Back
Purpose: Chronic paclitaxel (PTX) treatment causes excruciating pain in cancer patients, limiting its use in cancer chemotherapy. Herein, neuroprotective potential of synthetic cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD formulated in extracellular vesicles (CBD-EVs) isolated from human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells were studied against PTX-induced neuropathic pain (PIPN) in C57BL/6J mice
Methods: PTX (8 mg/kg, i.p,) was injected every other day (four doses) to induce neuropathy in C57BL/6J mice. CBD and CBD-EVs was administered (5 mg/kg, i.p) for 6 weeks with twice a week frequency. At the end of study, behavior of the animals towards pain perception were measured using Hargreaves plantar apparatus, hot and cold tail immersion test, vonfrey aesthesiometer and randalsellito apparatus. Dorsal root ganglions (DRGs) were isolated from animals for molecular studies. Further, invitro studies were conducted in DRG primary cultures to study the mitochondrial effects of CBD and CBD-EVs against PTX insult.
Results: EVs and CBD-EVs particle size, surface roughness, nanomechanical attributes, stability, and release studies were investigated. CBD-EVs treatment significantly improved mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity (P < 0.001) as compared to EVs or CBD alone. PTX-treated mice's dorsal root ganglions and spinal homogenates had mitochondrial dysfunction which was