Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP29: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology III
MP29-09: Aquablation: Multi-Pass Impact
Saturday, May 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 225
Thorsten Bach*, Hamburg, Germany, Steven Kaplan, New York, NY

Steven Abraham Kaplan, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Increasing evidence supports the robotically executed waterjet-based resection of the prostate (Aquablation) as an alternative to other tissue resection-based procedures for men with moderate-to-severe LUTS secondary to BPH. On occasion, surgeons performing Aquablation will do additional passes, i.e., another full resection cycle. The focus of this report is to determine whether existing data supports the use of multiple passes in Aquablation for LUTS due BPH.
Methods: Data for this analysis were combined from two sources. WATER (NCT02505919) is a prospective multicenter single-blind randomized controlled trial of Aquablation vs. TURP for patients with moderate-to-severe BPH and prostate volumes of 30-80ml. WATER II (NCT03123250) is a prospective single-arm multicenter trial of Aquablation in patients with moderate-to-severe BPH and prostate volumes of 80-150ml. Number of passes was determined by procedural data collected and the video recordings of all study cases. Each case was characterized as single pass or more than one pass. Subjects assigned to TURP (WATER only) were included in the analysis as a separate group; for TURP, number of passes is not applicable.
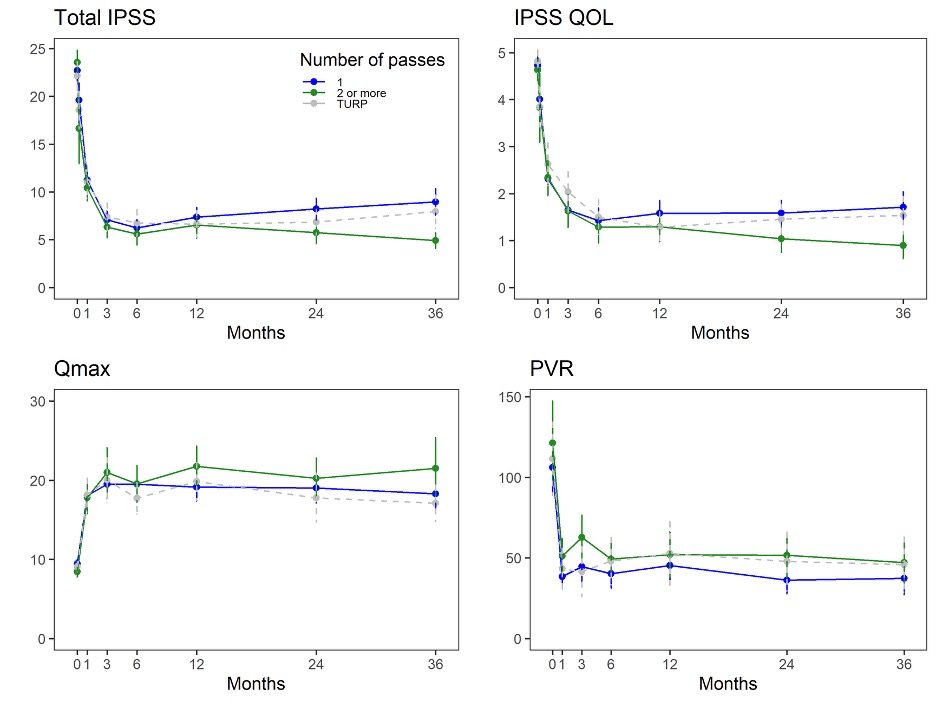
Results: In total, 127 Aquablation subjects underwent a single pass, 90 underwent multiple passes (80 had two passes and 10 underwent 3 passes); 65 subjects underwent TURP (in WATER only). Men undergoing a two or more passes with Aquablation had larger prostates but few differences in other baseline parameters including prostates size range treated. Compared to a single pass, use of two or more passes during Aquablation resulted in lower IPSS scores (by ~4 points, p=.0002) and lower IPSS QOL scores (by ~0.7 points, p=0.0096) at late follow-up (24 and 36 months, Figure 1). Similarly, 36-month Qmax values were higher (by ~5 ml/sec, p=.0220) in those with two or more passes compared to one pass. Post void residual (PVR) was higher at follow-up in those with two or more passes, but baseline PVR was also higher in this group. Changes in scores from baseline showed a similar pattern (Figure) with larger improvements in IPSS, IPSS QOL and Qmax. PVR change scores were similar across groups.
Conclusions: Despite larger prostate volume, multi-pass protocol leads to improved outcome and IPSS improvement. A same contour second pass run-through has emerged as standard scheme in Aquablation, independent of prostate volume.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: Data for this analysis were combined from two sources. WATER (NCT02505919) is a prospective multicenter single-blind randomized controlled trial of Aquablation vs. TURP for patients with moderate-to-severe BPH and prostate volumes of 30-80ml. WATER II (NCT03123250) is a prospective single-arm multicenter trial of Aquablation in patients with moderate-to-severe BPH and prostate volumes of 80-150ml. Number of passes was determined by procedural data collected and the video recordings of all study cases. Each case was characterized as single pass or more than one pass. Subjects assigned to TURP (WATER only) were included in the analysis as a separate group; for TURP, number of passes is not applicable.
Results: In total, 127 Aquablation subjects underwent a single pass, 90 underwent multiple passes (80 had two passes and 10 underwent 3 passes); 65 subjects underwent TURP (in WATER only). Men undergoing a two or more passes with Aquablation had larger prostates but few differences in other baseline parameters including prostates size range treated. Compared to a single pass, use of two or more passes during Aquablation resulted in lower IPSS scores (by ~4 points, p=.0002) and lower IPSS QOL scores (by ~0.7 points, p=0.0096) at late follow-up (24 and 36 months, Figure 1). Similarly, 36-month Qmax values were higher (by ~5 ml/sec, p=.0220) in those with two or more passes compared to one pass. Post void residual (PVR) was higher at follow-up in those with two or more passes, but baseline PVR was also higher in this group. Changes in scores from baseline showed a similar pattern (Figure) with larger improvements in IPSS, IPSS QOL and Qmax. PVR change scores were similar across groups.
Conclusions: Despite larger prostate volume, multi-pass protocol leads to improved outcome and IPSS improvement. A same contour second pass run-through has emerged as standard scheme in Aquablation, independent of prostate volume.
Source of Funding: none


.jpg)
.jpg)