Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP28: Health Services Research: Practice Patterns, Quality of Life and Shared Decision Making III
MP28-19: Contemporary trend analysis of intra-detrusor botox injection and augment cystoplasty for spina bifida population in US free-standing childrens hospitals
Saturday, May 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 228
Hsin-Hsiao Wang, Kenneth Softness*, John Panagides, Dylan Cahill, Rachel Saunders, Boston, MA, Ranveer Vasdev, Minneapolis, MN, Tanya Logvinenko, Carlos Estrada, Boston, MA

Kenneth Aaron Softness, MD
Harvard Medical School
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Intra-detrusor botulinum toxin (botox) injection has been utilized as a minimally invasive alternative to augmentation cystoplasty in patients with refractory neurogenic bladder. However, little data are available regarding its use on a national level. We sought to investigate the contemporary trends of intra-detrusor botox injection and augment cystoplasty in free-standing children’s hospitals.
Methods: We queried the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database to identify patients with spina bifida from 2013 to 2019 who underwent intra-detrusor botox injection and augment cystoplasty based on CPT and ICD9/10 codes. Total spina bifida population under care in the free-standing children’s hospitals was estimated by all inpatient and ambulatory surgery encounters as denominators to calculate frequency by time for both intra-detrusor botox injections and augmentation cystoplasty.
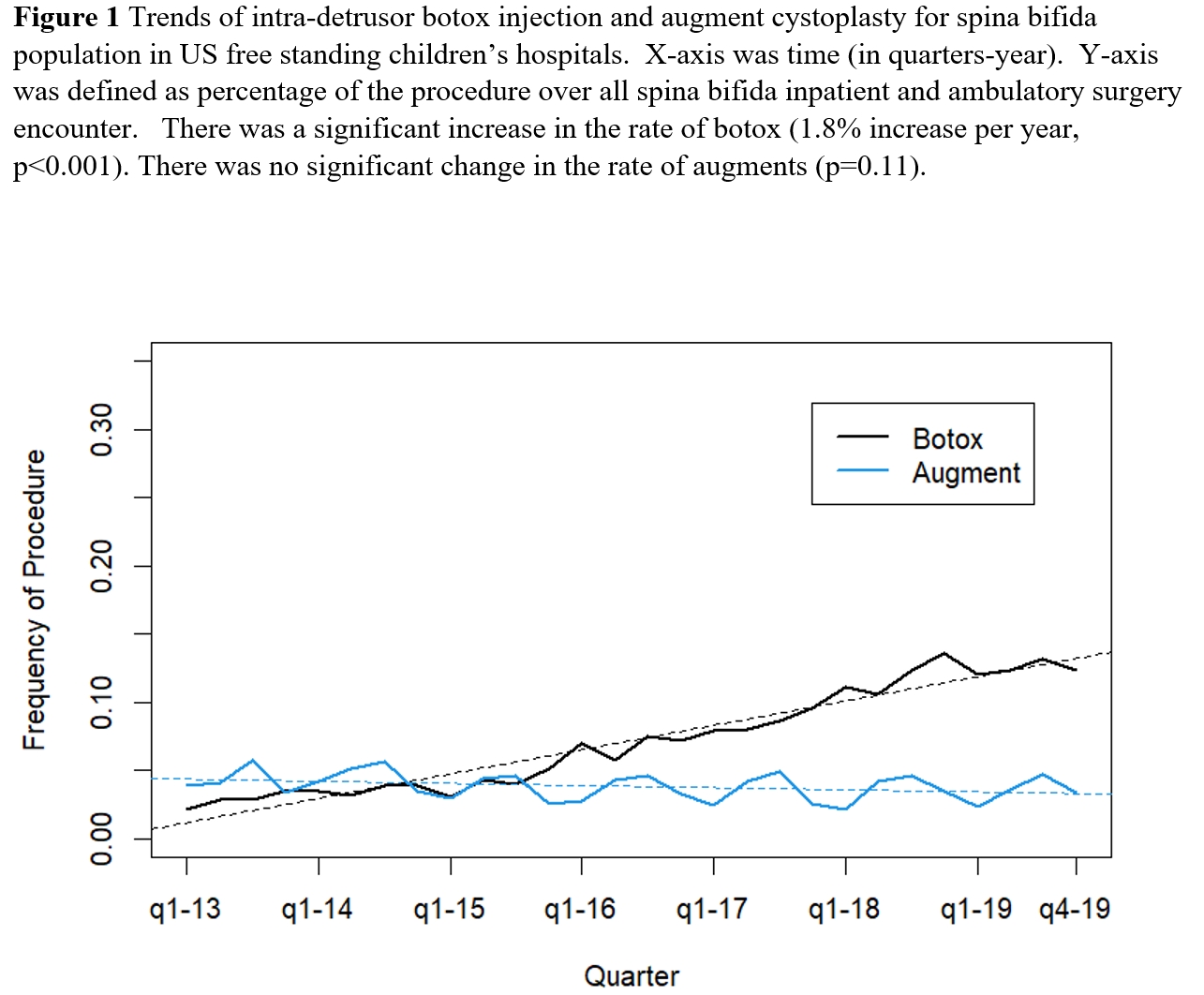
Results: In total, we included 3,153 intra-detrusor botox injections and 1,828 augment cystoplasties between 2013 to 2019. 46% of patients were male. Median age at surgery was 10.6 (IQR 7.1-15.0) years. The contemporary trend (in quarters) for botox injection and augment cystoplasty are shown in Figure 1. There was a significantly increasing trend for intra-detrusor botox injection in patients with spina bifida (from 2.0% in 2013q1 to 12.3% in 2019q4, p<0.001 for the trend). Conversely, there was a decreasing but not significant trend for augment cystoplasty (from 3.9% in 2013q1 to 3.3% in 2019q4, p=0.11 for the trend). Strong seasonality (higher in summer) was seen in augment cystoplasty but not intra-detrusor botox injection group. The sensitivity analysis using only first intra-detrusor botox injection per patient led to similarly significant increasing trend with time.
