Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP12: Kidney Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) I
MP12-17: Immunotherapy-based Combinations in the First-line Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with Sarcomatoid Features: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Friday, May 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 222
Fahad Quhal*, Keiichiro Mori, Ekaterina Laukhtina, Benjamin Pradere, Hadi Mostafaei, Pawel Rajwa, Shahrokh F. Shariat, Manuela Schmidinger, Vienna, Austria

Fahad Quhal, MD
Medical University of Vienna
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with sarcomatoid features (sRCC) is an aggressive tumor and commonly presents at an advanced or metastatic stage. Despite therapeutic improvements in metastatic RCC, the management of sRCC is still an unmet need. Randomized trials on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) -based combinations have shown promising results in the subset of sRCC patients. Comparisons of their efficacy are needed to guide the decision-making regarding first-line therapy in metastatic sRCC
Methods: We searched multiple databases and abstracts of major scientific meetings up to August 2021 to identify phase III randomized controlled trials of patients receiving first-line ICI-based combinations for sRCC. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were the primary endpoints. The secondary endpoints were objective response rates (ORR) and complete response rates (CRR).
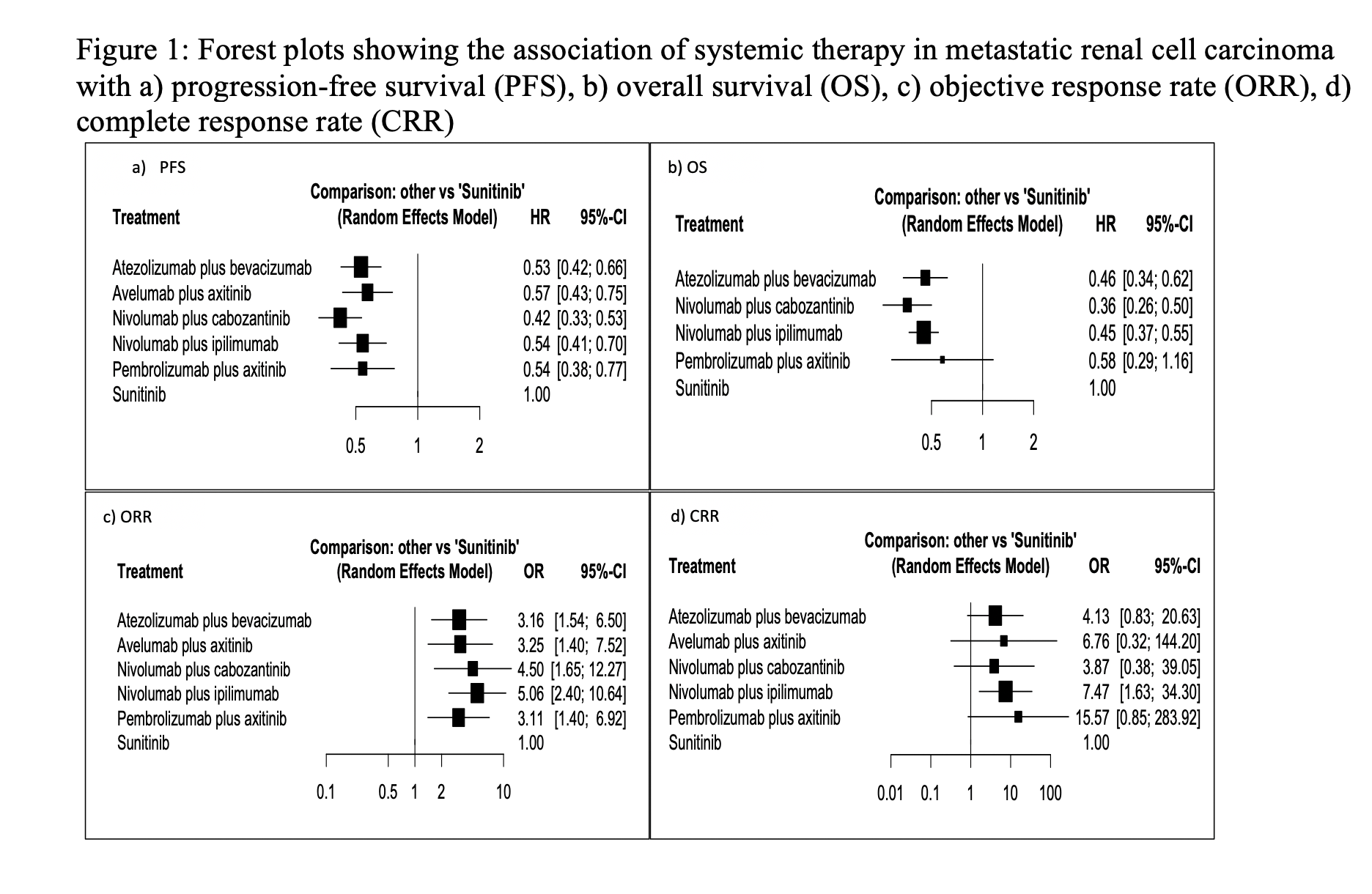
Results: For the analysis of PFS, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, nivolumab plus ipilimumab, pembrolizumab plus axitinib and avelumab plus axitinib resulted in significantly improved PFS (Fig.1a). Nivolumab plus cabozantinib had the highest likelihood of improving PFS (P score: 0.9311) based on treatment ranking analysis.
For the analysis of OS, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, nivolumab plus ipilimumab and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab resulted in significantly improved OS (Fig.1b). Based on analysis of the treatment ranking, nivolumab plus cabozantinibhad the highest likelihood of providing the maximal OS (P score: 0.9050).
For the analysis of ORR, nivolumab plus ipilimumab, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, avelumab plus axitinib, atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, and pembrolizumab plus axitinib, resulted in significantly higher ORR. While only nivolumab plus ipilimumab resulted in significantly higher CRR (Fig.1c, 1d).
