Back
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common form of liver cancer, which is often treated with chemotherapy. However, the long-term survival of HCC patients is hindered by high recurrence and drug resistance. To overcome drug resistance, two drugs instead of one, delivered through nanomicellar delivery systems can be a feasible option. For this study, a sonic hedgehog inhibitor, cyclopamine (CPA) was combined with paclitaxel (PTX), a mitosis inhibitor with antineoplastic effects, for a potentially greater effectiveness than a therapy with a physical mixture of the unformulated mono-agents in treating HCC. However, CPA and PTX are highly hydrophobic, which require an appropriate drug delivery system. In this study, we aim to utilize a nanoparticle delivery platform to co-deliver CPA and PTX (M-CPA/PTX) against HCC.
Methods: The size, PDI, and zeta potential of M-CPA/PTX were characterized by Malvern Zetasizer. The encapsulation efficiency of CPA and PTX was measured by UV-HPLC. The detection wavelengths for CPA and PTX were 210 nm and 227 nm, respectively. In vivo study, c-Myc-driven spontaneous HCC mice were given intravenous injections, 3 times a week for 12 weeks of either 5 mg/kg/drug/dose M-CPA/PTX or CPA+PTX in Cremophor EL/alcohol. The blood samples were collected, and tumor, liver, and spleen samples were harvested at 2 and 24 hours post the last dose. The PTX and CPA concentrations in blood, tumor, and organ samples were quantified using a validated LC-MS/MS assay with LLOQ of 0.5 ng/mL. Pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis was executed in Phoenix® NLMETM, version 8.2 (Certara L.P. Pharsight, St. Louis, MO, USA)
Results: The M-CPA/PTX was characterized (N=3) with small size (174.57 ± 0.003 nm in hydrodynamic diameter), good homogeneity (PDI 0.19 ± 0.03), zeta potential (0.0005 ± 0.0001 mA) and high encapsulation efficiency (CPA 69.76 ± 6.02% and PTX 94.07 ± 5.97%). The blood concentrations and biodistribution of M-CPA and M-PTX in the c-Myc-driven spontaneous HCC model were evaluated (Figure 1). The concentrations of CPA and PTX in the blood of mice injected with M-CPA/PTX were 4-5 times higher than those with a mixture of CPA and PTX in the Cremophor/alcohol at 2 hours (P < 0.05). The tumor concentrations of PTX from M-CPA/PTX, 703.29 ± 341.83 ng/g, were significantly higher in the M-CPA/PTX group than that from a mixture of CPA and PTX in Cremophor/alcohol group, 56.59 ± 2.93 ng/g (P < 0.05). The PK parameters were derived using one-compartment model via population analysis of two time points. This PK study revealed that the CL of CPA in M-CPA/PTX group was slower compared to that in unformulated group (2.46 ± 3.35 vs 8.40 ± 7.06 L/h/kg). Also, the volume distribution achieved in M-CPA/PTX group was smaller than unformulated CPA/PTX group on the same dose basis (6.67 ± 13.72vs 35.85 ± 31.19 L/kg). The difference between PTX kinetics in the M-CPA/PTX and unformulated CPA/PTX groups were less pronounced.
Conclusion: The M-CPA/PTX is developed and characterized with the desired physicochemical properties. The M-CPA/PTX is a promising delivery system for CPA and PTX against HCC. M-CPA/PTX enhanced the blood exposure of both CPA and PTX, and tumor accumulation of PTX after multiple injections. Increased tumor accumulation is anticipated to result in increased therapeutic effectiveness.
References: 1. Patil, M. A., J. Zhang, C. Ho, S. T. Cheung, S. T. Fan, and X. Chen. Hedgehog signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Jan; 5(1), 111-117.
2. Wang, N., S. Wang, M. Y. Li, B. G. Hu, L. P. Liu, S. L. Yang, S. Yang, Gong, Z. Lai, P. B. S. Chen, G. G. Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview and promising therapeutic strategies. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2018 Dec 21; 10:1758835918816287.