Conclusions: There is a significantly increased use of intra-detrusor botox injection in the management of neurogenic bladder in patients with spina bifida. The use of augmentation cystoplasty has slightly decreased, but not significantly. These trends are likely reflective of changing practice patterns, but the role of botox in the management of pediatric neurogenic bladder remains incompletely defined.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: We queried the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database to identify patients with spina bifida from 2013 to 2019 who underwent intra-detrusor botox injection and augment cystoplasty based on CPT and ICD9/10 codes. Total spina bifida population under care in the free-standing children’s hospitals was estimated by all inpatient and ambulatory surgery encounters as denominators to calculate frequency by time for both intra-detrusor botox injections and augmentation cystoplasty.
Results: In total, we included 3,153 intra-detrusor botox injections and 1,828 augment cystoplasties between 2013 to 2019. 46% of patients were male. Median age at surgery was 10.6 (IQR 7.1-15.0) years. The contemporary trend (in quarters) for botox injection and augment cystoplasty are shown in Figure 1. There was a significantly increasing trend for intra-detrusor botox injection in patients with spina bifida (from 2.0% in 2013q1 to 12.3% in 2019q4, p<0.001 for the trend). Conversely, there was a decreasing but not significant trend for augment cystoplasty (from 3.9% in 2013q1 to 3.3% in 2019q4, p=0.11 for the trend). Strong seasonality (higher in summer) was seen in augment cystoplasty but not intra-detrusor botox injection group. The sensitivity analysis using only first intra-detrusor botox injection per patient led to similarly significant increasing trend with time.
Conclusions: There is a significantly increased use of intra-detrusor botox injection in the management of neurogenic bladder in patients with spina bifida. The use of augmentation cystoplasty has slightly decreased, but not significantly. These trends are likely reflective of changing practice patterns, but the role of botox in the management of pediatric neurogenic bladder remains incompletely defined.
Source of Funding: none


.jpg)
.jpg)