Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP03: Bladder Cancer: Invasive I
MP03-04: Analysis of Complications after Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy between 2005-2020: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 222
Holly Houenstein, Umar Iqbal, Zhe Jing, Ahmed S. Elsayed, Yousuf Ramahi*, Buffalo, NY, Michael Stöckle, Homburg, Germany, Carl Wijburg, Arnhem, Netherlands, Abolfazl Hosseini, Peter Wiklund, Solna, Sweden, Eric Kim, St. Louis, MO, Jihad Kaouk, Cleveland, OH, Prokar Dasgupta, Mohammed S. Khan, London, United Kingdom, Andrew A. Wagner, Boston, MA, Johar R. Syed, James O. Peabody, Detroit, MI, Ketan K. Badani, Lee Richstone, New York, NY, Alexandre Mottrie, Aalst, Belgium, Thomas J. Maatman, Wyoming, MI, Derya Balbay, Istanbul, Turkey, Juan P. Redorta, Barcelona, Spain, Koon Ho Rha, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, Franco Gaboardi, Milan, Italy, Morgan Roupret, Paris, France, Ahmed Aboumohamed, Bronx, NY, Ahmed A. Hussein, Khurshid A. Guru, Buffalo, NY

Yousuf Omar Ramahi, BS
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: To identify trends in complications following robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) using a multi-institutional database, the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium (IRCC).
Methods: A retrospective review of the IRCC database was performed (2976 patients, 26 institutions from 14 countries). Postoperative complications were categorized as overall or high grade (= Clavien Dindo III) and were further categorized based on type/organ site. Descriptive statistics was used to summarize the data. Multivariate analysis (MVA) was used to identify variables associated with overall and high-grade complications. Cochran-Armitage trend test was used to describe the trend of complications over time.
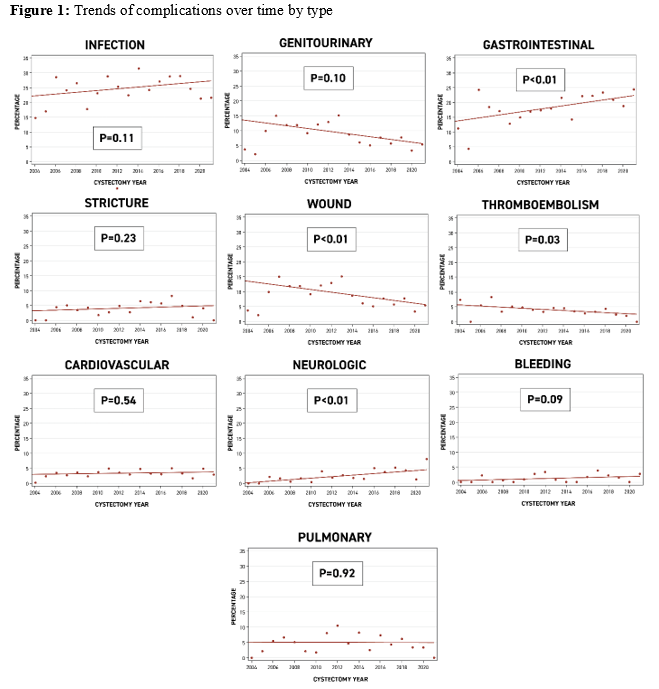
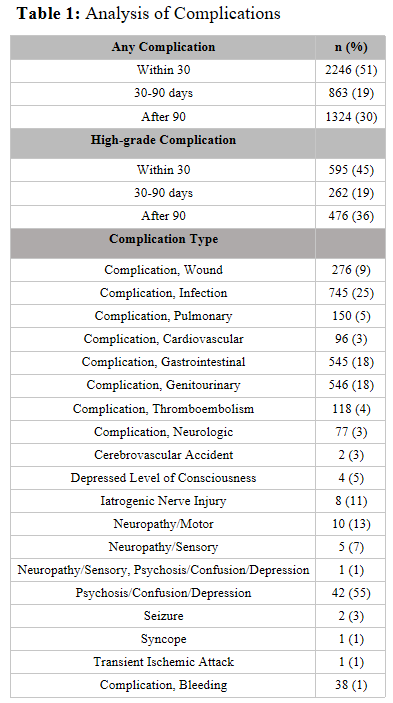
Results: 1777 (60%) patients developed postoperative complications following RARC, 51% of complications occurred within 30 days of RARC, 19% between 30-90 days, and 30% after 90 days. A total of 835 patients (28%) experienced high-grade complications (Table 1). The incidence of complications was stable between 2005-2020 (p>0.05). Infection (25%) was the highest reported complication, while bleeding (1%) was the lowest. Gastrointestinal and neurologic postoperative complications increased significantly (p < 0.01, for both) between 2005 and 2020 while thromboembolic (p=0.03) and wound complications (p < 0.01) decreased (Figure 1). On MVA, BMI (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.05, p<0.01), prior abdominal surgery (OR 1.26, 95%CI 1.03-1.56, p=0.03), receipt of neobladder (OR 1.52, 95%CI 1.17-1.99, p<0.01), lymph node yield (LNY) (OR 1.33, 1.05-1.70, p=0.02), length of inpatient stay (OR 1.04, 1.02-1.04, p<0.01) and ICU admission (OR 1.67, 95%CI 1.36-2.06, p<0.01) were associated with high-grade complications.
Conclusions: Overall and high-grade complications after RARC remained stable between 2005-2020. GI and neurologic complications increased, while thromboembolic and wound complications decreased.
Source of Funding: Roswell Park Alliance Foundation and Vattikuti Foundation
Methods: A retrospective review of the IRCC database was performed (2976 patients, 26 institutions from 14 countries). Postoperative complications were categorized as overall or high grade (= Clavien Dindo III) and were further categorized based on type/organ site. Descriptive statistics was used to summarize the data. Multivariate analysis (MVA) was used to identify variables associated with overall and high-grade complications. Cochran-Armitage trend test was used to describe the trend of complications over time.
Results: 1777 (60%) patients developed postoperative complications following RARC, 51% of complications occurred within 30 days of RARC, 19% between 30-90 days, and 30% after 90 days. A total of 835 patients (28%) experienced high-grade complications (Table 1). The incidence of complications was stable between 2005-2020 (p>0.05). Infection (25%) was the highest reported complication, while bleeding (1%) was the lowest. Gastrointestinal and neurologic postoperative complications increased significantly (p < 0.01, for both) between 2005 and 2020 while thromboembolic (p=0.03) and wound complications (p < 0.01) decreased (Figure 1). On MVA, BMI (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.05, p<0.01), prior abdominal surgery (OR 1.26, 95%CI 1.03-1.56, p=0.03), receipt of neobladder (OR 1.52, 95%CI 1.17-1.99, p<0.01), lymph node yield (LNY) (OR 1.33, 1.05-1.70, p=0.02), length of inpatient stay (OR 1.04, 1.02-1.04, p<0.01) and ICU admission (OR 1.67, 95%CI 1.36-2.06, p<0.01) were associated with high-grade complications.
Conclusions: Overall and high-grade complications after RARC remained stable between 2005-2020. GI and neurologic complications increased, while thromboembolic and wound complications decreased.
Source of Funding: Roswell Park Alliance Foundation and Vattikuti Foundation



.jpg)
.jpg)