Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP45: Prostate Cancer: Markers
MP45-15: PTEN Loss and Diffusive Ki67 Are Related to Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Validation Cohort Study
Sunday, May 15, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 225
Che Hsueh Yang*, Yi Sheng Lin, Wei Chun Weng, Chin Heng Lu, Chung Hsiao Chin, Tang Yi Tsao, Chao Yu Hsu, Min Che Tung, Yen Chuan Ou, Taichung, Taiwan

Che Hsueh Yang, MD
resident trainee
Tungs' Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Although Ki67 and PTEN emerge as promising markers of localized prostate cancer (PC) after radical prostatectomy (RP), they are still not recommended in National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline. This study aims to validate their prognostic values in time-to- castration-resistant PC (CRPC).
Methods: Between 2015 and 2017, men of localized PC after robot-assisted RP were retrospectively reviewed. Their specimens were re-stained with immunohistochemical (IHC) markers of Ki67 and PTEN and were interpreted according to suggestions of International Society of Urological Pathology. Diffusive Ki67 was defined as 30% positivity (diffusive: Ki67+, non-diffusive: Ki67-) and PTEN was categorized into intact (PTEN +), heterogenous loss (PTEN-) and homogenous loss (PTEN 2-). Independent variables of Ki67 and PTEN were examined through univariable and multivariable Cox regression, and dependent variables were time-to-non-metastatic CRPC (M0CRPC) and metastatic CRPC (M1CRPC). Kaplan Meier (KM) curve was applied to visualize and compare survival outcomes.
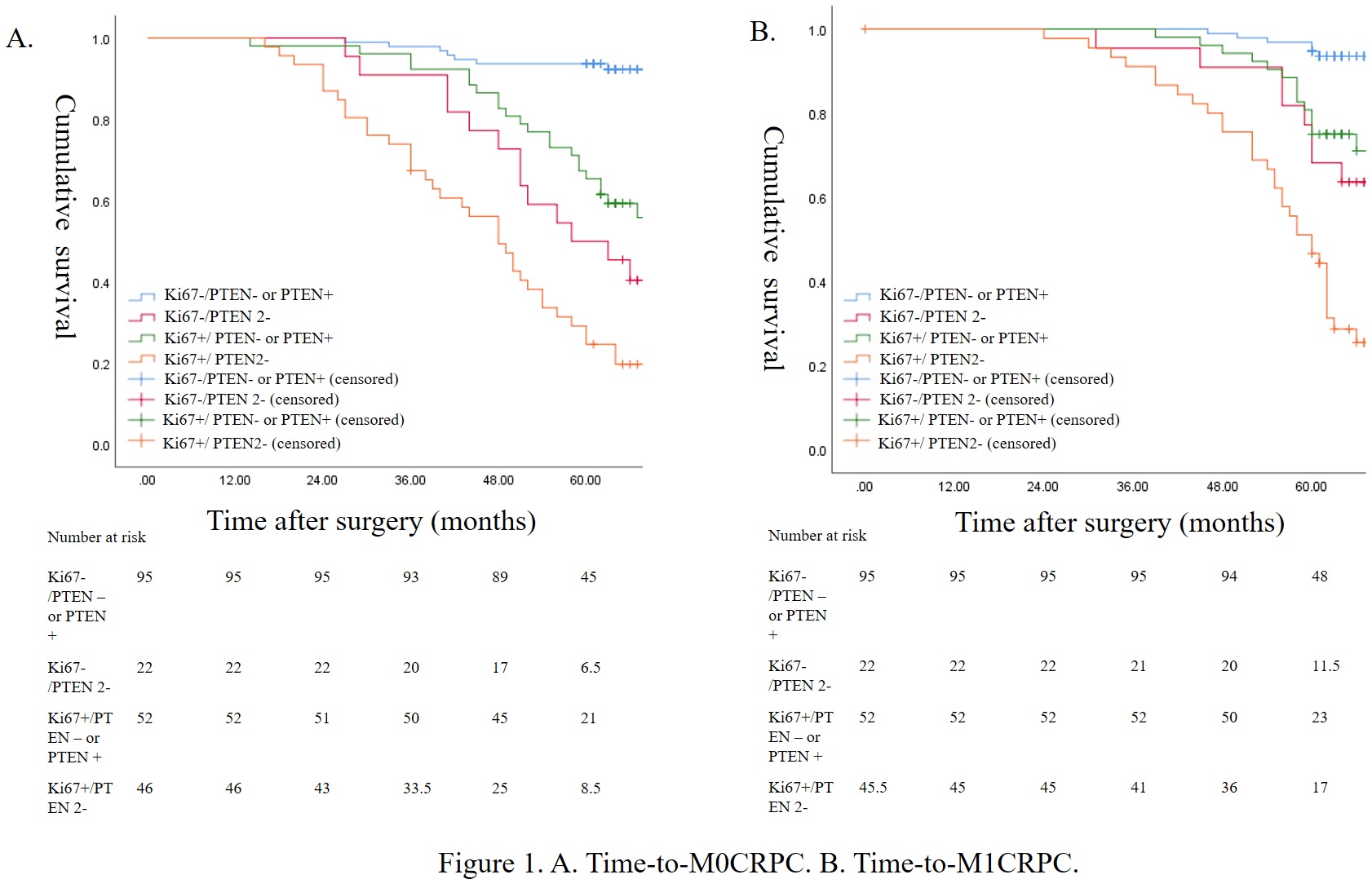
Results: A total of 215 men were reviewed with a mean surveillance of 66.85 months. In multivariable Cox regression of time-to-M0CRPC, PTEN 2- (HR:2.22(1.10-4.50)) and Ki67+ (HR:2.09 (1.13-3.89)) were significant while PTEN- (HR: 1.20 (0.56-1.59)) was not significant with reference to PTEN+. In multivariable Cox regression of time-to-M1CRPC, PTEN 2- (HR:2.76 (1.20-6.31)) and Ki67+ (HR:1.36 (1.06-2.72)) were significant while PTEN- (HR: 1.54 (0.62-3.81)) was not significant with reference