significantly improved by CBD and CBD-EVs by regulating the AMPK pathway (P < 0.001). Blocking studies with 5HT1A receptors and AMPK demonstrated that CBD had no effect on PIPN neurobehavioral or mitochondrial function (Fig 1,2&3).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that CBD-EVs can be a novel therapeutic option for the treatment of PIPN and CBD treatment activates AMPK axis in regulating PIPN.
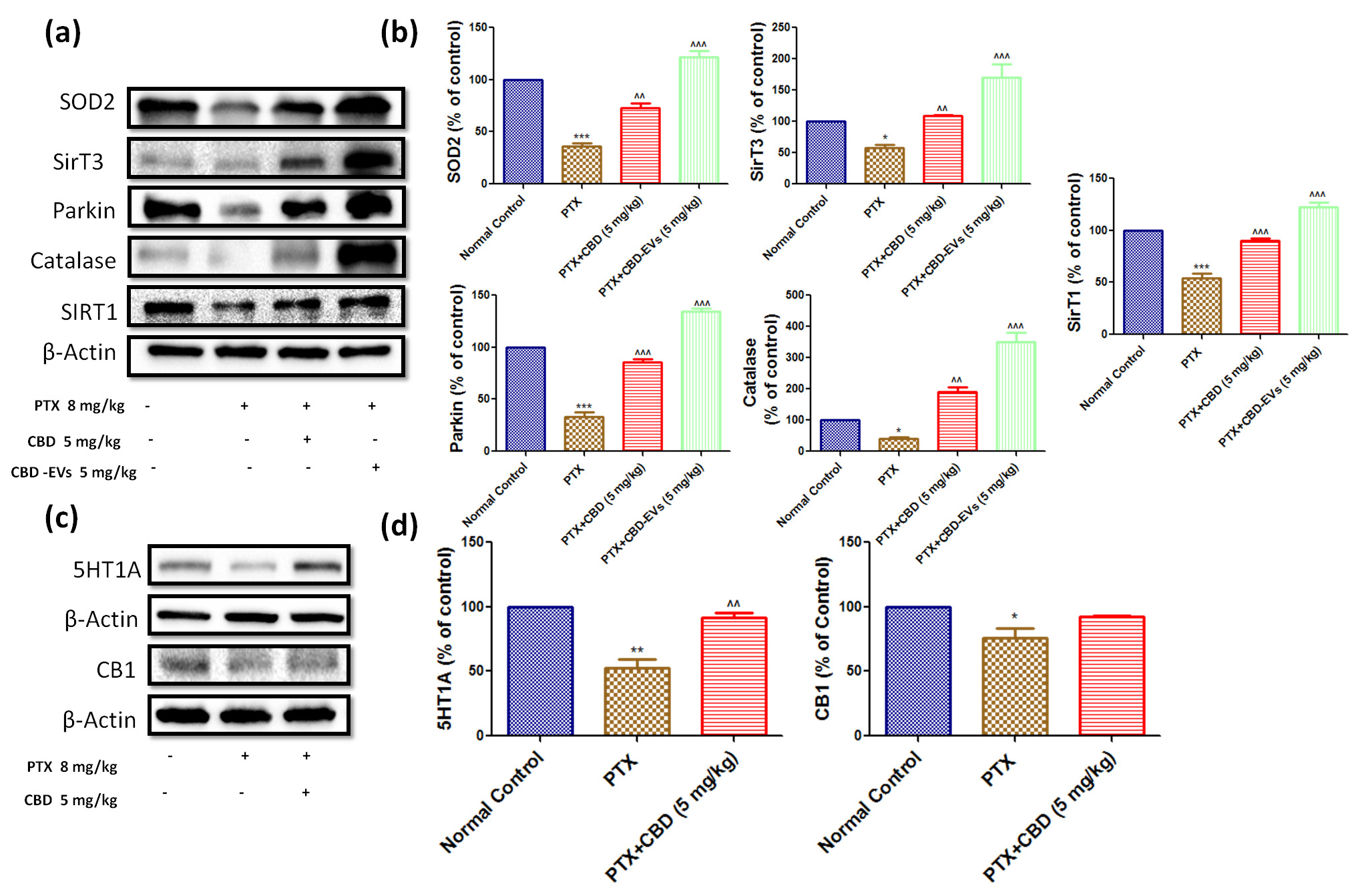
Effect of CBD and CBDEVs on AMPK-SIRT1-NRF1/2 Axis in spinal homogenates and effect of CBD on CB1 and 5HT1A receptors expression in DRG homogenates of PTX induced neuropathic mice. (a) Western blots of spinal homogenates show treatment with CBD (5 mg/kg) and CBD-EVs (5 mg/kg) and (c) Western blots of DRG homogenates show treatment with CBD (5 mg/kg) in PTX treated mice for six weeks after last dose of PTX administration. (b) & (d) Bar graphs represent the respective western blots quantification. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=3). ***p < 0.001 Vs Normal control, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg)
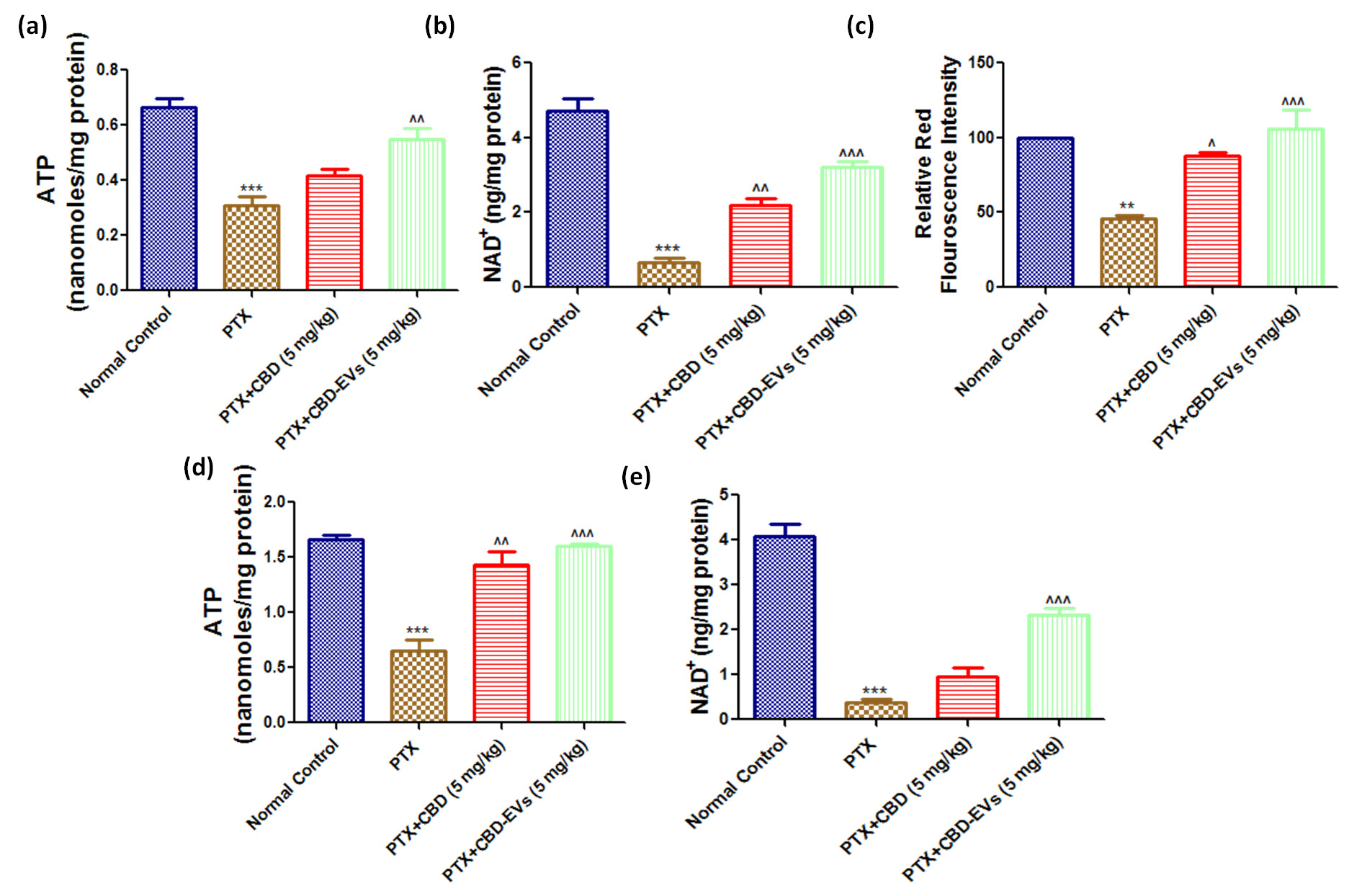
Effect of CBD and CBD-EVs on Mitochondrial Function and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). (a) Representative bar graphs showing the ATP levels in Fresh DRG homogenates and (d) spinal homogenates of PTX treated mice, (b) bar graph showing NAD+ levels in DRG homogenates and (e) in spinal homogenates of PTX treated mice, (c) Bar graph represents the JC1 trimer aggregates relative red florescence intensity. