Back
Purpose: Docetaxel (DTX) is a potential anticancer chemotherapeutic drug with a broad spectrum of action. However, due to their low water solubility, commercial formulations need to rely on nonionic surfactants, which can cause major side effects in humans such as hypersensitivity reactions and peripheral neuropathy [1]. To overcome these problems, it is required to develop a smart delivery system, which can reduce the toxicity by preventing the non-specific distribution of the drug and delivering them to the tumor site. One of the many potential approaches, liposomes as a carrier can show many advantages including offering the opportunity for surface modification by targeting ligands to exploit active targeting. Therefore, in this research, to improve the targeting efficiency of DTX to TAMs, we synthesized a ligand (L)-PEG2000-DSPE conjugate and decorated it on the DTX-loaded liposomes. The liposome formulations were to optimize, characterize, and evaluate anti-cancer effects in vitro.
Methods: L-PEG2000-DSPE was synthesized by conjugation of L to DSPE-PEG2000-COOH. Docetaxel conventional liposome (DTX-CL), docetaxel loaded in DSPE-PEG2000 modified liposome (DTX-PL) and docetaxel loaded in L-PEG2000-DSPE modified liposome (DTX-LPL) were prepared by ethanol injection method, and follow by lyophilization. Then, the liposomes were characterized by particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficacy (%EE), drug loading, release in vitro, and stability. In vitro anticancer effect on MCF-7 breast cancer cells was also investigated.
Results: L-PEG2000-DSPE was synthesized successfully. All formulations achieve small particle sizes, below 100 nm. The particle sizes of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL were obtained at 90.6±0.73 nm, 93.02±4.47 nm, and 96.23±4.05 nm, respectively. Modification of the liposome surface slightly increases the particle size. In addition, the formulas also achieve uniformity in particle size distribution, which shows that all PDI values are less than 0.3 (PDI of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL were 0.11±0.04, 0.22±0.07 and 0.19±0.02, respectively). The ability to encapsulate the drug into the lipid bilayer was also measured and showed a high % of Encapsulation efficacy (%EE of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL achieved 98.16±0.04%, 96.05±2.89%, and 98.05± 0.27%, respectively ). All 3 formulas obtained the negative surface charge. Modified liposome surface by DSPE-PEG2000 or L-PEG2000-DSPE showed a higher negative charge value than conventional liposome (-26.24±1.53 for DTX-PL and -27.4±1.28 for DTX-LPL versus -4.97±1.1 for DTX-CL). At the same time, the conjugation of L did not change the surface charge properties of the liposomes. Both conventional, PEGylated or L-modified docetaxel-liposomes were stable at 4°C after 30 days, with no significant changes in particle size and %EE. The L-modified liposome showed a better inhibition effect on breast cancer cell lines than other formulations (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Ligand-modified liposome formula has been successfully formulated and optimized with small particle size, negative surface charge, high %EE, and maintained stability after 30 days. The in vitro drug release properties of liposomes were not affected by the addition of a L moiety. Targeted liposomes based on L ligand have shown potential results in breast cancer cell lines in vitro.
References: [1] ten Tije, Albert J., et al. "Pharmacological effects of formulation vehicles." Clinical pharmacokinetics 42.7 (2003): 665-685.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2021R1A2C1011176).
