Back
Purpose: STK-001 is a chemically synthesized antisense oligonucleotide that is being developed by Stoke Therapeutics for the treatment of Dravet syndrome in children of age 2 to 18 years. STK-001 is administered intrathecally and is being investigated in Phase 1/2 and Open Label Extension studies in US and UK. To assess the potential immunogenicity response due to ADA generation induced by STK-001 administration in NHP and Human, we developed reliable and sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based methods for detection and titration of STK-001 ADA.
Methods: STK-001 was conjugated to KLH and BSA for generating immunogens. STK-001 BSA or KLH conjugates were injected to rabbits, using three different protocols and titers were evaluated periodically to monitor for antibody production. Affinity-purification methods were developed and optimized to obtain a high-quality ADA positive control (PC). Various Enzyme-linked immunoassays formats (ELISA/ECL) were compared and investigated for sensitivity and specificity. Reliable ELISA methods meeting regulatory criteria were developed and validated in monkey and human serum.
Results: The ADA titers measured by ELISA in rabbit serum showed over 100-fold difference between the three protocols. The highest titers were observed with alternate KLH-STK-001 and BSA-STK-001 administrations (Protocol 3, Figure). The affinity-purification of PC was investigated by using different coating materials. The optimized affinity purification method used Affi-Gel 10 (Bio-Rad) and amino STK-001 for coating, which yielded the highest quality PC. All purifications were conducted under controlled temperature conditions and the yield of positive control was approx. 1%.With purified PC, various Streptavidin coated plates and covalent binding plates were compared to increase sensitivity and to reduce non-specific binding for both ELISA and ECL platforms. A reliable ELISA method with covalent binding surface plate was developed with MRD 25 to monitor ADA in serum. The method was validated for ADA assessments in human and monkey serum. Sensitivity, cut-point, selectivity, titer precision, intra-assay and inter-assay precision, and tolerance were evaluated and met acceptance criteria.The methods are reliable and are being successfully used to support monkey toxicity and human clinical studies.
Conclusion: An immunization protocol using alternate injections with KLH-STK-001 and BSA-STK-001 resulted in high antibody titers in rabbits. High quality ADA was purified from serum using an optimized affinity purification protocol, Sensitive and reliable ELISA methods were successfully developed, validated, and used to support monkey toxicity and human clinical studies.
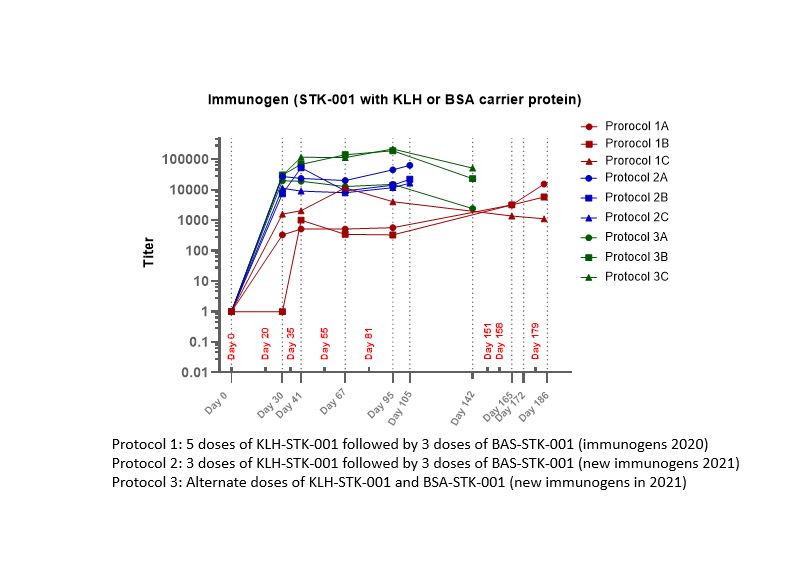
Figure: Comparison of ADA Titers in Rabbits for Three Protocols
Bioanalytics - Biomolecular - Immunogenicity
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(W1030-09-50) Challenges and Solutions for Successful Generation of Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) Positive Control (PC) for Development of ADA assay for STK-001 in Monkey and Human Serum
Wednesday, October 19, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:30 AM ET
- YC
Yanyan Cui, Ph.D.
Stoke Therapeutics
Bedford, Massachusetts, United States - YC
Yanyan Cui, Ph.D.
Stoke Therapeutics
Bedford, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: STK-001 is a chemically synthesized antisense oligonucleotide that is being developed by Stoke Therapeutics for the treatment of Dravet syndrome in children of age 2 to 18 years. STK-001 is administered intrathecally and is being investigated in Phase 1/2 and Open Label Extension studies in US and UK. To assess the potential immunogenicity response due to ADA generation induced by STK-001 administration in NHP and Human, we developed reliable and sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based methods for detection and titration of STK-001 ADA.
Methods: STK-001 was conjugated to KLH and BSA for generating immunogens. STK-001 BSA or KLH conjugates were injected to rabbits, using three different protocols and titers were evaluated periodically to monitor for antibody production. Affinity-purification methods were developed and optimized to obtain a high-quality ADA positive control (PC). Various Enzyme-linked immunoassays formats (ELISA/ECL) were compared and investigated for sensitivity and specificity. Reliable ELISA methods meeting regulatory criteria were developed and validated in monkey and human serum.
Results: The ADA titers measured by ELISA in rabbit serum showed over 100-fold difference between the three protocols. The highest titers were observed with alternate KLH-STK-001 and BSA-STK-001 administrations (Protocol 3, Figure). The affinity-purification of PC was investigated by using different coating materials. The optimized affinity purification method used Affi-Gel 10 (Bio-Rad) and amino STK-001 for coating, which yielded the highest quality PC. All purifications were conducted under controlled temperature conditions and the yield of positive control was approx. 1%.With purified PC, various Streptavidin coated plates and covalent binding plates were compared to increase sensitivity and to reduce non-specific binding for both ELISA and ECL platforms. A reliable ELISA method with covalent binding surface plate was developed with MRD 25 to monitor ADA in serum. The method was validated for ADA assessments in human and monkey serum. Sensitivity, cut-point, selectivity, titer precision, intra-assay and inter-assay precision, and tolerance were evaluated and met acceptance criteria.The methods are reliable and are being successfully used to support monkey toxicity and human clinical studies.
Conclusion: An immunization protocol using alternate injections with KLH-STK-001 and BSA-STK-001 resulted in high antibody titers in rabbits. High quality ADA was purified from serum using an optimized affinity purification protocol, Sensitive and reliable ELISA methods were successfully developed, validated, and used to support monkey toxicity and human clinical studies.

Figure: Comparison of ADA Titers in Rabbits for Three Protocols
