Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP33: Uroradiology I
MP33-13: Impact of Prostatic Urethral Lift Device on Prostate MR Image Quality
Saturday, May 14, 2022
4:30 PM – 5:45 PM
Location: Room 228
Tarik Benidir*, Ryan Ward, Justin Ream, Ethan Austhof, Eric Klein, Cleveland, OH, Ismail Turkbey, Bethesda, MD, Andrei Purysko, Cleveland, OH
- TB
Tarik Benidir, MD, FRCS, MSc
Resident
Cleveland Clinic
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Prostatic urethral lift (PUL) using the UroLift device is a non-pharmacological treatment option for patients with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Patients with this device can safely undergo prostate MRI, but the influence of this device on prostate MR image quality has not been assessed. The aim of this study is to evaluate prostate MR image quality in patients with UroLift.
Methods: This retrospective study included 43 adult men (mean age 65.2yrs; mean PSA 5.86 ng/mL) with UroLift who underwent prostate MRI at two institutions. Images from one of the institutions (n = 36) were reviewed and scored based on severity of artifacts caused by the device on T2-weighted (T2W), Diffusion weighted images (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps in the peripheral zone (PZ) and transition zone (TZ) using a 5-point scale (1- no impact on interpretation; 5 – non-diagnostic). Total prostate gland volumes and the prostate volumes obscured by the artifacts on T2W, ADC maps and dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) images were measured. The means of the scores assigned for severity of artifacts and percentage of gland volumes affected by the artifacts were calculated. T-test was used to compare differences in image quality scores.
Results: The average prostate volume was 59.1 cc (IQR: 42.7-79). The mean image quality scores were worse for DWI/ADC than T2W both in the PZ (1.7 vs 1, p = 0.0001) and in the TZ (3.2 vs 1.7 p=0.001). Worse scores were observed on DWI/ADC in the TZ at the base and mid gland compared to the apex (means scores 3.8, 3.5 and 2.5, respectively; p <0.05). The mean prostate volumes obscured by artifact on T2W, ADC map and DCE were 3.3 cc (IQR:2.0-4.5), 16.2 cc (IQR:10.5-21.6) and 6.4 cc (IQR:3.4-7.3). The mean percentage of prostate volume obscured by artifacts on T2W, ADC map and DCE were 0.06 (95% CI 0.05 to 0.07), 0.3 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.35) and 0.11 (95% CI 0.08 to 0.14), respectively.
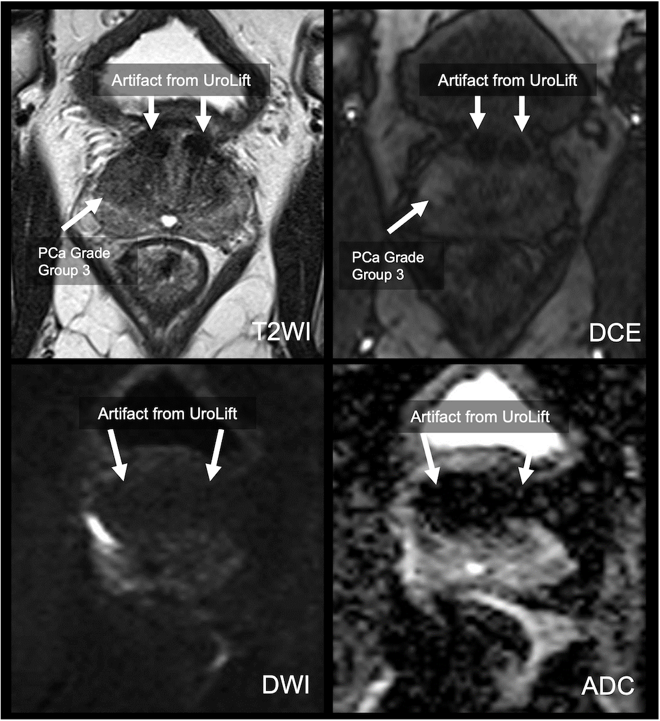
Conclusions: UroLift causes artifacts that can affect prostate MRI interpretation, with greater impact in the TZ and on DWI/ADC maps (Figure 1). Men considering undergoing PUL procedure should be counseled on the negative impact of this device on quality of prostate MRI.
Source of Funding: Cleveland Clinic imaging department
Methods: This retrospective study included 43 adult men (mean age 65.2yrs; mean PSA 5.86 ng/mL) with UroLift who underwent prostate MRI at two institutions. Images from one of the institutions (n = 36) were reviewed and scored based on severity of artifacts caused by the device on T2-weighted (T2W), Diffusion weighted images (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps in the peripheral zone (PZ) and transition zone (TZ) using a 5-point scale (1- no impact on interpretation; 5 – non-diagnostic). Total prostate gland volumes and the prostate volumes obscured by the artifacts on T2W, ADC maps and dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) images were measured. The means of the scores assigned for severity of artifacts and percentage of gland volumes affected by the artifacts were calculated. T-test was used to compare differences in image quality scores.
Results: The average prostate volume was 59.1 cc (IQR: 42.7-79). The mean image quality scores were worse for DWI/ADC than T2W both in the PZ (1.7 vs 1, p = 0.0001) and in the TZ (3.2 vs 1.7 p=0.001). Worse scores were observed on DWI/ADC in the TZ at the base and mid gland compared to the apex (means scores 3.8, 3.5 and 2.5, respectively; p <0.05). The mean prostate volumes obscured by artifact on T2W, ADC map and DCE were 3.3 cc (IQR:2.0-4.5), 16.2 cc (IQR:10.5-21.6) and 6.4 cc (IQR:3.4-7.3). The mean percentage of prostate volume obscured by artifacts on T2W, ADC map and DCE were 0.06 (95% CI 0.05 to 0.07), 0.3 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.35) and 0.11 (95% CI 0.08 to 0.14), respectively.
Conclusions: UroLift causes artifacts that can affect prostate MRI interpretation, with greater impact in the TZ and on DWI/ADC maps (Figure 1). Men considering undergoing PUL procedure should be counseled on the negative impact of this device on quality of prostate MRI.
Source of Funding: Cleveland Clinic imaging department


.jpg)
.jpg)