Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD02: Pediatric Urology: Neurogenic Bladder, Reconstruction & DSD
PD02-02: Characterizing clinical heterogeneity in hostile bladder criteria among neurogenic bladder children
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:10 AM – 7:20 AM
Location: Room 255
Ranveer Vasdev*, Minneapolis, MN, Kenneth Softness, Rachel Saunders, Carlos Estrada, Jr., Scott Wang, Boston, MA
- RV
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Neurogenic bladder (NGB) and management play significant roles in the patient outcomes. The CDC/National Spina Bifida Registry has set up hostile bladder (HB) criteria to help clinicians research and monitor at-risk individuals. However, little is known regarding the clinical characteristics associated with HB criteria in Urodynamic Studies (UDS). Our objective was to investigate factors associated with HB UDS findings in NGB children.
Methods: We reviewed the institutional records of NGB between 2013-2019. Patients younger than 1 year old, studies with calibration issues, and bladder augmentation patients were excluded. The following factors were evaluated: age, sex, febrile UTI, UDS parameters (detrusor leak point pressure (DLPP), maximal detrusor filling pressure (PdetMax), overactive contractions (OAC), detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD), post void residuals (PVR)), medications, catheterization, incontinence, and vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
HB was defined as having DLPP/PdetMax > 40 cmH2O with DSD (criteria 1) or OAC with DSD (criteria 2). Univariate and Multivariate analyses were performed determine association between covariates and HB criteria with generalized estimating equations to adjust for repeat measurements.
Results: We identified 581 NGB studies. The mean age at UDS was 10.9 years and 42.9% of patients were male. 39.6% of UDS recordings had HB. Criteria 1 HB, compared to no HB, was significantly associated with older age, anticholinergic use, CIC, febrile UTI, high-grade hydronephrosis and high PVR. Compared to those without HB, Criteria 2 HB was significantly associated with only CIC.
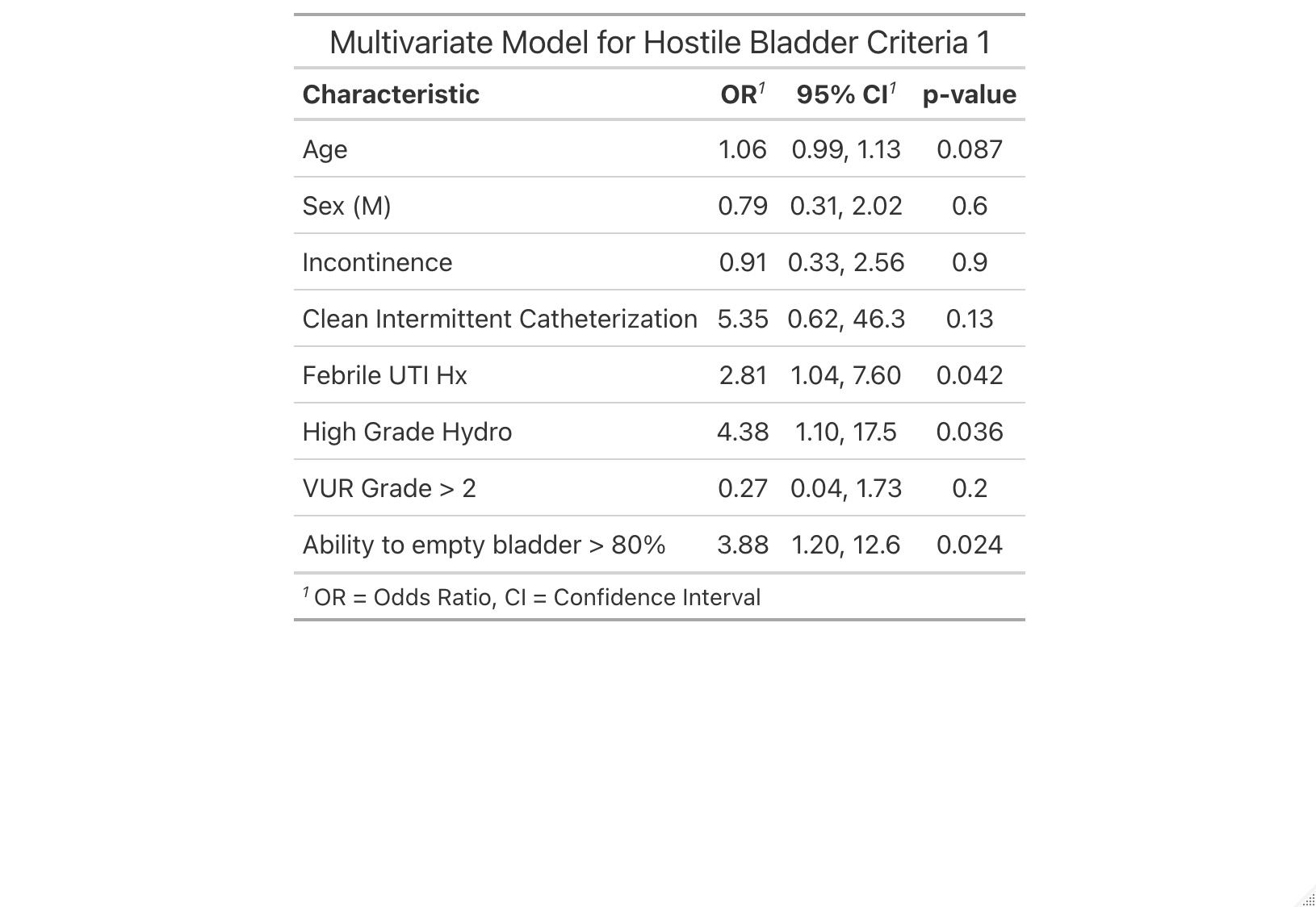
After adjusting for age, sex, incontinence, CIC, high-grade VUR (>=grade 3), and repeated measurements (Table 1), HB by criteria 1 remained significantly associated with recent febrile UTI (OR=2.8(1.04-7.60), p=0.04), high-grade hydronephrosis (OR=4.4(1.10- 17.50), p=0.04) and high grade PVR (>20% capacity, OR=3.88(1.20-12.6), p=0.02). After adjusting for the same set of covariates, only CIC remained significantly associated with HB with criteria 2.
