Back
Purpose: Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid isolated from Cannabis sativa. It reportedly demonstrated anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and anti-inflammatory effects and was approved by the FDA as a treatment for pediatric epilepsy. Despite the many pharmacological potentials of CBD, its drawbacks have limited its applications in therapeutics. Poor water solubility is a major drawback in addition to significant first-pass metabolism and low bioavailability (approximately 6%). The main objective of the current project was to develop CBD mucoadhesive buccal film using Hot-Melt Extrusion (HME) technology to enhance the CBD solubility and avoid the effect of first-pass metabolism.
Methods: Different films were developed by mixing 10% w/w of CBD with polymeric carrier/s and other excipients, as shown in Table 1. The resulted physical mixtures were fed into Thermo Scientific HAAKE Mini lab II (Thermo Fisher Scientific), a film die (1 mm thickness) used to produce the CBD films. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC (TA DSC 25) was performed for CBD, the polymeric carriers and the extruded films to determine their thermal characterization. Samples were weighed in T-zero pans (3–5 mg). The temperature was elevated from 25 to 200 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min under a flow of ultrahigh purity nitrogen gas. CBD drug content and content uniformity were evaluated using HPLC-UV. Bio-adhesion test was performed using a texture analyzer (TA-XT2) to evaluate the adhesiveness properties of each film. Solubility studies were performed for the developed films and the pure CBD using the shake-flask method at room temperature for 48 hours to evaluate the improvement of CBD solubility in the HME films. A drug release study was performed using a multi-position Stirring Hot Plate. The dissolution media used was 100 mL of simulated saliva (pH 6.8), 0.1 % w/v SLS at 37 ± 0.5 ºC. Samples withdrawal were at 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180 and 240 minutes for analysis using HPLC.
Results: The drug content in all the formulations was in the range of 91- 103%. The DSC results show melting peaks at 69 ºC and 65 ºC for CBD and PEO N80 respectively. The CBD endothermic peak disappeared in all prepared HME films indicating the transformation of CBD from crystalline to amorphous state (Figure 1). The bio-adhesion results demonstrate higher adhesiveness for the formulation containing PEO N80 and carbopol than the other formulations that confirm the bio-adhesion activity of these excipients. The solubility studies showed an enhancement in CBD solubility for all HME buccal films. The CBD water solubility showed 125.60, 307.56, 318.22, and 362.72 µg/mL for formulations F4, F6, F7, and F8 respectively. While the pure CBD water solubility was below the LOD of the analytical method. The drug release studies, as shown in Figure 2 showed a significant enhancement in the CBD release of F4, F6, F7 and F8 (2 to 5 fold) compared to the pure CBD.
Conclusion: Successfully mucoadhesive buccal films have been developed using HME technology. The results of this study showed an enhancement of the solubility and drug release of CBD. The developed formulations promise to enhance the CBD bioavailability.
References: 1. Moltke J, Hindocha C. Reasons for cannabidiol use: a cross-sectional study of CBD users, focusing on self-perceived stress, anxiety, and sleep problems. Journal of cannabis research. 2021 Dec;3(1):1-2.
2. Mannila J, Järvinen T, Järvinen K, Jarho P. Precipitation complexation method produces cannabidiol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex suitable for sublingual administration of cannabidiol. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2007 Feb 1;96(2):312-9.
3. Repka MA, Langley N, DiNunzio J, editors. Melt extrusion: materials, technology and drug product design. New York, NY, USA:: Springer; 2013 Oct 11.