3. Yang, R., G. Mondal, D. Wen, and R. I. Mahato. Combination therapy of paclitaxel and cyclopamine polymer-drug conjugates to treat advanced prostate cancer. Nanomedicine, 2017 Feb; 13(2), 391-401.
4. Zhao, J., H. Wang, C. H. Hsiao, D. S. Chow, E. J. Koay, Y. Kang, X. Wen, Huang, Q. Ma, Y. Bankson, J. A. Ullrich, S. E. Overwijk, W. Maitra, A. Piwnica-Worms, D. Fleming, J. B. Li, C. Simultaneous inhibition of hedgehog signaling and tumor proliferation remodels stroma and enhances pancreatic cancer therapy. Biomaterials, 2018 Mar; 159, 215-228.
Acknowledgements: Funding source: Gillson Longenbaugh Foundation
.jpg)
Figure 1. Drug concentrations in whole blood (ng/mL) and each organ (ng/g) after three injections of drugs from M-CPA/PTX or unformulated physical mixture in cosolvents. (A) cyclopamine (CPA), (B) paclitaxel (PTX). Expressed as Mean ± SD (**** P < 0.0001, *** P=0.0002, ** P = 0.0071)
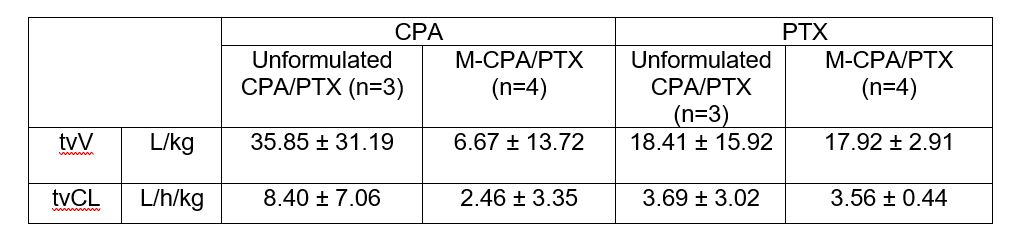
Table 1. Comparative PK parameters for M-CPA/PTX and unformulated CPA/PTX
Discovery and Basic Research - Pharmacology
Category: Poster Abstract
(W1130-05-28) Polymeric Delivery with Dual Drug Payloads for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Therapy
Wednesday, October 19, 2022
11:30 AM – 12:30 PM ET
- LD
Lu Dai, MS
Research Assistant
University of Houston
Houston, Texas, United States - LD
Lu Dai, MS
Research Assistant
University of Houston
Houston, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common form of liver cancer, which is often treated with chemotherapy. However, the long-term survival of HCC patients is hindered by high recurrence and drug resistance. To overcome drug resistance, two drugs instead of one, delivered through nanomicellar delivery systems can be a feasible option. For this study, a sonic hedgehog inhibitor, cyclopamine (CPA) was combined with paclitaxel (PTX), a mitosis inhibitor with antineoplastic effects, for a potentially greater effectiveness than a therapy with a physical mixture of the unformulated mono-agents in treating HCC. However, CPA and PTX are highly hydrophobic, which require an appropriate drug delivery system. In this study, we aim to utilize a nanoparticle delivery platform to co-deliver CPA and PTX (M-CPA/PTX) against HCC.
