Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD22: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Radiation Therapy
PD22-04: Immediate Radiotherapy versus Observation in Patients with Node-Positive Prostate Cancer after Radical Prostatectomy
Saturday, May 14, 2022
10:00 AM – 10:10 AM
Location: Room 252
Christian Schaufler, Sumedh Kaul, Aaron Fleishman, Ruslan Korets, Peter Chang, Andrew Wagner, Boston, MA, Simon Kim, Aurora, CO, Joaquim Bellmunt, Irving Kaplan, Aria F. Olumi, Boris Gershman*, Boston, MA
- BG
Boris Gershman, MD
Rhode Island Hospital and The Miriam Hospital
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: The optimal management of node-positive (pN1) prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy (RP) remains uncertain. Despite randomized evidence, use of immediate, life-long androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) remains poor, and recent trials of early salvage radiotherapy included only a minority of pN1 patients. We therefore emulated a hypothetical pragmatic trial of immediate (adjuvant) radiotherapy versus observation in men with pN1 prostate cancer.
Methods: Using RADICALS-RT to inform the design of a hypothetical target trial, we identified men aged 50-69 years with pT2-3 Rany pN1 M0, pre-treatment PSA <50 ng/mL prostate cancer in the NCDB from 2006-2015 treated with 60-72 Gy of adjuvant RT (aRT) ± ADT within 26 weeks of RP or observation. After estimating a propensity score for receipt of aRT, we estimated absolute and relative treatment effects using stabilized inverse probability of treatment (sIPW) re-weighting.
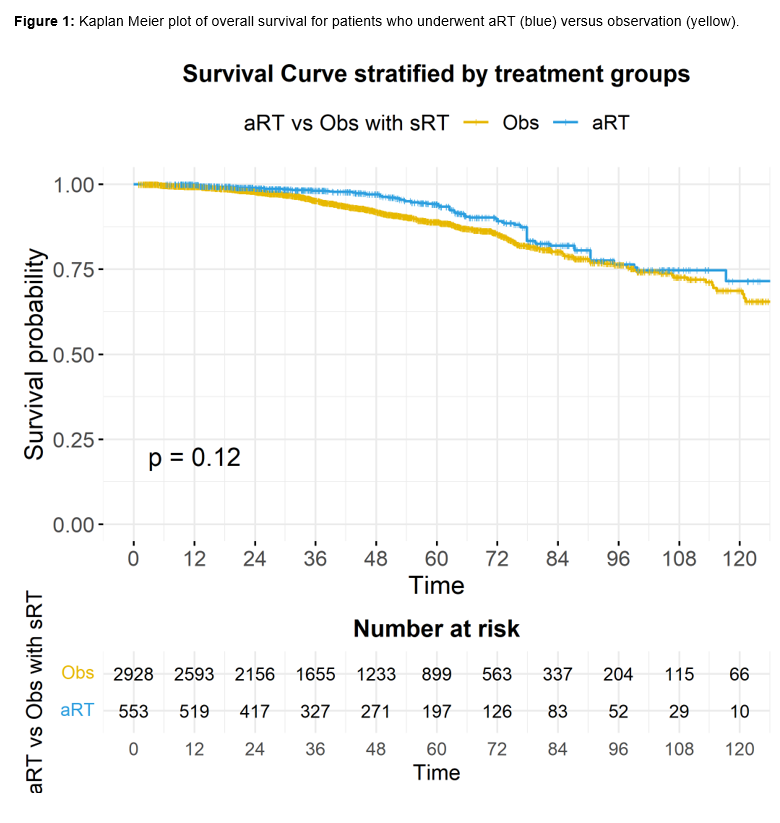
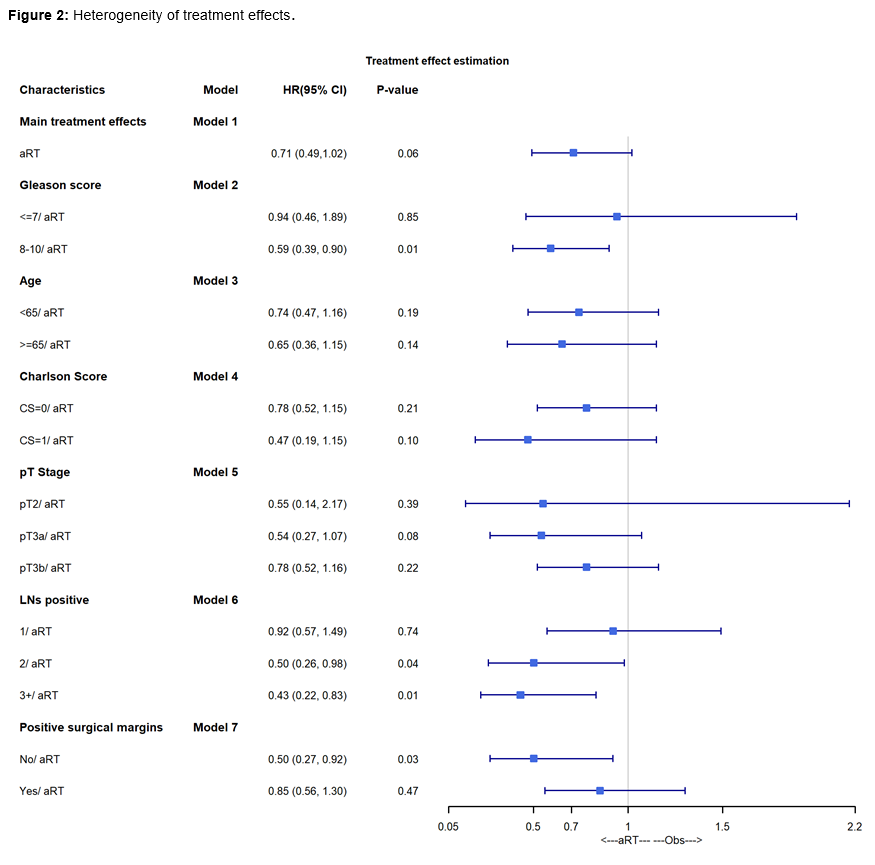
Results: A total of 3,510 patients were included in the study, of whom 587 (17%) received aRT (73% with concurrent ADT). Median follow-up was 42.3 months, during which time 333 deaths occurred. After sIPW re-weighting, baseline characteristics were well-balanced. Adjusted OS was 94% versus 89% at 5-years and 82% versus 80% at 8-years for aRT versus observation (Figure 1; p=0.12). In IPW-reweighted Cox regression modelling, aRT was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality than observation, but this did not reach statistical significance (HR 0.71, p=0.06). In analyses examining heterogeneity of treatment effects, aRT was associated with improved OS only for men with Gleason 8-10 disease (HR 0.59, p=0.01), ³2 positive LNs (HR 0.50, p=0.04 for 2 positive LNs; HR 0.43, p=0.01 for ³3 positive LNs), or negative surgical margins (HR 0.50, p=0.03).