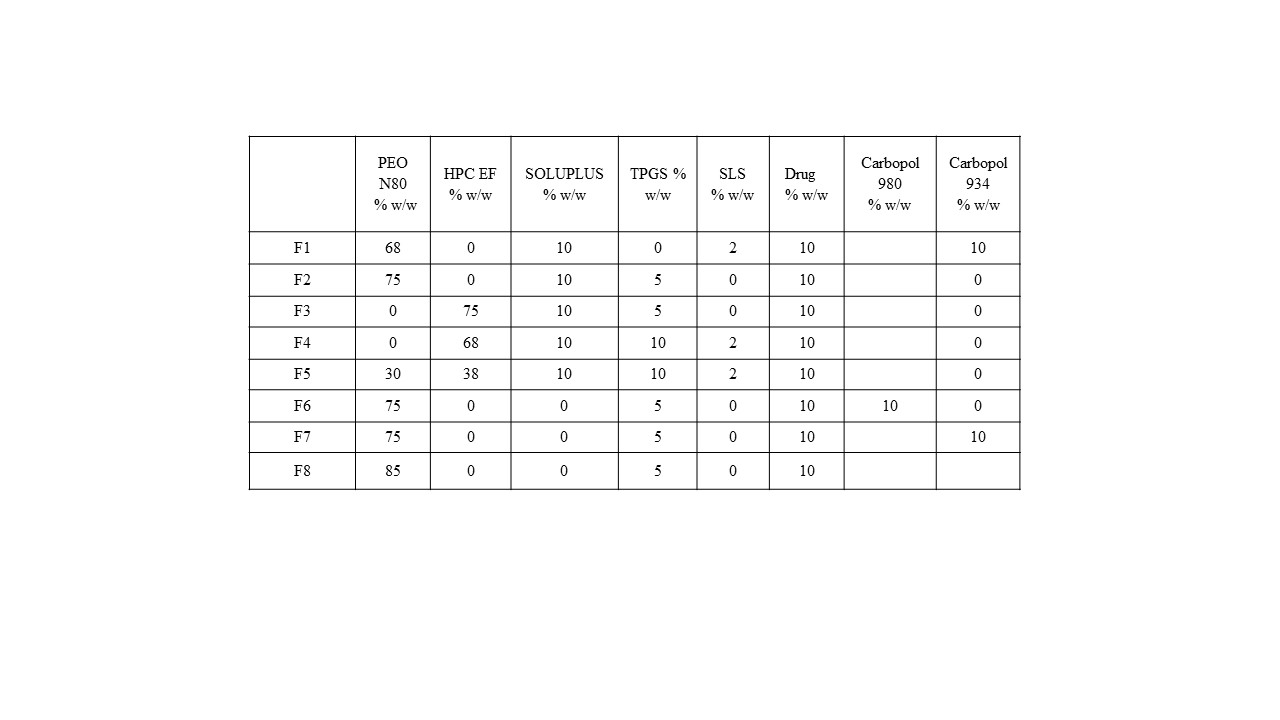
Table.1 CBD formulation composition
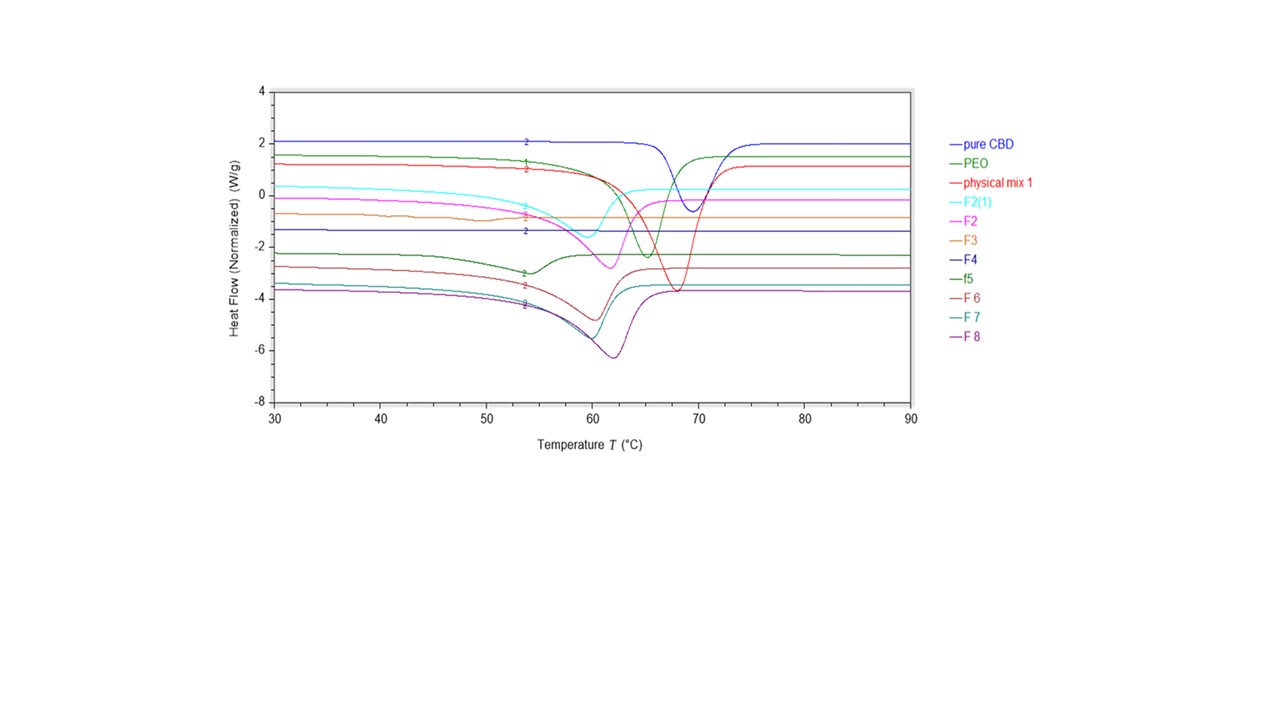
Figure 1. DSC Thermogram of CBD, polymers, and HME films
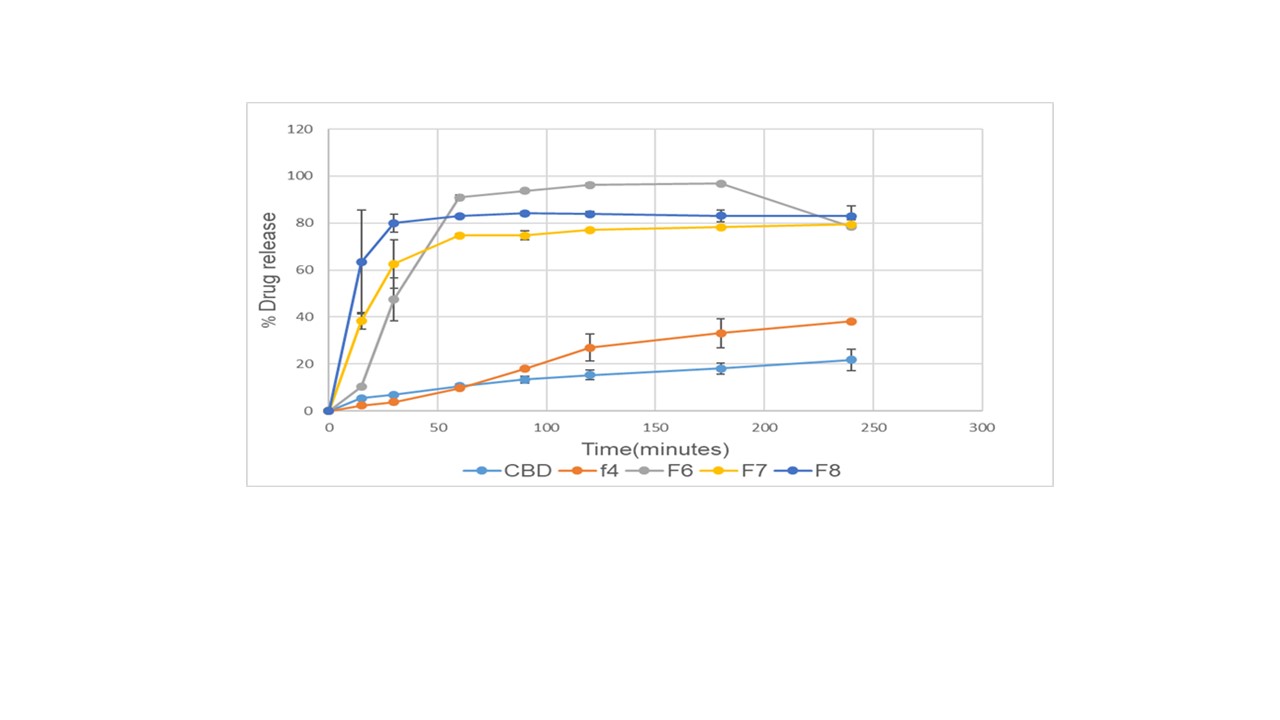
Figure 2. Drug release study for CBD, F4, F6, F7, and F8
Formulation and Delivery - Chemical - Formulation
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1030-03-13) Employing Hot-Melt Extrusion Technology to Enhance the Solubility of Cannabidiol (CBD)
Monday, October 17, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:30 AM ET
- EA
Eman Ashour, Ph.D.
