Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP17: Pediatric Urology: Upper & Lower Urinary Tract
MP17-07: Impact of delay in surgical intervention on functional outcome in children with unilateral uretero-pelvic junction obstruction.
Friday, May 13, 2022
4:30 PM – 5:45 PM
Location: Room 225
Mohamed Soltan*, Ahmed Abdelhalim, Ahmed Elkashef, Mohamed Edwan, Ahmed Atwa, Mohamed Abou-El_Ghar, Tamer Helmy, Ashraf Tarek, Mohamed Dawaba, Ahmed Shokier, Mansoura, Egypt
- MS
Mohamed Ahmed Soltan, MD
Fellow of pediatric urology
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Uretero-pelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) is the commonest cause of obstructive uropathy in children. Timing of surgical intervention is debatable, meanwhile the effect of delay surgical intervention is not well understood.
The objective of the study is to identify surgery delay effect on renal function in cases of UPJO and factors affecting it.
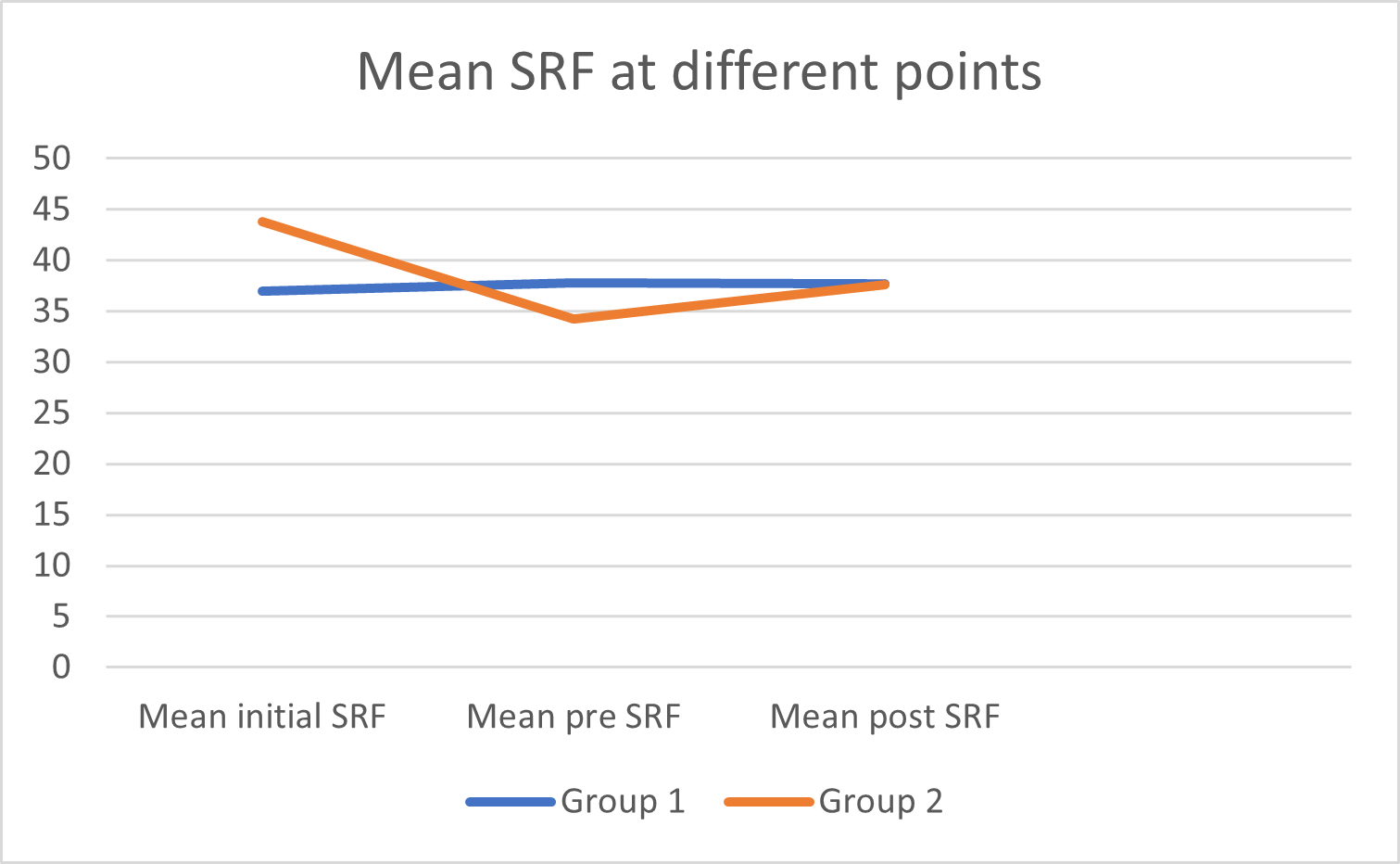
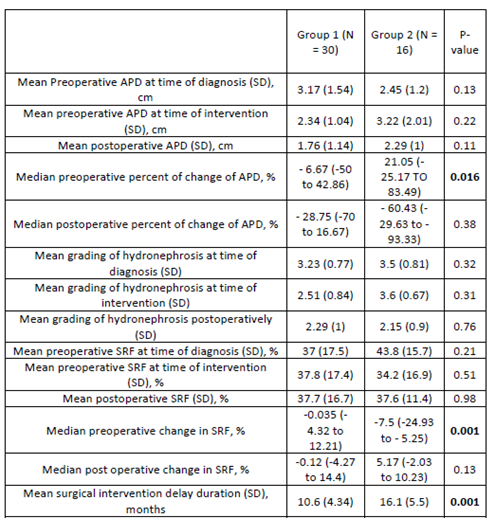
Methods: Data base of patients who underwent pyeloplasty for unilateral UPJO in a tertiary center from January 2016 to October 2020 was reviewed. Patients who had a delay in pyeloplasty for more than 3 months from time of diagnosis were identified. Patients for whom 3 renograms were performed at the time of surgical decision, immediately before surgery and within 1 year postoperative were included in the study. Deterioration was defined as 5 % or more decline in the split renal function SRF between 2 consecutive renograms.
Patients were then categorized into 2 groups: preserved renal function (group 1) and deteriorated renal function (group 2) based on the difference in preoperative renograms. Both groups were compared regarding pre and postoperative Antero-posterior diameter (APD), hydronephrosis grading, percent of change of hydronephrosis, change in SRF, and delay duration in months.
Results: A total 46 patients were included in the analysis: 30 cases had preserved renal function while 16 had significant deterioration of SRF. Group 2 showed higher precent increase of APD and more delay in surgical intervention (table) on univariate analysis (P value 0.016 and 0.001 respectively). On multivariate analysis these factors showed significant difference between groups. Other factors did not show significant difference between the groups. No significant difference was found in postoperative change of SRF.