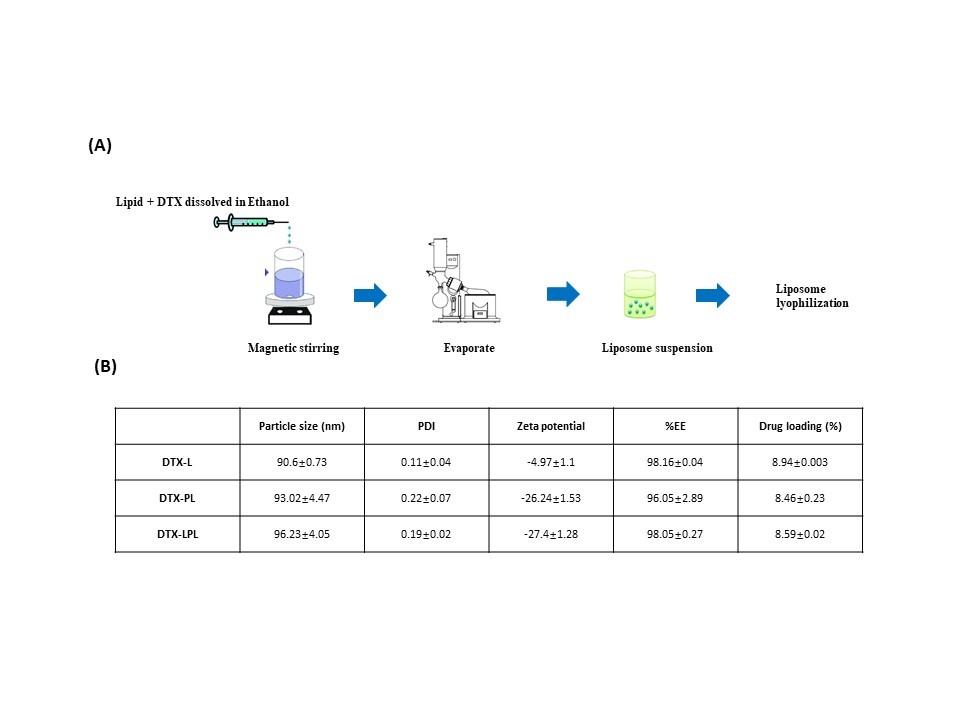
Fig.1. Preparation method for DTX liposomes (A) and Liposomes properties (B)
.jpg)
Fig.2. Storage stability at 4oC of docetaxel-loaded conventional liposome (A), Docetaxel-loaded PEGylated liposome (B) and docetaxel-loaded ligand-modified liposome (C)
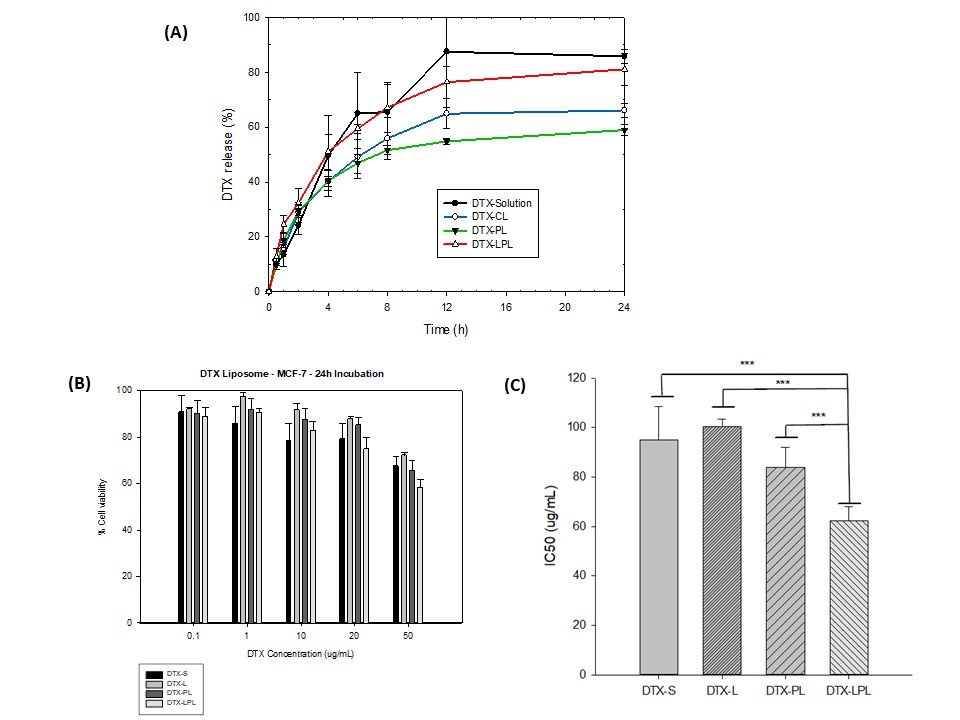
Fig.3. In vitro release properties of Docetaxel liposomes (A). % Cell viability of MCF-7 cells after 24h incubation with different DTX formulations (B). IC50 value of DTX formulations for MCF-7 cells (C)
Category: Poster Abstract
(T1230-12-72) Surface-Modified Liposome for Targeted Delivery of Docetaxel: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation
Tuesday, October 18, 2022
12:30 PM – 1:30 PM ET
.jpg)
Nhan Phan Tran, MS
Student
ChungNam National University
Daejeon, Taejon-jikhalsi, Republic of Korea.jpg)
Nhan Phan Tran, MS
Student
ChungNam National University
Daejeon, Taejon-jikhalsi, Republic of Korea
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Docetaxel (DTX) is a potential anticancer chemotherapeutic drug with a broad spectrum of action. However, due to their low water solubility, commercial formulations need to rely on nonionic surfactants, which can cause major side effects in humans such as hypersensitivity reactions and peripheral neuropathy [1]. To overcome these problems, it is required to develop a smart delivery system, which can reduce the toxicity by preventing the non-specific distribution of the drug and delivering them to the tumor site. One of the many potential approaches, liposomes as a carrier can show many advantages including offering the opportunity for surface modification by targeting ligands to exploit active targeting. Therefore, in this research, to improve the targeting efficiency of DTX to TAMs, we synthesized a ligand (L)-PEG2000-DSPE conjugate and decorated it on the DTX-loaded liposomes. The liposome formulations were to optimize, characterize, and evaluate anti-cancer effects in vitro.