Conclusions: Unlike the HB criteria 2 (OAB/DSD), HB criteria 1(high DLPP/PdetMax) was associated with febrile UTI, high grade hydronephrosis, and high grade PVR. This suggests significant heterogeneity exists among hostile neurogenic bladder patients with distinct subsets by their HB criteria.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: We reviewed the institutional records of NGB between 2013-2019. Patients younger than 1 year old, studies with calibration issues, and bladder augmentation patients were excluded. The following factors were evaluated: age, sex, febrile UTI, UDS parameters (detrusor leak point pressure (DLPP), maximal detrusor filling pressure (PdetMax), overactive contractions (OAC), detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD), post void residuals (PVR)), medications, catheterization, incontinence, and vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
HB was defined as having DLPP/PdetMax > 40 cmH2O with DSD (criteria 1) or OAC with DSD (criteria 2). Univariate and Multivariate analyses were performed determine association between covariates and HB criteria with generalized estimating equations to adjust for repeat measurements.
Results: We identified 581 NGB studies. The mean age at UDS was 10.9 years and 42.9% of patients were male. 39.6% of UDS recordings had HB. Criteria 1 HB, compared to no HB, was significantly associated with older age, anticholinergic use, CIC, febrile UTI, high-grade hydronephrosis and high PVR. Compared to those without HB, Criteria 2 HB was significantly associated with only CIC.
After adjusting for age, sex, incontinence, CIC, high-grade VUR (>=grade 3), and repeated measurements (Table 1), HB by criteria 1 remained significantly associated with recent febrile UTI (OR=2.8(1.04-7.60), p=0.04), high-grade hydronephrosis (OR=4.4(1.10- 17.50), p=0.04) and high grade PVR (>20% capacity, OR=3.88(1.20-12.6), p=0.02). After adjusting for the same set of covariates, only CIC remained significantly associated with HB with criteria 2.
Conclusions: Unlike the HB criteria 2 (OAB/DSD), HB criteria 1(high DLPP/PdetMax) was associated with febrile UTI, high grade hydronephrosis, and high grade PVR. This suggests significant heterogeneity exists among hostile neurogenic bladder patients with distinct subsets by their HB criteria.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)