University of Mississippi
University, Mississippi, United States - IE
Iman E. Taha, BS
University of Mississippi
University, Mississippi, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid isolated from Cannabis sativa. It reportedly demonstrated anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and anti-inflammatory effects and was approved by the FDA as a treatment for pediatric epilepsy. Despite the many pharmacological potentials of CBD, its drawbacks have limited its applications in therapeutics. Poor water solubility is a major drawback in addition to significant first-pass metabolism and low bioavailability (approximately 6%). The main objective of the current project was to develop CBD mucoadhesive buccal film using Hot-Melt Extrusion (HME) technology to enhance the CBD solubility and avoid the effect of first-pass metabolism.
Methods: Different films were developed by mixing 10% w/w of CBD with polymeric carrier/s and other excipients, as shown in Table 1. The resulted physical mixtures were fed into Thermo Scientific HAAKE Mini lab II (Thermo Fisher Scientific), a film die (1 mm thickness) used to produce the CBD films. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC (TA DSC 25) was performed for CBD, the polymeric carriers and the extruded films to determine their thermal characterization. Samples were weighed in T-zero pans (3–5 mg). The temperature was elevated from 25 to 200 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min under a flow of ultrahigh purity nitrogen gas. CBD drug content and content uniformity were evaluated using HPLC-UV. Bio-adhesion test was performed using a texture analyzer (TA-XT2) to evaluate the adhesiveness properties of each film. Solubility studies were performed for the developed films and the pure CBD using the shake-flask method at room temperature for 48 hours to evaluate the improvement of CBD solubility in the HME films. A drug release study was performed using a multi-position Stirring Hot Plate. The dissolution media used was 100 mL of simulated saliva (pH 6.8), 0.1 % w/v SLS at 37 ± 0.5 ºC. Samples withdrawal were at 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180 and 240 minutes for analysis using HPLC.
Results: The drug content in all the formulations was in the range of 91- 103%. The DSC results show melting peaks at 69 ºC and 65 ºC for CBD and PEO N80 respectively. The CBD endothermic peak disappeared in all prepared HME films indicating the transformation of CBD from crystalline to amorphous state (Figure 1). The bio-adhesion results demonstrate higher adhesiveness for the formulation containing PEO N80 and carbopol than the other formulations that confirm the bio-adhesion activity of these excipients. The solubility studies showed an enhancement in CBD solubility for all HME buccal films. The CBD water solubility showed 125.60, 307.56, 318.22, and 362.72 µg/mL for formulations F4, F6, F7, and F8 respectively. While the pure CBD water solubility was below the LOD of the analytical method. The drug release studies, as shown in Figure 2 showed a significant enhancement in the CBD release of F4, F6, F7 and F8 (2 to 5 fold) compared to the pure CBD.
Conclusion: Successfully mucoadhesive buccal films have been developed using HME technology. The results of this study showed an enhancement of the solubility and drug release of CBD. The developed formulations promise to enhance the CBD bioavailability.
References: 1. Moltke J, Hindocha C. Reasons for cannabidiol use: a cross-sectional study of CBD users, focusing on self-perceived stress, anxiety, and sleep problems. Journal of cannabis research. 2021 Dec;3(1):1-2.
2. Mannila J, Järvinen T, Järvinen K, Jarho P. Precipitation complexation method produces cannabidiol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex suitable for sublingual administration of cannabidiol. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2007 Feb 1;96(2):312-9.
3. Repka MA, Langley N, DiNunzio J, editors. Melt extrusion: materials, technology and drug product design. New York, NY, USA:: Springer; 2013 Oct 11.

Table.1 CBD formulation composition

Figure 1. DSC Thermogram of CBD, polymers, and HME films

Figure 2. Drug release study for CBD, F4, F6, F7, and F8
