Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP29: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology III
MP29-02: Salvage Versus Primary Holmium Laser Enucleation for BPH: An Outcomes and Safety Analysis
Saturday, May 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 225
Adri Durant*, Sandeep Voleti, Sarah Wu, Phoenix, AZ, Jonathan Moore, Davis, CA, Gopal Narang, Scott Cheney, Mitchell Humphreys, Phoenix, AZ
- AD
Adri Durant, MD
Mayo Clinic Arizona
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Repeat surgical treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is not uncommon. Minimally invasive surgical therapies (MIST) and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) have known retreatment rates ranging from 5% to 13% at 5 years. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is an effective primary treatment for BPH but also as can be utilized as a salvage modality. This study assesses the safety and efficacy of salvage HoLEP (s-HoLEP) after prior BPH surgery.
Methods: A retrospective review of HoLEP at a single institution between 2006 and 2020 was performed. Patients who had a s-HoLEP were evaluated and compared to those undergoing a primary HoLEP (p-HoLEP). Out of a total of 1960 HoLEPs, 217 were s-HoLEP and these were matched 2:1 to 416 p-HoLEPs to compare preoperative, operative and post-operative characteristics. The primary endpoint was Clavien complications within 90 days of surgery. Secondary endpoints included quantitative measurements of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), International Prostate Symptoms Score (IPSS), maximum urinary flow (Qmax) and postvoid residual volumes (PVR). Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test was used for analysis of continuous variables and Fischer’s exact test was used for categorical variables.
Results: The s-HoLEP cohort was older, median age of 71.2 years, compared to p-HoLEP at 68.8 years (p = 0.03). All other factors were well matched. Pre-operative prostate volume, IPSS and Qmax were not different (p = 0.783, 0.278, and 0.759, respectively). However, rates of pre-op urinary retention and PVRs were higher in the p-HOLEP group (p = <0.001 and 0.045, respectively). Intra-operatively, the s-HOLEP cohort had longer procedure and morcellation times (p = 0.011 and 0.007). Post-operatively, the s-HOLEP required longer catheter duration and hospitalization (both p < 0.001). There was no difference in Qmax, IPSS or 90-day complication rates (p = 0.108, 0.247, and 0.506, respectively).