Conclusions: In observational analyses designed to emulate a hypothetical target trial of aRT versus observation in pN1 prostate cancer, aRT was associated with improved OS only for men with Gleason 8-10 disease, ³ 2 positive LNs, or negative surgical margins.
Source of Funding: The authors have no funding disclosures.
Methods: Using RADICALS-RT to inform the design of a hypothetical target trial, we identified men aged 50-69 years with pT2-3 Rany pN1 M0, pre-treatment PSA <50 ng/mL prostate cancer in the NCDB from 2006-2015 treated with 60-72 Gy of adjuvant RT (aRT) ± ADT within 26 weeks of RP or observation. After estimating a propensity score for receipt of aRT, we estimated absolute and relative treatment effects using stabilized inverse probability of treatment (sIPW) re-weighting.
Results: A total of 3,510 patients were included in the study, of whom 587 (17%) received aRT (73% with concurrent ADT). Median follow-up was 42.3 months, during which time 333 deaths occurred. After sIPW re-weighting, baseline characteristics were well-balanced. Adjusted OS was 94% versus 89% at 5-years and 82% versus 80% at 8-years for aRT versus observation (Figure 1; p=0.12). In IPW-reweighted Cox regression modelling, aRT was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality than observation, but this did not reach statistical significance (HR 0.71, p=0.06). In analyses examining heterogeneity of treatment effects, aRT was associated with improved OS only for men with Gleason 8-10 disease (HR 0.59, p=0.01), ³2 positive LNs (HR 0.50, p=0.04 for 2 positive LNs; HR 0.43, p=0.01 for ³3 positive LNs), or negative surgical margins (HR 0.50, p=0.03).
Conclusions: In observational analyses designed to emulate a hypothetical target trial of aRT versus observation in pN1 prostate cancer, aRT was associated with improved OS only for men with Gleason 8-10 disease, ³ 2 positive LNs, or negative surgical margins.
Source of Funding: The authors have no funding disclosures.

.jpg)
.jpg)