Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP48: Prostate Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) III
MP48-07: The neurotoxicity of androgen deprivation therapy: a pharmacovigilance study
Sunday, May 15, 2022
2:45 PM – 4:00 PM
Location: Room 225
Logan Briggs*, Stephen Reese, Peter Herzog, David-Dan Nguyen, Muhieddine Labban, Khalid Alkhatib, Quoc-Dien Trinh, Alicia K Morgans, Boston, MA
- LB
Logan Briggs, MD (he/him/his)
Urology Resident
Mayo Clinic Arizona
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: There is conflicting evidence regarding whether androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is associated with neurotoxicity. Thus, we aim to characterize the association between different types of ADT and cognitive impairment or dementia in a real-world pharmacovigilance data set.
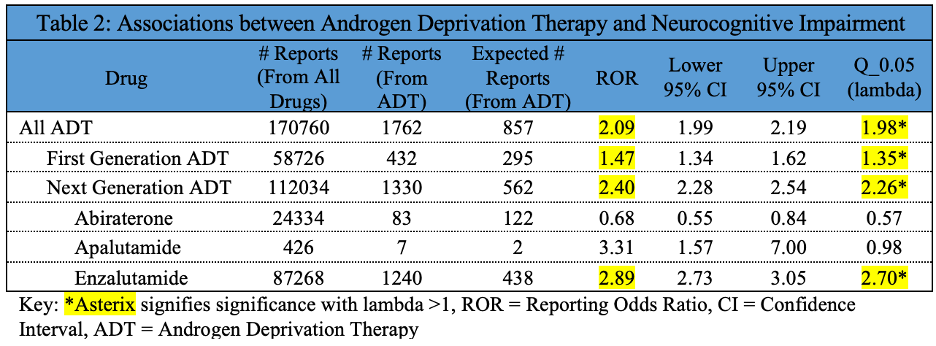
Methods: VigiBase, the World Health Organization’s international pharmacovigilance database, was queried for reports of cognitive impairment or dementia (together termed neurocognitive impairment) among men who took ADT from 1968 to 2021. Disproportionality analysis was performed to compare rates of neurocognitive impairment with different types of ADT versus other Vigibase drugs. Differences were assessed using reporting odds ratio (ROR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and lambda values (Q=1.0 was considered statistically significant).
Results: Odds of neurocognitive impairment were significantly elevated with first-generation (ROR 1.47, 95% CI 1.34-1.62, Q =1.35) and next-generation ADT (ROR 2.40, 95% CI 2.28-2.54, Q =2.26). Odds of neurocognitive impairment were significantly elevated with enzalutamide (ROR 2.89, 95% CI 2.73-3.05, Q =2.70) and numerically increased with apalutamide (ROR 3.31, 95% CI 1.57-7.00, Q =0.98), but were decreased with abiraterone (ROR 0.68, 95% CI 0.55-0.84, Q =0.57).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that ADT has elevated odds of neurocognitive impairment in a real-world data set. Risk of neurotoxicity was higher with next-generation than first-generation ADT, and higher with enzalutamide than abiraterone. Due to limitations inherent to disproportionality analysis (measuring associations, not risk) and incomplete data prohibiting the ability to control for factors such as age or use of secondary drugs, results should be considered exploratory in nature. This data may contribute to clinical decision-making for men with prostate cancer eligible for ADT, especially those with neurologic comorbidities.
Source of Funding: LGB reports research funding from the Office of Scholarly Engagement at Harvard Medical School.
