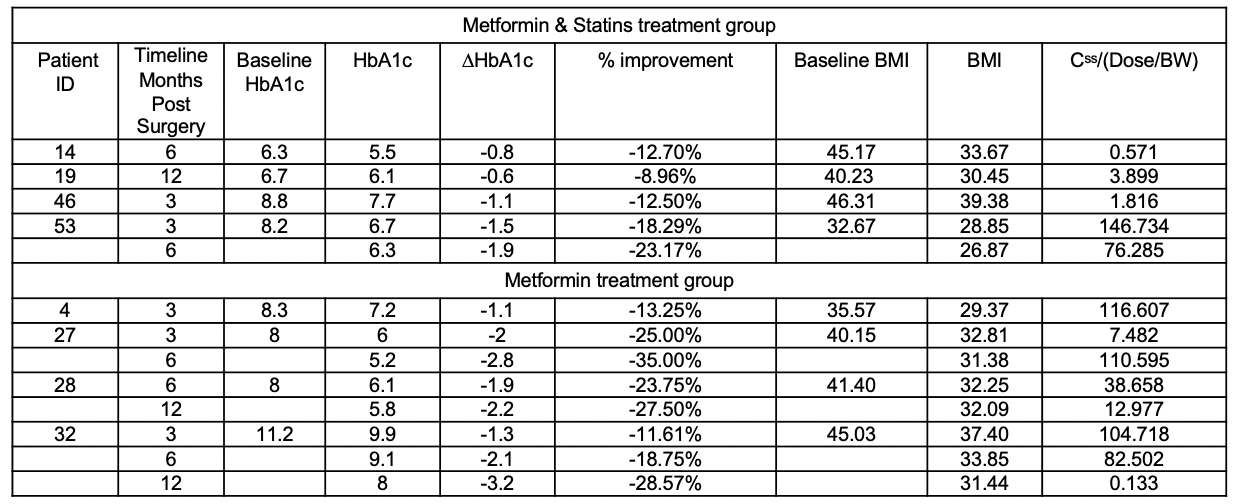
Table PK/PD Data
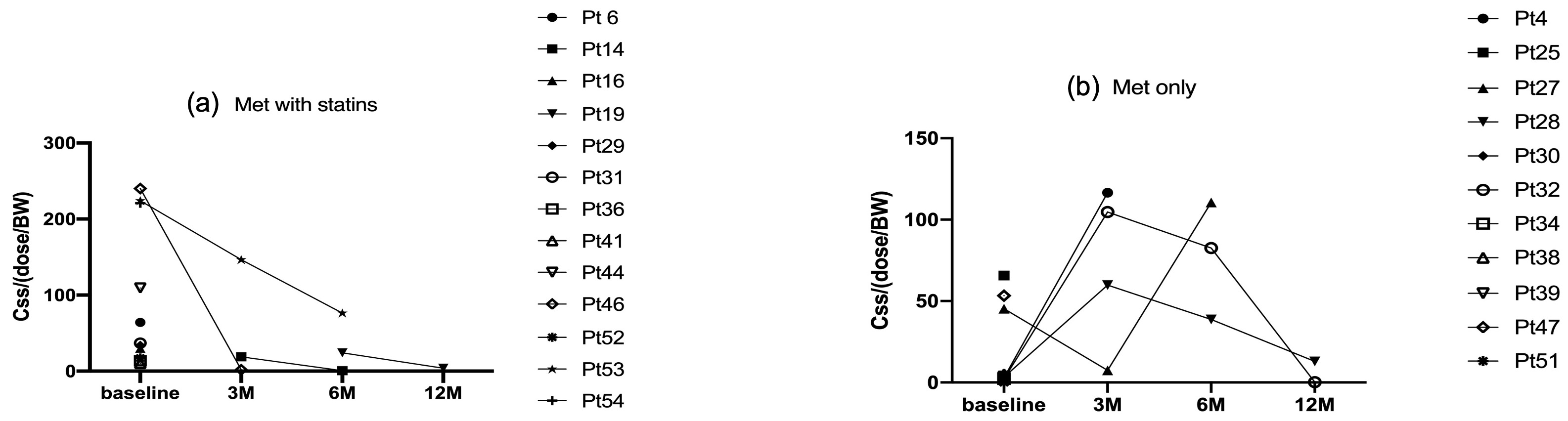
Figure 1. Correlation of Css/(Dose/BW) of (a) Metformin with statins (b) Metformin only treatment with pre- and post-surgery timepoint
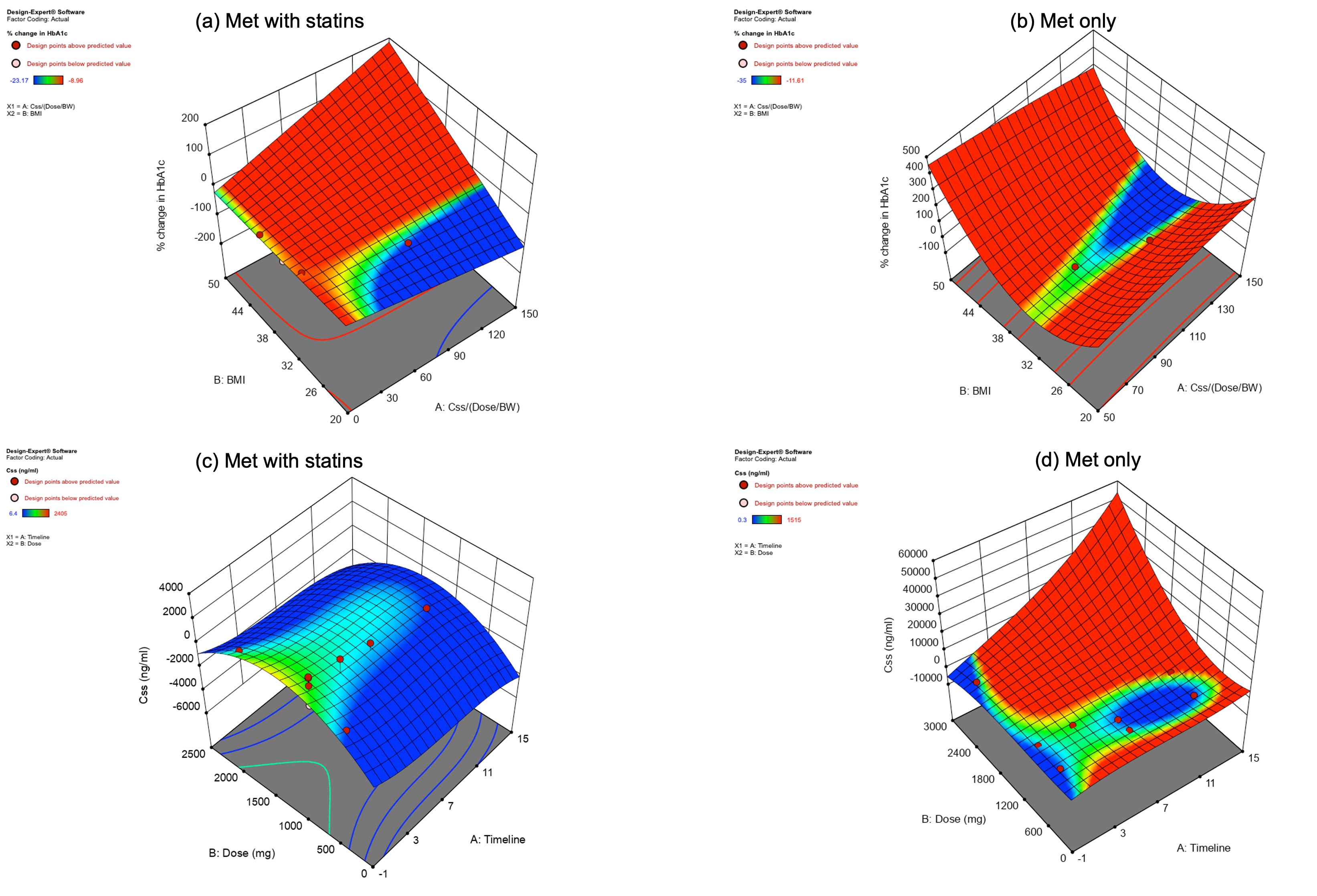
Figure 2. 3D PK/PD Correlations of % HbA1c Changes of (a) Metformin with statins (b) Metformin only treatment, with Css/(Dose/BW) and BMIs Post RYGB Surgery; 3D correlations of Css of (c) Metformin with statins (d) Metformin only treatment with Dose and pre- and post-surgery timepoint
Clinical Pharmacology - Chemical - Type of Human Studies
Category: Poster Abstract
(T0930-11-65) Metformin Treatment or Cotreatment with Statins Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics on Diabetes Patients Before or Post Gastric Bypass Surgery
Tuesday, October 18, 2022
9:30 AM – 10:30 AM ET

Hanyue Liao, MS
PhD Student
University of Houston
Houston, Texas, United States- AE
Asma El-Zailik, Ph.D.
University of Houston
Houston, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Obesity is a habitus disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the tissues. Continuous fat accumulation has been linked to several serious health problems, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, chronic inflammation, and even cancers. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) surgery is one of the recommended treatments for patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 40 or ≥ 35 with obesity-related disease. The surgery causes changes in the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) of metformin and statins post-surgery. The purpose of the study is to establish a 3D PK/PD correlation for two dosing groups: metformin only treatment and cotreatment of metformin and statins on obese patients post-RYGB surgery, and 3D correlation for these two dosing groups of Css with their pre- and post-surgery time points, and doses, which may offer guidance to individualize treatment regimens post-surgery, against the current practices of either entirely discontinuing or continuing with the same regimen of metformin and/or statins.