Conclusions: S-HoLEP is a safe treatment option for patients requiring repeat BPH surgical therapy. S-HoLEP patients had longer operative times and hospital stay but equivalent long-term efficacy compared to p-HoLEP.
Source of Funding: None
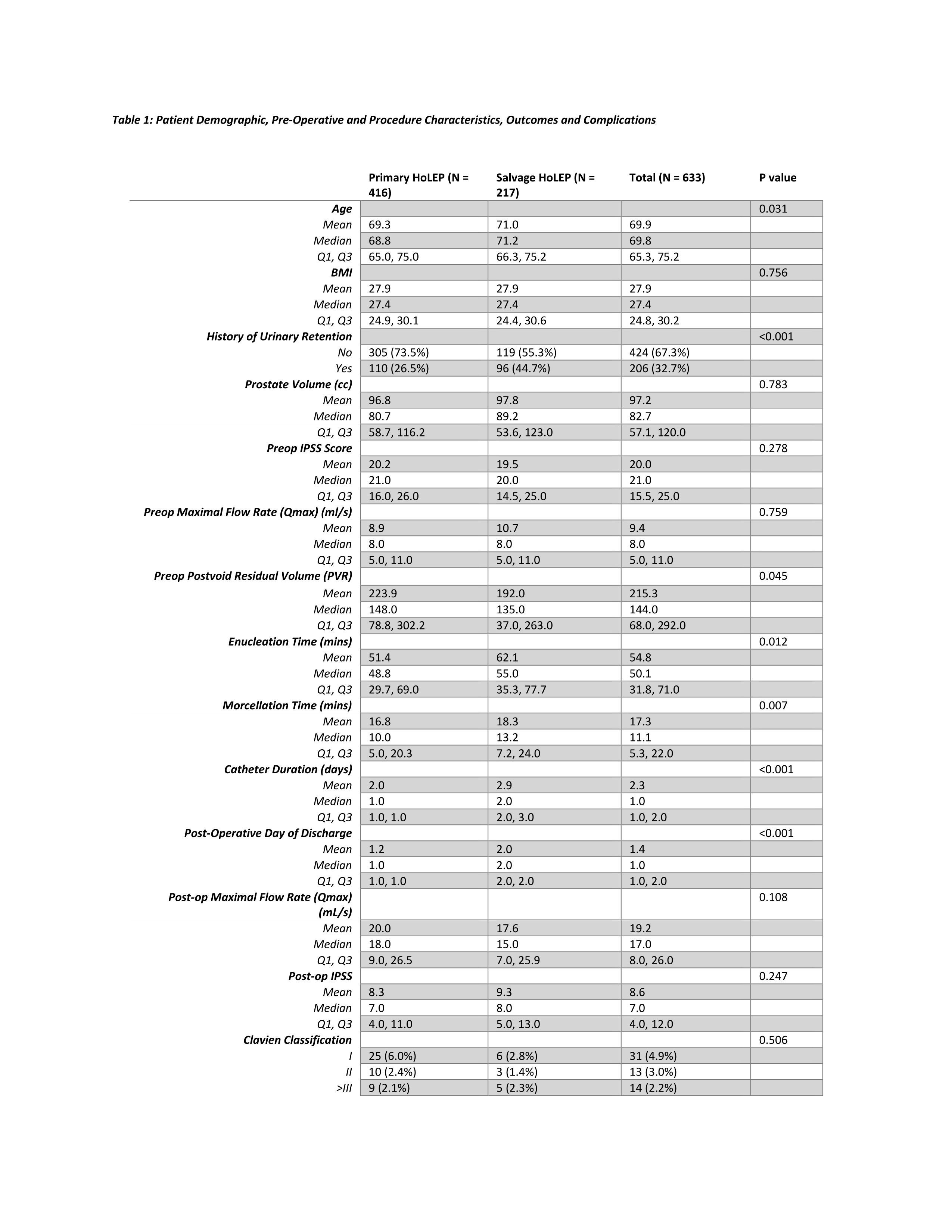
Methods: A retrospective review of HoLEP at a single institution between 2006 and 2020 was performed. Patients who had a s-HoLEP were evaluated and compared to those undergoing a primary HoLEP (p-HoLEP). Out of a total of 1960 HoLEPs, 217 were s-HoLEP and these were matched 2:1 to 416 p-HoLEPs to compare preoperative, operative and post-operative characteristics. The primary endpoint was Clavien complications within 90 days of surgery. Secondary endpoints included quantitative measurements of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), International Prostate Symptoms Score (IPSS), maximum urinary flow (Qmax) and postvoid residual volumes (PVR). Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test was used for analysis of continuous variables and Fischer’s exact test was used for categorical variables.
Results: The s-HoLEP cohort was older, median age of 71.2 years, compared to p-HoLEP at 68.8 years (p = 0.03). All other factors were well matched. Pre-operative prostate volume, IPSS and Qmax were not different (p = 0.783, 0.278, and 0.759, respectively). However, rates of pre-op urinary retention and PVRs were higher in the p-HOLEP group (p = <0.001 and 0.045, respectively). Intra-operatively, the s-HOLEP cohort had longer procedure and morcellation times (p = 0.011 and 0.007). Post-operatively, the s-HOLEP required longer catheter duration and hospitalization (both p < 0.001). There was no difference in Qmax, IPSS or 90-day complication rates (p = 0.108, 0.247, and 0.506, respectively).
Conclusions: S-HoLEP is a safe treatment option for patients requiring repeat BPH surgical therapy. S-HoLEP patients had longer operative times and hospital stay but equivalent long-term efficacy compared to p-HoLEP.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)