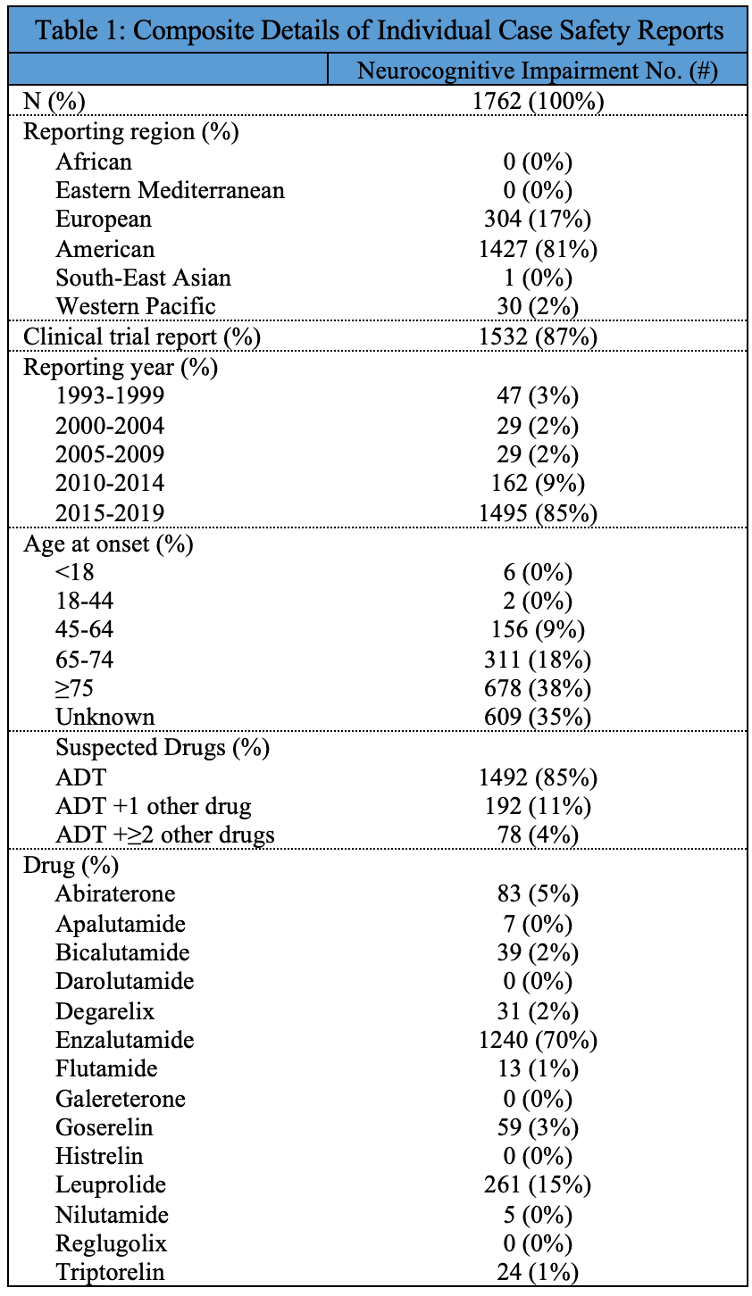
Methods: VigiBase, the World Health Organization’s international pharmacovigilance database, was queried for reports of cognitive impairment or dementia (together termed neurocognitive impairment) among men who took ADT from 1968 to 2021. Disproportionality analysis was performed to compare rates of neurocognitive impairment with different types of ADT versus other Vigibase drugs. Differences were assessed using reporting odds ratio (ROR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and lambda values (Q=1.0 was considered statistically significant).
Results: Odds of neurocognitive impairment were significantly elevated with first-generation (ROR 1.47, 95% CI 1.34-1.62, Q =1.35) and next-generation ADT (ROR 2.40, 95% CI 2.28-2.54, Q =2.26). Odds of neurocognitive impairment were significantly elevated with enzalutamide (ROR 2.89, 95% CI 2.73-3.05, Q =2.70) and numerically increased with apalutamide (ROR 3.31, 95% CI 1.57-7.00, Q =0.98), but were decreased with abiraterone (ROR 0.68, 95% CI 0.55-0.84, Q =0.57).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that ADT has elevated odds of neurocognitive impairment in a real-world data set. Risk of neurotoxicity was higher with next-generation than first-generation ADT, and higher with enzalutamide than abiraterone. Due to limitations inherent to disproportionality analysis (measuring associations, not risk) and incomplete data prohibiting the ability to control for factors such as age or use of secondary drugs, results should be considered exploratory in nature. This data may contribute to clinical decision-making for men with prostate cancer eligible for ADT, especially those with neurologic comorbidities.
Source of Funding: LGB reports research funding from the Office of Scholarly Engagement at Harvard Medical School.



.jpg)
.jpg)