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=3). ***p < 0.001 Vs Normal control, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg)
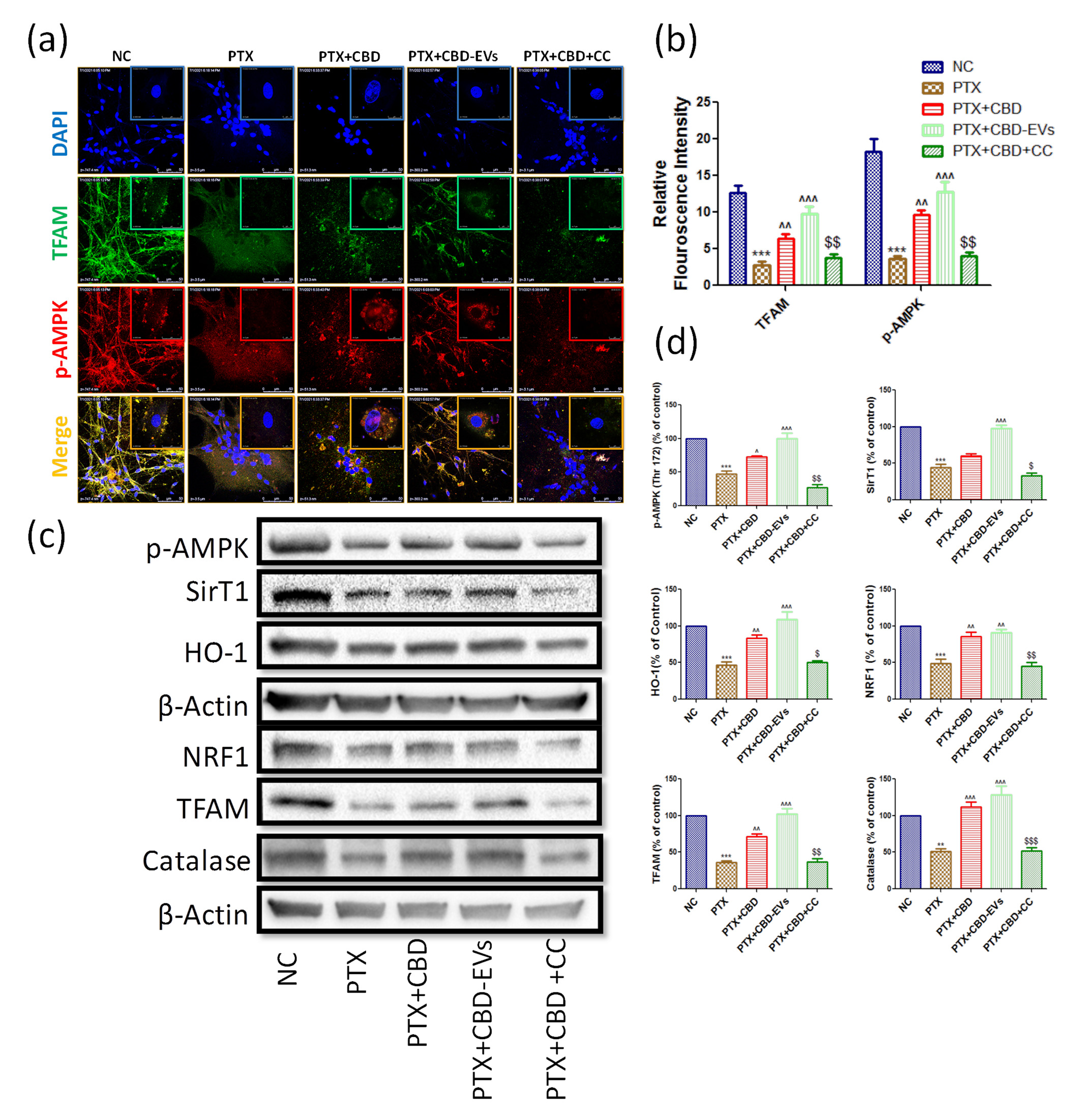
Immunoexpressions of AMPK pathway in cultured DRG primary cells (a) Representative confocal microscope images showing the upper panel nuclear (DAPI) staining, middle panel: immuno expression of TFAM tagged with Alexa488 fluorochrome and lower panel: immuno expression of p-AMPK labeled with rhodamine, (b) quantified relative red and green florescence intensities of confocal images using LASX software associated with confocal microscopy.(c) Western blots of cultured DRG lysates show treatment with 12 μM either of CBD and CBD-EVs in PTX treated neuronal cells for 48 hours (d) Bar graphs represent the respective western blots quantification. ***p < 0.001 Vs NC, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg). $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01 and $$$P < 0.001 Vs PTX+CBD
Clinical Pharmacology - Biomolecular - Biomarkers
Category: Poster Abstract
(M0930-11-61) Cannabidiol Loaded Extracellular Vesicles from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Paclitaxel Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Monday, October 17, 2022
9:30 AM – 10:30 AM ET
- MS
Mandip Singh, Ph.D.