Methods: The size, PDI, and zeta potential of M-CPA/PTX were characterized by Malvern Zetasizer. The encapsulation efficiency of CPA and PTX was measured by UV-HPLC. The detection wavelengths for CPA and PTX were 210 nm and 227 nm, respectively. In vivo study, c-Myc-driven spontaneous HCC mice were given intravenous injections, 3 times a week for 12 weeks of either 5 mg/kg/drug/dose M-CPA/PTX or CPA+PTX in Cremophor EL/alcohol. The blood samples were collected, and tumor, liver, and spleen samples were harvested at 2 and 24 hours post the last dose. The PTX and CPA concentrations in blood, tumor, and organ samples were quantified using a validated LC-MS/MS assay with LLOQ of 0.5 ng/mL. Pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis was executed in Phoenix® NLMETM, version 8.2 (Certara L.P. Pharsight, St. Louis, MO, USA)
Results: The M-CPA/PTX was characterized (N=3) with small size (174.57 ± 0.003 nm in hydrodynamic diameter), good homogeneity (PDI 0.19 ± 0.03), zeta potential (0.0005 ± 0.0001 mA) and high encapsulation efficiency (CPA 69.76 ± 6.02% and PTX 94.07 ± 5.97%). The blood concentrations and biodistribution of M-CPA and M-PTX in the c-Myc-driven spontaneous HCC model were evaluated (Figure 1). The concentrations of CPA and PTX in the blood of mice injected with M-CPA/PTX were 4-5 times higher than those with a mixture of CPA and PTX in the Cremophor/alcohol at 2 hours (P < 0.05). The tumor concentrations of PTX from M-CPA/PTX, 703.29 ± 341.83 ng/g, were significantly higher in the M-CPA/PTX group than that from a mixture of CPA and PTX in Cremophor/alcohol group, 56.59 ± 2.93 ng/g (P < 0.05). The PK parameters were derived using one-compartment model via population analysis of two time points. This PK study revealed that the CL of CPA in M-CPA/PTX group was slower compared to that in unformulated group (2.46 ± 3.35 vs 8.40 ± 7.06 L/h/kg). Also, the volume distribution achieved in M-CPA/PTX group was smaller than unformulated CPA/PTX group on the same dose basis (6.67 ± 13.72vs 35.85 ± 31.19 L/kg). The difference between PTX kinetics in the M-CPA/PTX and unformulated CPA/PTX groups were less pronounced.
Conclusion: The M-CPA/PTX is developed and characterized with the desired physicochemical properties. The M-CPA/PTX is a promising delivery system for CPA and PTX against HCC. M-CPA/PTX enhanced the blood exposure of both CPA and PTX, and tumor accumulation of PTX after multiple injections. Increased tumor accumulation is anticipated to result in increased therapeutic effectiveness.
References: 1. Patil, M. A., J. Zhang, C. Ho, S. T. Cheung, S. T. Fan, and X. Chen. Hedgehog signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Jan; 5(1), 111-117.
2. Wang, N., S. Wang, M. Y. Li, B. G. Hu, L. P. Liu, S. L. Yang, S. Yang, Gong, Z. Lai, P. B. S. Chen, G. G. Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview and promising therapeutic strategies. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2018 Dec 21; 10:1758835918816287.
3. Yang, R., G. Mondal, D. Wen, and R. I. Mahato. Combination therapy of paclitaxel and cyclopamine polymer-drug conjugates to treat advanced prostate cancer. Nanomedicine, 2017 Feb; 13(2), 391-401.
4. Zhao, J., H. Wang, C. H. Hsiao, D. S. Chow, E. J. Koay, Y. Kang, X. Wen, Huang, Q. Ma, Y. Bankson, J. A. Ullrich, S. E. Overwijk, W. Maitra, A. Piwnica-Worms, D. Fleming, J. B. Li, C. Simultaneous inhibition of hedgehog signaling and tumor proliferation remodels stroma and enhances pancreatic cancer therapy. Biomaterials, 2018 Mar; 159, 215-228.
Acknowledgements: Funding source: Gillson Longenbaugh Foundation
.jpg)
Figure 1. Drug concentrations in whole blood (ng/mL) and each organ (ng/g) after three injections of drugs from M-CPA/PTX or unformulated physical mixture in cosolvents. (A) cyclopamine (CPA), (B) paclitaxel (PTX). Expressed as Mean ± SD (**** P < 0.0001, *** P=0.0002, ** P = 0.0071)

Table 1. Comparative PK parameters for M-CPA/PTX and unformulated CPA/PTX
