Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP58: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening VII
MP58-19: Comparison of UroNav TRUS and Cognitive Fusion TP Biopsy in Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Monday, May 16, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 228
Amanda Sherman*, Daneil Kuftinec, Burlington, MA, Lori Lyn Price, Boston, MA, Alireza Moinzadeh, William Faust, Burlington, MA

Amanda Sherman, MD
Fellow
Lahey Hospital and Medical Center
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Transperineal (TP) prostate biopsy is a safe and effective technique to sample the prostate gland with less risk of infection and bleeding. Targeting of abnormal lesions on MRI at time of biopsy can be performed with cognitive fusion or software-based platforms. The success of TP MRI-guided biopsy, particularly cognitive fusion, remains unclear. This study compares cancer detection rates between software-based transrectal US (TRUS)/MRI fusion biopsy and cognitive fusion TP prostate biopsy.
Methods: Biopsies (n=495) taken between 2019 and 2021 were performed using either TRUS with UroNav (TRUSUN) guidance, or via TP approach with cognitive fusion (TPCF) to target MRI lesion. Demographic characteristics, PSA, prostate volume, DRE status, highest PIRADS lesion on MRI and final biopsy pathology were collected. Cancer Detection Rate (CDR), clinically significant Cancer Detection Rate (csCDR), and clinically significant cancer detection rate in target only (csCDRt) were compared by technique type. Statistical analysis was performed using Chi-squared, Fisher's exact, and t-tests as appropriate.
