Back
Industry Encore Posters
JL1039E: Tumor agnostic efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with advanced solid tumors with prespecified fibroblast growth factor receptor alterations (FGFRalt) in RAGNAR: interim analysis results
Saturday, October 22, 2022
10:00 AM – 11:00 AM ET


Kristen Crowley, RN, MSN, APRN
Medical Science Liaison
Janssen Research & Development
Poster Presenter(s)
Background:
Erdafitinib is an oral selective pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved to treat locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) in adults with susceptible FGFR3/2alt who have progressed during or after ≥1 line of platinum-containing chemotherapy. FGFRalt are observed across a wide range of malignancies and may function as oncogenic drivers independent of the underlying tumor type. RAGNAR (NCT04083976) is an ongoing phase 2 open label, single-arm tumor agnostic trial investigating the efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in pretreated adult and pediatric patients with advanced solid tumors and FGFRalt. Here, we report results from a planned interim analysis of RAGNAR.
Methods:
Patients aged ≥6 years with advanced or metastatic solid tumors of any histology (except UC) with predefined FGFR1-4alt (mutations/fusions based on local/central test) and documented disease progression on ≥1 prior line of systemic therapy and no alternative standard therapy received oral erdafitinib until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The primary end point is objective response rate (ORR) by independent review committee (IRC). Secondary end points include investigator assessed ORR, duration of response (DOR), disease control rate (DCR), clinical benefit rate (CBR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
Results:
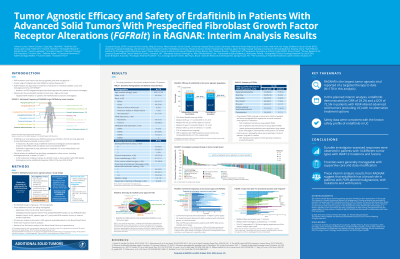
As of the interim analysis data cutoff, 178 patients were treated (median age 56.5 years [range 12-79], median 2 prior systemic therapies). Only 9.0% of patients responded to last line of therapy prior to study entry. ORR by IRC was 29.2% (95% CI, 22.7-36.5). Investigator-assessed ORR was 26.4% (95% CI, 20.1-33.5). Responses were observed in 14 distinct tumor types, including gliomas, thoracic, gastrointestinal, gynecological, and rare tumors (Table). ORR by investigator assessment in patients with FGFR mutations vs fusions was comparable (26.8% vs 27.0%, respectively). Investigator-assessed median DOR, PFS, and OS were 7.1 months (95% CI, 5.5-9.3), 5.2 months (95% CI, 4.0-5.6), and 10.9 months (95% CI, 7.9-14.3), respectively; DCR was 75.3% and CBR was 48.9%. All patients experienced TEAEs, including 69.1% with grade ≥3. Treatment-related serious TEAEs occurred in 7.3% of patients.
Conclusion:
RAGNAR data show, for the first time, evidence of efficacy for erdafitinib in heavily pretreated patients with a variety of hard to treat advanced FGFR+ malignancies, including glioblastoma, pancreatic, and salivary gland cancers. Safety was consistent with the known erdafitinib safety profile.
© 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology, Inc. Reused with permission. This abstract was accepted and previously presented at the 2022 ASCO Annual Meeting. All rights reserved.
Table
JL1039E Table
To view the table, please click on this link from the e-poster gallery on jadprolive.com
Erdafitinib is an oral selective pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved to treat locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) in adults with susceptible FGFR3/2alt who have progressed during or after ≥1 line of platinum-containing chemotherapy. FGFRalt are observed across a wide range of malignancies and may function as oncogenic drivers independent of the underlying tumor type. RAGNAR (NCT04083976) is an ongoing phase 2 open label, single-arm tumor agnostic trial investigating the efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in pretreated adult and pediatric patients with advanced solid tumors and FGFRalt. Here, we report results from a planned interim analysis of RAGNAR.
Methods:
Patients aged ≥6 years with advanced or metastatic solid tumors of any histology (except UC) with predefined FGFR1-4alt (mutations/fusions based on local/central test) and documented disease progression on ≥1 prior line of systemic therapy and no alternative standard therapy received oral erdafitinib until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The primary end point is objective response rate (ORR) by independent review committee (IRC). Secondary end points include investigator assessed ORR, duration of response (DOR), disease control rate (DCR), clinical benefit rate (CBR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
Results:
As of the interim analysis data cutoff, 178 patients were treated (median age 56.5 years [range 12-79], median 2 prior systemic therapies). Only 9.0% of patients responded to last line of therapy prior to study entry. ORR by IRC was 29.2% (95% CI, 22.7-36.5). Investigator-assessed ORR was 26.4% (95% CI, 20.1-33.5). Responses were observed in 14 distinct tumor types, including gliomas, thoracic, gastrointestinal, gynecological, and rare tumors (Table). ORR by investigator assessment in patients with FGFR mutations vs fusions was comparable (26.8% vs 27.0%, respectively). Investigator-assessed median DOR, PFS, and OS were 7.1 months (95% CI, 5.5-9.3), 5.2 months (95% CI, 4.0-5.6), and 10.9 months (95% CI, 7.9-14.3), respectively; DCR was 75.3% and CBR was 48.9%. All patients experienced TEAEs, including 69.1% with grade ≥3. Treatment-related serious TEAEs occurred in 7.3% of patients.
Conclusion:
RAGNAR data show, for the first time, evidence of efficacy for erdafitinib in heavily pretreated patients with a variety of hard to treat advanced FGFR+ malignancies, including glioblastoma, pancreatic, and salivary gland cancers. Safety was consistent with the known erdafitinib safety profile.
© 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology, Inc. Reused with permission. This abstract was accepted and previously presented at the 2022 ASCO Annual Meeting. All rights reserved.
Table
JL1039E Table
To view the table, please click on this link from the e-poster gallery on jadprolive.com