None of the patients who had surgery within 6 months showed functional deterioration.
Conclusions: Delaying of surgical intervention for less than 6 months doesn`t lead to significant functional deterioration. Worsening hydronephrosis precedes functional deterioration.
Source of Funding: No
The objective of the study is to identify surgery delay effect on renal function in cases of UPJO and factors affecting it.
Methods: Data base of patients who underwent pyeloplasty for unilateral UPJO in a tertiary center from January 2016 to October 2020 was reviewed. Patients who had a delay in pyeloplasty for more than 3 months from time of diagnosis were identified. Patients for whom 3 renograms were performed at the time of surgical decision, immediately before surgery and within 1 year postoperative were included in the study. Deterioration was defined as 5 % or more decline in the split renal function SRF between 2 consecutive renograms.
Patients were then categorized into 2 groups: preserved renal function (group 1) and deteriorated renal function (group 2) based on the difference in preoperative renograms. Both groups were compared regarding pre and postoperative Antero-posterior diameter (APD), hydronephrosis grading, percent of change of hydronephrosis, change in SRF, and delay duration in months.
Results: A total 46 patients were included in the analysis: 30 cases had preserved renal function while 16 had significant deterioration of SRF. Group 2 showed higher precent increase of APD and more delay in surgical intervention (table) on univariate analysis (P value 0.016 and 0.001 respectively). On multivariate analysis these factors showed significant difference between groups. Other factors did not show significant difference between the groups. No significant difference was found in postoperative change of SRF.
None of the patients who had surgery within 6 months showed functional deterioration.
Conclusions: Delaying of surgical intervention for less than 6 months doesn`t lead to significant functional deterioration. Worsening hydronephrosis precedes functional deterioration.
Source of Funding: No



.jpg)
.jpg)