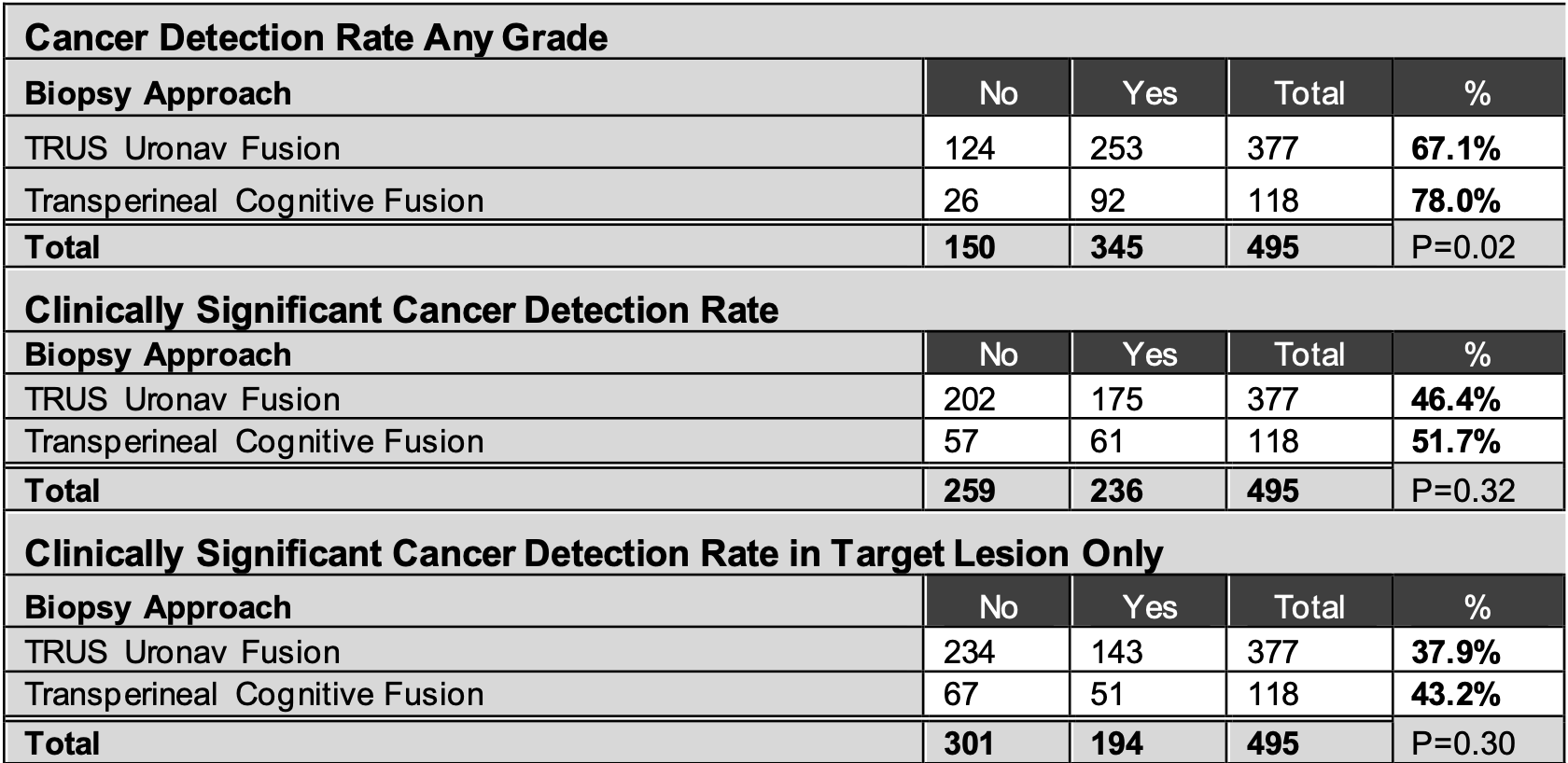
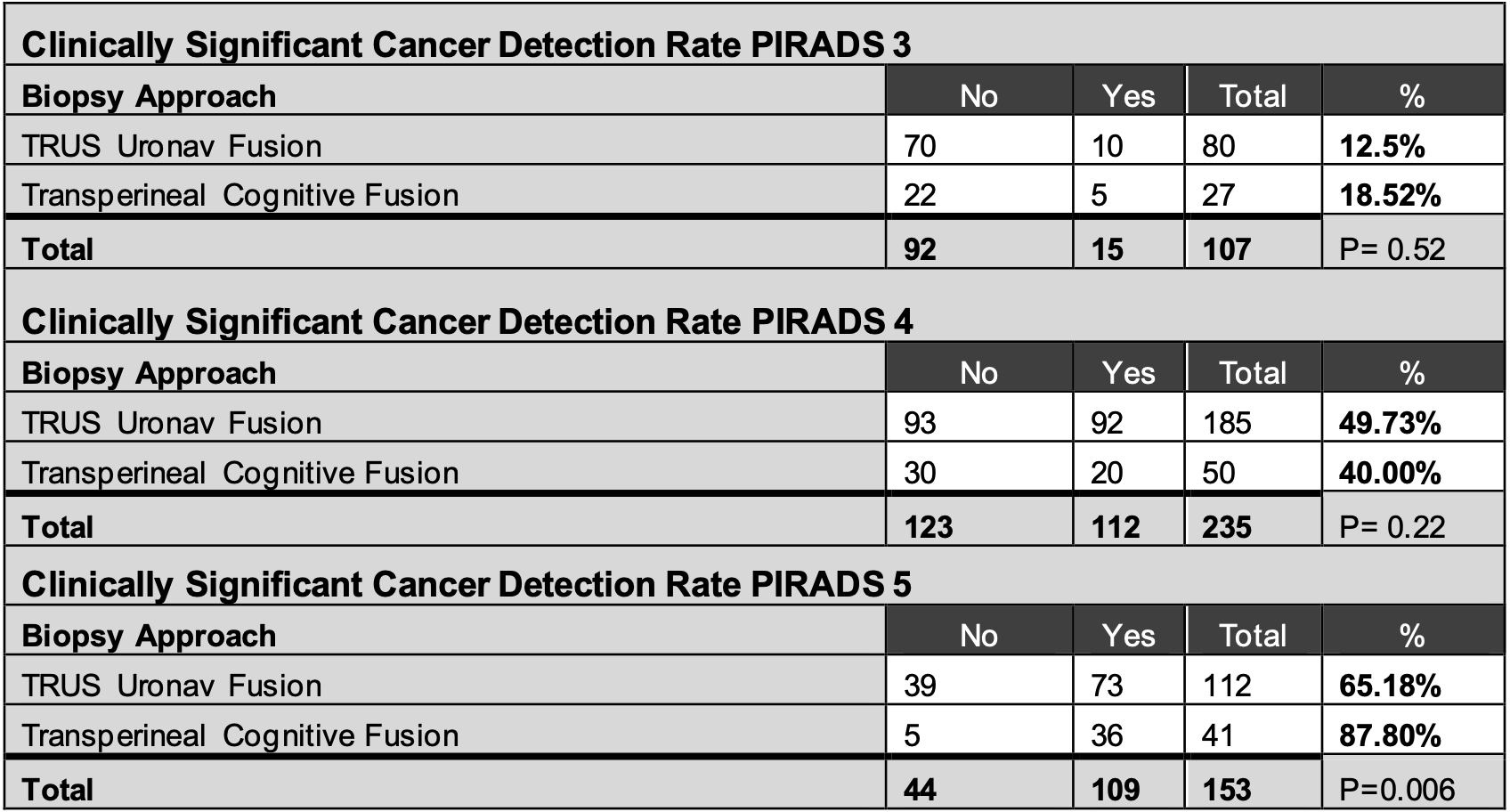
Results: A total of 377 TRUSUN and 118 TPCF prostate biopsies were performed. TPCF detected more cancers of any grade (p=0.02), but there was no difference in csCDR or csCDRt. When stratified by lesion, there was no difference in cancer detection except in the PIRADS 5 group, where TPCF outperformed TRUSUN biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (p=0.006). Further analysis of the PIRADS 5 group found no difference in baseline characteristics except for age (mean age 72.2y in TP group, 68.7y in TRUS p=0.008).
Conclusions: TPCF prostate biopsy showed similar rates of csCDR and csCDRt as TRUSUN prostate biopsy. When analyzed by PI-RADS score, TPCF was found to have similar or, in the case of PI-RADS 5 lesion, superior csCDRt. Subgroup analysis did not find significant group differences, aside from age, to explain this finding. This data suggests that TPCF is as effective at detecting clinically significant prostate cancer as TRUSUN.