Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP55: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Ablative Therapy
MP55-09: Early Percent Prostate-Specific Antigen Reduction Post Cryotherapy can Predict Biochemical Recurrence in Men with Prostate Cancer
Monday, May 16, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Jessica Sommer*, Garden City, NY, Ashley Monaco, Glen Head, NY, Meredith Akerman, Mineola, NY, Aaron Katz, Garden City, NY

Jessica Sommer, BS
NYU Langone Health -- Long Island
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Predictors of response to therapy and biochemical recurrence (BCR) following cryotherapy (cryo) are not well established. We evaluated whether percent (%) prostate-specific antigen (PSA) reduction can be used as a prognostic indicator of biochemical recurrence (BCR) in patients (pts) who received both focal and total cryo for primary or salvage Tx.
Methods: Our IRB approved PCa database was reviewed for pts treated with cryo. Pts missing baseline PSA or PSA 3 months (mo.) post treatment (Tx) were excluded. Tumor risk was categorized by D’Amico criteria. Mann-Whitney test measured %PSA reduction (ratio between pre-procedural PSA and PSA at two post-procedural instances) and BCR based on Phoenix criteria. Chi-square/Fisher’s exact tests assessed BCR across 3 and 6 mo. %reduction categories. Descriptive statistics and a univariate screen of primary total, primary focal, salvage total, salvage focal groups was performed. Repeated measures ANOVA model on log-transformed PSA compared groups after adjustment of confounding variables in univariate screen. P<0.05 was significant.
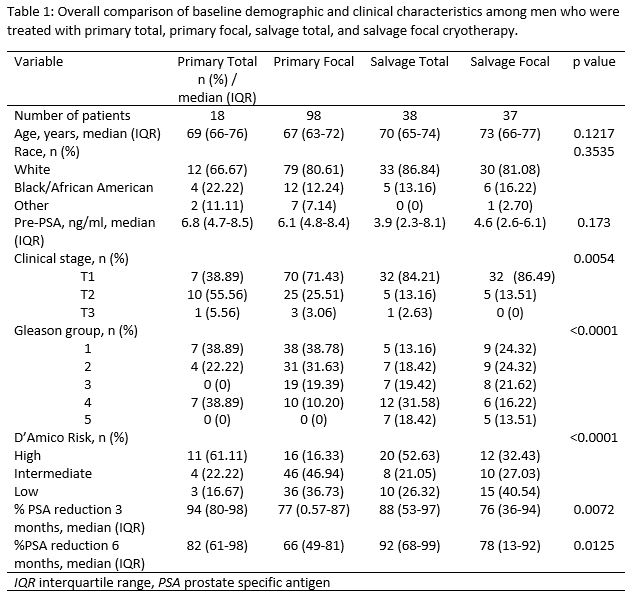
Results: 191 men with median follow up of 57.6 (8.5-104.2) mo. were included (Table 1). 3 mo. post Tx, BCR was highest in pts with %reduction <10% and lowest in pts with %reduction >90% (81.25% vs. 40.74%, p<0.0035). Further demonstrated amongst salvage cryo pts, 83.33% experienced <10% reduction and 41.38% a >90% reduction (p < 0.0436). At 3 and 6 mo., median %PSA reduction post-cryo was greater in pts with no BCR (n=80) than with (n=111) (86% vs. 77%, p=0.0003 and 81% vs. 60%, p<0.0001). 58 (30%) men who received primary or salvage total cryo had greater %PSA reduction, at both time points, than focal (p=0.0072 and p=0.0125). After adjustment of clinical stage, Gleason group and D’Amico risk, interaction between each group and time (0, 3, 6 mo.) was significant (p < 0.0175). Primary total pts had greatest %PSA decrease 6 mo. post Tx, while salvage focal pts had smallest decrease (Figure 1).
Conclusions: We found that pts treated with total cryo and those with no BCR experienced greater rates of PSA reduction at 3 and 6 mo. post therapy. Although not statistically significant, those who received primary total cryo have a lower rate of BCR than other Tx groups. These findings add to limited existing data regarding predictors of response to therapy.
Source of Funding: Department of Urology, NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island
Methods: Our IRB approved PCa database was reviewed for pts treated with cryo. Pts missing baseline PSA or PSA 3 months (mo.) post treatment (Tx) were excluded. Tumor risk was categorized by D’Amico criteria. Mann-Whitney test measured %PSA reduction (ratio between pre-procedural PSA and PSA at two post-procedural instances) and BCR based on Phoenix criteria. Chi-square/Fisher’s exact tests assessed BCR across 3 and 6 mo. %reduction categories. Descriptive statistics and a univariate screen of primary total, primary focal, salvage total, salvage focal groups was performed. Repeated measures ANOVA model on log-transformed PSA compared groups after adjustment of confounding variables in univariate screen. P<0.05 was significant.
Results: 191 men with median follow up of 57.6 (8.5-104.2) mo. were included (Table 1). 3 mo. post Tx, BCR was highest in pts with %reduction <10% and lowest in pts with %reduction >90% (81.25% vs. 40.74%, p<0.0035). Further demonstrated amongst salvage cryo pts, 83.33% experienced <10% reduction and 41.38% a >90% reduction (p < 0.0436). At 3 and 6 mo., median %PSA reduction post-cryo was greater in pts with no BCR (n=80) than with (n=111) (86% vs. 77%, p=0.0003 and 81% vs. 60%, p<0.0001). 58 (30%) men who received primary or salvage total cryo had greater %PSA reduction, at both time points, than focal (p=0.0072 and p=0.0125). After adjustment of clinical stage, Gleason group and D’Amico risk, interaction between each group and time (0, 3, 6 mo.) was significant (p < 0.0175). Primary total pts had greatest %PSA decrease 6 mo. post Tx, while salvage focal pts had smallest decrease (Figure 1).
Conclusions: We found that pts treated with total cryo and those with no BCR experienced greater rates of PSA reduction at 3 and 6 mo. post therapy. Although not statistically significant, those who received primary total cryo have a lower rate of BCR than other Tx groups. These findings add to limited existing data regarding predictors of response to therapy.
Source of Funding: Department of Urology, NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island

.jpg)
.jpg)