Methods: L-PEG2000-DSPE was synthesized by conjugation of L to DSPE-PEG2000-COOH. Docetaxel conventional liposome (DTX-CL), docetaxel loaded in DSPE-PEG2000 modified liposome (DTX-PL) and docetaxel loaded in L-PEG2000-DSPE modified liposome (DTX-LPL) were prepared by ethanol injection method, and follow by lyophilization. Then, the liposomes were characterized by particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficacy (%EE), drug loading, release in vitro, and stability. In vitro anticancer effect on MCF-7 breast cancer cells was also investigated.
Results: L-PEG2000-DSPE was synthesized successfully. All formulations achieve small particle sizes, below 100 nm. The particle sizes of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL were obtained at 90.6±0.73 nm, 93.02±4.47 nm, and 96.23±4.05 nm, respectively. Modification of the liposome surface slightly increases the particle size. In addition, the formulas also achieve uniformity in particle size distribution, which shows that all PDI values are less than 0.3 (PDI of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL were 0.11±0.04, 0.22±0.07 and 0.19±0.02, respectively). The ability to encapsulate the drug into the lipid bilayer was also measured and showed a high % of Encapsulation efficacy (%EE of DTX-CL, DTX-PL, and DTX-LPL achieved 98.16±0.04%, 96.05±2.89%, and 98.05± 0.27%, respectively ). All 3 formulas obtained the negative surface charge. Modified liposome surface by DSPE-PEG2000 or L-PEG2000-DSPE showed a higher negative charge value than conventional liposome (-26.24±1.53 for DTX-PL and -27.4±1.28 for DTX-LPL versus -4.97±1.1 for DTX-CL). At the same time, the conjugation of L did not change the surface charge properties of the liposomes. Both conventional, PEGylated or L-modified docetaxel-liposomes were stable at 4°C after 30 days, with no significant changes in particle size and %EE. The L-modified liposome showed a better inhibition effect on breast cancer cell lines than other formulations (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Ligand-modified liposome formula has been successfully formulated and optimized with small particle size, negative surface charge, high %EE, and maintained stability after 30 days. The in vitro drug release properties of liposomes were not affected by the addition of a L moiety. Targeted liposomes based on L ligand have shown potential results in breast cancer cell lines in vitro.
References: [1] ten Tije, Albert J., et al. "Pharmacological effects of formulation vehicles." Clinical pharmacokinetics 42.7 (2003): 665-685.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2021R1A2C1011176).

Fig.1. Preparation method for DTX liposomes (A) and Liposomes properties (B)
.jpg)
Fig.2. Storage stability at 4oC of docetaxel-loaded conventional liposome (A), Docetaxel-loaded PEGylated liposome (B) and docetaxel-loaded ligand-modified liposome (C)

Fig.3. In vitro release properties of Docetaxel liposomes (A). % Cell viability of MCF-7 cells after 24h incubation with different DTX formulations (B). IC50 value of DTX formulations for MCF-7 cells (C)