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Biopsies (n=495) taken between 2019 and 2021 were performed using either TRUS with UroNav (TRUSUN) guidance, or via TP approach with cognitive fusion (TPCF) to target MRI lesion. Demographic characteristics, PSA, prostate volume, DRE status, highest PIRADS lesion on MRI and final biopsy pathology were collected. Cancer Detection Rate (CDR), clinically significant Cancer Detection Rate (csCDR), and clinically significant cancer detection rate in target only (csCDRt) were compared by technique type. Statistical analysis was performed using Chi-squared, Fisher's exact, and t-tests as appropriate.
Results: A total of 377 TRUSUN and 118 TPCF prostate biopsies were performed. TPCF detected more cancers of any grade (p=0.02), but there was no difference in csCDR or csCDRt. When stratified by lesion, there was no difference in cancer detection except in the PIRADS 5 group, where TPCF outperformed TRUSUN biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (p=0.006). Further analysis of the PIRADS 5 group found no difference in baseline characteristics except for age (mean age 72.2y in TP group, 68.7y in TRUS p=0.008).
Conclusions: TPCF prostate biopsy showed similar rates of csCDR and csCDRt as TRUSUN prostate biopsy. When analyzed by PI-RADS score, TPCF was found to have similar or, in the case of PI-RADS 5 lesion, superior csCDRt. Subgroup analysis did not find significant group differences, aside from age, to explain this finding. This data suggests that TPCF is as effective at detecting clinically significant prostate cancer as TRUSUN.
Source of Funding: None



.jpg)
.jpg)