Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP01: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology I
MP01-13: Comparison of Traditional Outcome Measures and Self-Assessed Goal Achievement in Patients Treated Surgically for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 228
Manolis Pratsinis*, Gautier Müllhaupt, Sabine Güsewell, Patrick Betschart, Valentin Zumstein, Daniel Engeler, Hans-Peter Schmid, St. Gallen, Switzerland, Dominik Abt, Biel, Switzerland
- MP
Manolis A. Pratsinis, MD, MSC
Cantonal Hospital St. Gallen
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Recently, a multitude of novel treatment options for men suffering from lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) due to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) have been introduced. Current research often compares treatments using peak urinary flow rate (Qmax), post-void residual urine (PVR) and the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). This study compares these outcomes with self-assessed goal achievement (SAGA) and satisfaction with the procedure in patients treated with different modalities for LUTS/BPH.
Methods: Patients requiring surgical/interventional treatment for LUTS were enrolled in a prospective cohort, with assessment of individual goals at baseline. Follow-up was performed six to twelve weeks after treatment and included SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure as well as Qmax, PVR and IPSS. Statistical analysis was performed to assess the correlation between the different outcomes.
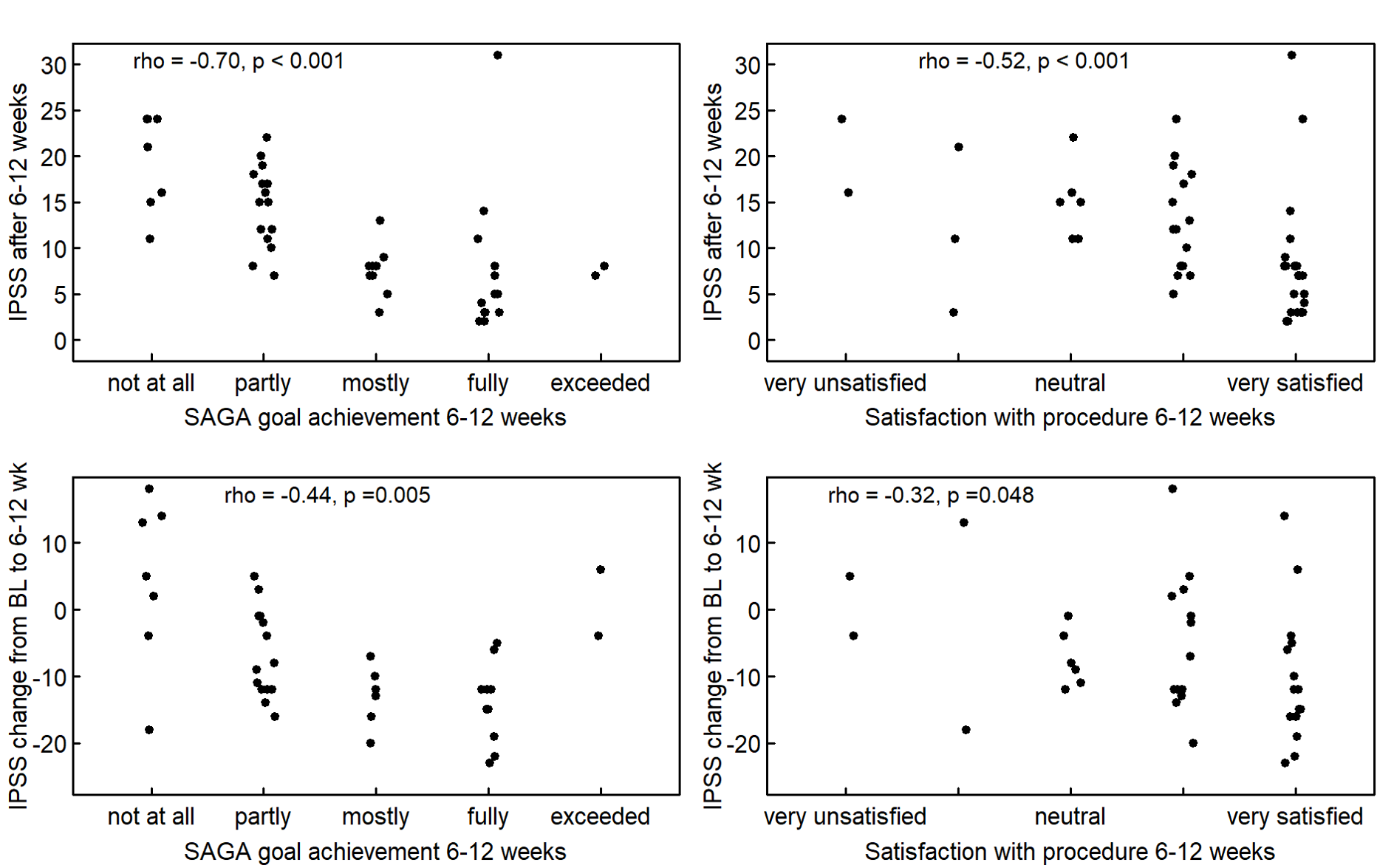
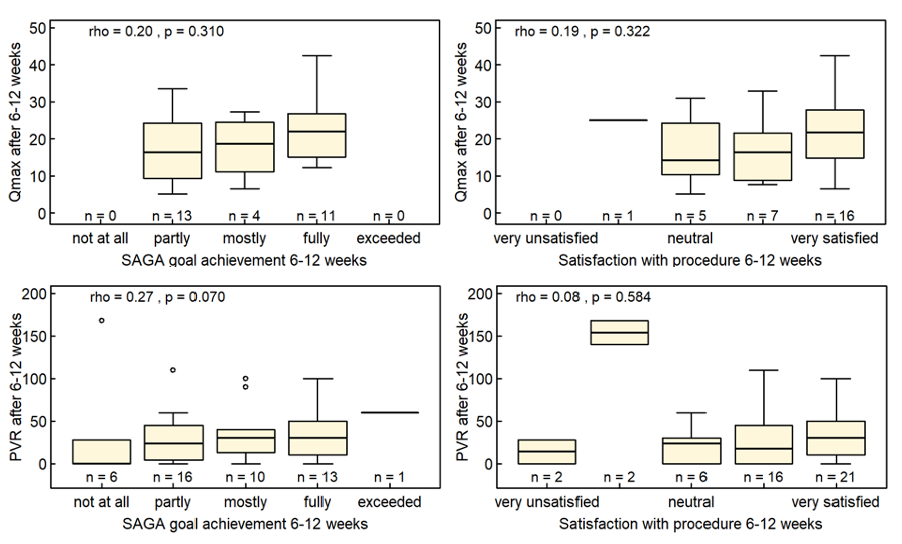
Results: Sixty-eight patients completed the goal formulation at baseline. At follow-up SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure were significantly correlated (Spearman rank correlation rho = 0.78, p < 0.001). There was a statistically significant correlation between IPSS and SAGA (rho = -0.70, p < 0.001) as well as IPSS and satisfaction with the procedure (rho = -0.52, p < 0.001) (Figure 1). There was no statistically significant correlation between SAGA and Qmax (rho = 0.20, p = 0.310) or PVR (rho = 0.27, p = 0.07) nor between satisfaction with the procedure and Qmax (rho = 0.19, p = 0.322) or PVR (rho = 0.08, p = 0.584) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates a significant correlation of SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure and IPSS, while failing to demonstrate a correlation of SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure and Qmax or PVR. These findings highlight the value of patient-reported outcome measures and further support the inclusion of self-assessed goal achievement in clinical practice and comparative LUTS/BPH research.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: Patients requiring surgical/interventional treatment for LUTS were enrolled in a prospective cohort, with assessment of individual goals at baseline. Follow-up was performed six to twelve weeks after treatment and included SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure as well as Qmax, PVR and IPSS. Statistical analysis was performed to assess the correlation between the different outcomes.
Results: Sixty-eight patients completed the goal formulation at baseline. At follow-up SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure were significantly correlated (Spearman rank correlation rho = 0.78, p < 0.001). There was a statistically significant correlation between IPSS and SAGA (rho = -0.70, p < 0.001) as well as IPSS and satisfaction with the procedure (rho = -0.52, p < 0.001) (Figure 1). There was no statistically significant correlation between SAGA and Qmax (rho = 0.20, p = 0.310) or PVR (rho = 0.27, p = 0.07) nor between satisfaction with the procedure and Qmax (rho = 0.19, p = 0.322) or PVR (rho = 0.08, p = 0.584) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates a significant correlation of SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure and IPSS, while failing to demonstrate a correlation of SAGA and satisfaction with the procedure and Qmax or PVR. These findings highlight the value of patient-reported outcome measures and further support the inclusion of self-assessed goal achievement in clinical practice and comparative LUTS/BPH research.
Source of Funding: None.



.jpg)
.jpg)