Conclusions: Our network meta-analysis demonstrates that sRCC are responsive to ICI-based combinations. The dual ICI with nivolumab plus ipilimumab improved all efficacy outcomes and achieved the highest CRR. Although the association of nivolumab plus cabozantinib with CRR was not statistically significant, this combination demonstrated the highest likelihood of PFS and OS improvements.
Source of Funding: no
Methods: We searched multiple databases and abstracts of major scientific meetings up to August 2021 to identify phase III randomized controlled trials of patients receiving first-line ICI-based combinations for sRCC. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were the primary endpoints. The secondary endpoints were objective response rates (ORR) and complete response rates (CRR).
Results: For the analysis of PFS, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, nivolumab plus ipilimumab, pembrolizumab plus axitinib and avelumab plus axitinib resulted in significantly improved PFS (Fig.1a). Nivolumab plus cabozantinib had the highest likelihood of improving PFS (P score: 0.9311) based on treatment ranking analysis.
For the analysis of OS, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, nivolumab plus ipilimumab and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab resulted in significantly improved OS (Fig.1b). Based on analysis of the treatment ranking, nivolumab plus cabozantinibhad the highest likelihood of providing the maximal OS (P score: 0.9050).
For the analysis of ORR, nivolumab plus ipilimumab, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, avelumab plus axitinib, atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, and pembrolizumab plus axitinib, resulted in significantly higher ORR. While only nivolumab plus ipilimumab resulted in significantly higher CRR (Fig.1c, 1d).
Conclusions: Our network meta-analysis demonstrates that sRCC are responsive to ICI-based combinations. The dual ICI with nivolumab plus ipilimumab improved all efficacy outcomes and achieved the highest CRR. Although the association of nivolumab plus cabozantinib with CRR was not statistically significant, this combination demonstrated the highest likelihood of PFS and OS improvements.
Source of Funding: no


.jpg)
.jpg)