Methods: In this study, thirty-one patients had been taking metformin before the surgery (BMI range of 32.7-62.0 kg/m2). Including thirteen patients taking only metformin and eighteen patients taking metformin and statins at the same time. The blood samples were collected, and body weights and hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels were monitored at pre-surgery (baseline), and 3, 6, and 12 months (M) post-surgery. Validated LC-MS/MS assay with LLOQ of 0.25 ng/ml was used to quantify the concentrations of metformin. The 3D PK/PD correlation of % HbA1C change [(HbA1C level at post-RYGB surgery time point- baseline HbA1C)/baseline HbA1C] *100, with weight-loss outcomes BMI, and drug exposure: Css/(dose/BW) of the two groups (metformin treatment only and metformin and statins cotreatment) were analyzed by using Design Expert 9. Furthermore, a 3D correlation of Css with Dose and timeline pre- or post-RYGB of the two treatment groups were also analyzed by using Design Expert 9.
Results: The effects of the RYGB surgery on the PK PD of metformin were analyzed. In the metformin and statin cotreatment group, according to figure 1 (a), there was a clear trend of continuous decrease in metformin concentration on the same dose basis from baseline to 3-, 6-, and 12-months post-surgery. For the metformin-only treatment group compared to baseline, according to figure 1 (b) the trend was less apparent with a slight increase in metformin concentrations in three patients’ post-surgery at the three-month time point but starting decreasing concentrations of metformin at the time points between 3 and 6 months in two patients. The surgery caused bypassing of certain parts of the absorption site for metformin, that might be accounted for the initial concentration decrease of metformin. Further continuous decrease in metformin concentrations may be attributed to the enhancement of cardiac and renal functions thus leading to a higher elimination rate of metformin since metformin is 100% excreted by the renal route. Recent clinical research reports that statins may associate with an escalation of diabetes treatment alert us to take into consideration balancing the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy with the risk of diabetes progression. For the 3D PK/PD correlations of the two dosing groups shown in figure 2 (a) and (b) (data shown in the PK/PD data table), a quadratic model with equation of [% change in HbA1c = 1394.05+2.52*Css/(dose/BW)-91.96*BMI-0.07*Css/(dose/BW)*BMI-0.004*Css/(dose/BW)2+1.48*BMI2] best described the metformin treatment group and a 2FI model with equation of [% change in HbA1c = 4.40-2.02*Css/(dose/BW)- 0.47*BMI+ 0.07*Css/(dose/BW)*BMI] captured the metformin and statins cotreatment group. The 3D correlation of Css with Dose and the timeline pre- or post-RYGB in figure 2. (c) and (d), fitted cubic models with equation of Css= 965.13+1002.76*A-3.52*B-1.14*AB-144.87*A2+0.0038* B2+0.042* A2B+0.00056*AB2+6.33*A2-1.02E-06* B2 (A: Timeline; B: Dose) for the metformin treatment group and Css=638.93-217.48*A+469.54*B+12.96* A2-3100.57* B2-977.47* A3 (A: Timeline; B: Dose) for metformin/statin co-treatment groups.
Conclusion: The clinical 3D correlations of PK/PD in obese patients post-RYGB surgery and clinical 3D correlations of Css with Dose and timeline pre- or post-RYGB are established for both metformin treatment and metformin and statins cotreatment groups, but of obviously different patterns. Showing that statins cotreatment with metformin may affect the PK/PD of metformin. These results indicate possible rational dose modifications of metformin regimens in obese patients post-RYGB surgery depending on the type of treatment: metformin only or cotreatment with statins. These models may guide individualized dose regimen modifications of metformin post-RYGB surgery, pending further validation. Properly modified regimens post-surgery may offer significant benefits to patients, reducing the recurrence of hyperglycemia and thus substantial medical costs.
References: 1. El-Zailik, A., Cheung, L. K., Wang, Y., Sherman, V., & Chow, D. S. (2019). Longitudinal Impacts of Gastric Bypass Surgery on Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of Statins. Obesity surgery, 29(8), 2571–2583.
2. Mansi, I. A., Chansard, M., Lingvay, I., Zhang, S., Halm, E. A., & Alvarez, C. A. (2021). Association of Statin Therapy Initiation With Diabetes Progression: A Retrospective Matched-Cohort Study. JAMA internal medicine, 181(12), 1562–1574.
Acknowledgements: Funding sources: Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI), grant number 5G12MD007605-23

Table PK/PD Data

Figure 1. Correlation of Css/(Dose/BW) of (a) Metformin with statins (b) Metformin only treatment with pre- and post-surgery timepoint

Figure 2. 3D PK/PD Correlations of % HbA1c Changes of (a) Metformin with statins (b) Metformin only treatment, with Css/(Dose/BW) and BMIs Post RYGB Surgery; 3D correlations of Css of (c) Metformin with statins (d) Metformin only treatment with Dose and pre- and post-surgery timepoint
