Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP06: Bladder Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology I
MP06-19: Anti-tumor effect in bladder cancer model of tumor vasculature-targeted 10B delivery mediated boron neutron capture therapy.
Friday, May 13, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 222
Tohru Yoneyama*, Shingo Hatakeyama, Mihoko Sutoh Yoneyama, Hirosaki, Japan, Taku Yoshiya, Tsuyoshi Uemura, Takehiro Ishizu, Minoru Suzuki, Osaka, Japan, Shingo Hachinohe, Kamikita-gun, Japan, Shintaro Ishiyama, Hirosaki, Japan, Motohiro Nonaka, Kyoto, Japan, Michiko N. Fukuda, La jolla, Japan, Chikara Ohyama, Hirosaki, Japan

Tohru Yoneyama, PhD
Hirosaki University Graduate school of medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
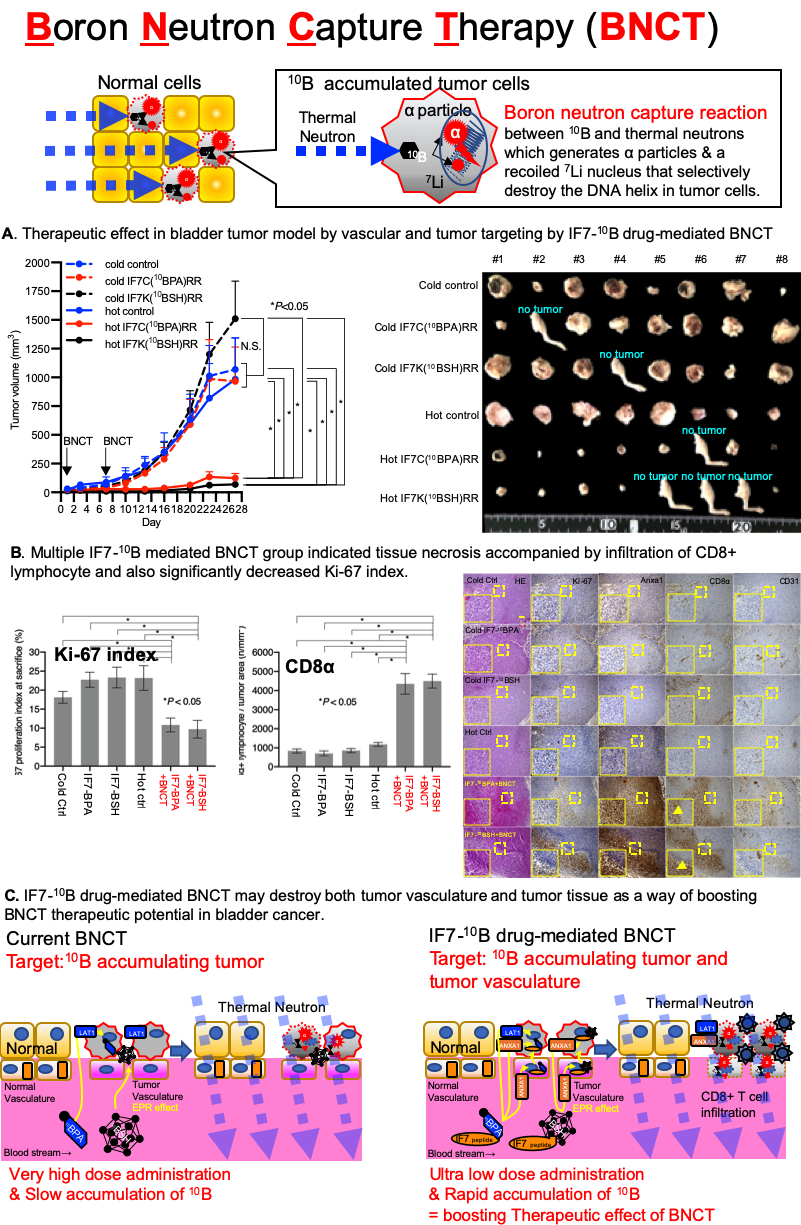
Introduction: p-Boronophenylalanine (10BPA) is a powerful 10B drug used in current clinical trials of BNCT. For BNCT to be successful, a high (500 mg/kg) dose of 10BPA must be administered over a few hours. Here, we report BNCT efficacy after rapid, ultralow-dose administration of either tumor vasculature-specific annexin A1-targeting IFLLWQR (IF7)-conjugated 10BPA or borocaptate sodium (10BSH).