Florida A&M University
Tallahassee, Florida, United States - AK
Anil Kumar Kalvala, Ph.D.
Florida A&M University
Tallahassee, Florida, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Chronic paclitaxel (PTX) treatment causes excruciating pain in cancer patients, limiting its use in cancer chemotherapy. Herein, neuroprotective potential of synthetic cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD formulated in extracellular vesicles (CBD-EVs) isolated from human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells were studied against PTX-induced neuropathic pain (PIPN) in C57BL/6J mice
Methods: PTX (8 mg/kg, i.p,) was injected every other day (four doses) to induce neuropathy in C57BL/6J mice. CBD and CBD-EVs was administered (5 mg/kg, i.p) for 6 weeks with twice a week frequency. At the end of study, behavior of the animals towards pain perception were measured using Hargreaves plantar apparatus, hot and cold tail immersion test, vonfrey aesthesiometer and randalsellito apparatus. Dorsal root ganglions (DRGs) were isolated from animals for molecular studies. Further, invitro studies were conducted in DRG primary cultures to study the mitochondrial effects of CBD and CBD-EVs against PTX insult.
Results: EVs and CBD-EVs particle size, surface roughness, nanomechanical attributes, stability, and release studies were investigated. CBD-EVs treatment significantly improved mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity (P < 0.001) as compared to EVs or CBD alone. PTX-treated mice's dorsal root ganglions and spinal homogenates had mitochondrial dysfunction which was significantly improved by CBD and CBD-EVs by regulating the AMPK pathway (P < 0.001). Blocking studies with 5HT1A receptors and AMPK demonstrated that CBD had no effect on PIPN neurobehavioral or mitochondrial function (Fig 1,2&3).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that CBD-EVs can be a novel therapeutic option for the treatment of PIPN and CBD treatment activates AMPK axis in regulating PIPN.

Effect of CBD and CBDEVs on AMPK-SIRT1-NRF1/2 Axis in spinal homogenates and effect of CBD on CB1 and 5HT1A receptors expression in DRG homogenates of PTX induced neuropathic mice. (a) Western blots of spinal homogenates show treatment with CBD (5 mg/kg) and CBD-EVs (5 mg/kg) and (c) Western blots of DRG homogenates show treatment with CBD (5 mg/kg) in PTX treated mice for six weeks after last dose of PTX administration. (b) & (d) Bar graphs represent the respective western blots quantification. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=3). ***p < 0.001 Vs Normal control, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg)

Effect of CBD and CBD-EVs on Mitochondrial Function and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). (a) Representative bar graphs showing the ATP levels in Fresh DRG homogenates and (d) spinal homogenates of PTX treated mice, (b) bar graph showing NAD+ levels in DRG homogenates and (e) in spinal homogenates of PTX treated mice, (c) Bar graph represents the JC1 trimer aggregates relative red florescence intensity. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=3). ***p < 0.001 Vs Normal control, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg)

Immunoexpressions of AMPK pathway in cultured DRG primary cells (a) Representative confocal microscope images showing the upper panel nuclear (DAPI) staining, middle panel: immuno expression of TFAM tagged with Alexa488 fluorochrome and lower panel: immuno expression of p-AMPK labeled with rhodamine, (b) quantified relative red and green florescence intensities of confocal images using LASX software associated with confocal microscopy.(c) Western blots of cultured DRG lysates show treatment with 12 μM either of CBD and CBD-EVs in PTX treated neuronal cells for 48 hours (d) Bar graphs represent the respective western blots quantification. ***p < 0.001 Vs NC, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01 and ^^^p < 0.001 Vs PTX (8 mg/kg). $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01 and $$$P < 0.001 Vs PTX+CBD