to PTEN+. KM curves of time-to-M0CRPC and time-to-M1CRPC were given in Fig 1. Except for Ki67-/PTEN 2- and Ki67+/ PTEN- or PTEN+ (p=0.226) in time-to-M0CRPC, all subgroups' comparisons were significantly different in log-rank test (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Both Ki67+ and PTEN 2- are associated with CRPC, and PTEN 2- is in higher risk than Ki67+ in developing M1CRPC.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Between 2015 and 2017, men of localized PC after robot-assisted RP were retrospectively reviewed. Their specimens were re-stained with immunohistochemical (IHC) markers of Ki67 and PTEN and were interpreted according to suggestions of International Society of Urological Pathology. Diffusive Ki67 was defined as 30% positivity (diffusive: Ki67+, non-diffusive: Ki67-) and PTEN was categorized into intact (PTEN +), heterogenous loss (PTEN-) and homogenous loss (PTEN 2-). Independent variables of Ki67 and PTEN were examined through univariable and multivariable Cox regression, and dependent variables were time-to-non-metastatic CRPC (M0CRPC) and metastatic CRPC (M1CRPC). Kaplan Meier (KM) curve was applied to visualize and compare survival outcomes.
Results: A total of 215 men were reviewed with a mean surveillance of 66.85 months. In multivariable Cox regression of time-to-M0CRPC, PTEN 2- (HR:2.22(1.10-4.50)) and Ki67+ (HR:2.09 (1.13-3.89)) were significant while PTEN- (HR: 1.20 (0.56-1.59)) was not significant with reference to PTEN+. In multivariable Cox regression of time-to-M1CRPC, PTEN 2- (HR:2.76 (1.20-6.31)) and Ki67+ (HR:1.36 (1.06-2.72)) were significant while PTEN- (HR: 1.54 (0.62-3.81)) was not significant with reference to PTEN+. KM curves of time-to-M0CRPC and time-to-M1CRPC were given in Fig 1. Except for Ki67-/PTEN 2- and Ki67+/ PTEN- or PTEN+ (p=0.226) in time-to-M0CRPC, all subgroups' comparisons were significantly different in log-rank test (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Both Ki67+ and PTEN 2- are associated with CRPC, and PTEN 2- is in higher risk than Ki67+ in developing M1CRPC.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)