Methods: IF7 conjugates of either 10B drugs intravenously injected into MBT2 bladder tumor-bearing mice and biodistribution of 10B in tumors and normal organs analyzed by prompt gamma-ray analysis. Therapeutic effect of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT was assessed by either MBT2 bladder tumor bearing C3H/He mice and YTS-1 tumor bearing nude mice.
Results: Intravenous injection of IF7C conjugates of either 10B drugs into MBT2 bladder tumor-bearing mice promoted rapid 10B accumulation in tumor tissues and suppressed tumor growth. Moreover, multiple treatments at ultralow (10–20 mg/kg) doses of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT significantly suppressed tumor growth in a mouse model of human YTS-1 bladder cancer, with increased Anxa1 expression in tumors and infiltration by CD8-positive lymphocytes. Our findings suggest BNCT treatment induces an immune response by the host against tumor cells, triggering a strong cytotoxic reaction and also inflammatory and immune responses that increase after BNCT upregulate Anxa1 expression in tumor tissues. Moreover, we hypothesize that if the first BNCT treatment upregulates Anxa1 in tumor tissues due to an inflammatory response or induced immunogenicity, more effective 10B accumulation in tumor tissues might occur following the second injection of IF7-10B drugs. Thus, multiple ultralow doses of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT likely boost BNCT therapeutic potential.
Conclusions: We conclude that IF7 serves as an efficient 10B delivery vehicle by targeting bladder tumor tissues via the tumor vasculature and could serve as a relevant vehicle for BNCT drugs.
Source of Funding: This study was supported by a Center of Innovation program grant for the young scientist collaborative research fund project (no. R02W16) from the Japan Science and Technology Agency and supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (grants nos. 17K11119, 20K09517, and 19H05556). The study was also supported by the Kobayashi Foundation for Cancer Research and by the Aomori Prefecture Quantum Science Center.
Methods: IF7 conjugates of either 10B drugs intravenously injected into MBT2 bladder tumor-bearing mice and biodistribution of 10B in tumors and normal organs analyzed by prompt gamma-ray analysis. Therapeutic effect of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT was assessed by either MBT2 bladder tumor bearing C3H/He mice and YTS-1 tumor bearing nude mice.
Results: Intravenous injection of IF7C conjugates of either 10B drugs into MBT2 bladder tumor-bearing mice promoted rapid 10B accumulation in tumor tissues and suppressed tumor growth. Moreover, multiple treatments at ultralow (10–20 mg/kg) doses of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT significantly suppressed tumor growth in a mouse model of human YTS-1 bladder cancer, with increased Anxa1 expression in tumors and infiltration by CD8-positive lymphocytes. Our findings suggest BNCT treatment induces an immune response by the host against tumor cells, triggering a strong cytotoxic reaction and also inflammatory and immune responses that increase after BNCT upregulate Anxa1 expression in tumor tissues. Moreover, we hypothesize that if the first BNCT treatment upregulates Anxa1 in tumor tissues due to an inflammatory response or induced immunogenicity, more effective 10B accumulation in tumor tissues might occur following the second injection of IF7-10B drugs. Thus, multiple ultralow doses of IF7-10B drug-mediated BNCT likely boost BNCT therapeutic potential.
Conclusions: We conclude that IF7 serves as an efficient 10B delivery vehicle by targeting bladder tumor tissues via the tumor vasculature and could serve as a relevant vehicle for BNCT drugs.
Source of Funding: This study was supported by a Center of Innovation program grant for the young scientist collaborative research fund project (no. R02W16) from the Japan Science and Technology Agency and supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (grants nos. 17K11119, 20K09517, and 19H05556). The study was also supported by the Kobayashi Foundation for Cancer Research and by the Aomori Prefecture Quantum Science Center.


.jpg)
.jpg)