Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD19: Stone Disease: Surgical Therapy (including ESWL) II
PD19-08: Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Prediction of Septic Shock after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Sub-analysis of a Multi-Center Prospective Trial from the EDGE Consortium
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:10 AM – 8:20 AM
Location: Room 245
Jillian J. Gerrity*, Jonathan H. Berger, San Diego, CA, Naren Nimmagadda, Nicholas Kavoussi, Nashville, TN, Tony T. Chen, San Diego, CA, Amy E. Krambeck, Chicago, IL, Tim Large, Indianapolis, IN, Seth K. Bechis, San Diego, CA, David F. Friedlander, Chapel Hill, NC, Manoj Monga, San Diego, CA, Ryan S. Hsi, Nicole L. Miller, Nashville, TN, Ben H. Chew, Dirk Lange, Vancouver, Canada, Bodo Knudsen, Michael W. Sourial, Columbus, OH, Mitchell R. Humphreys, Karen L. Stern, Scottsdale, AZ, Ojas Shah, New York, NY, Joel E. Abbott, Garen Abedi, Roger L. Sur, San Diego, CA
- JG
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Recent retrospective literature suggests that the quick sequential organ failure assessment scoring (qSOFA) tool is a potentially superior tool over use of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria (SIRS) to predict septic shock after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) surgery.1 In this abstract, we examine use of qSOFA and SIRS to predict septic shock within a data series collected prospectively on PCNL patients as part of a greater study of infectious complications.2
Methods: We performed a sub-analysis of a prospective multicenter study including PCNL patients across seven institutions. Clinical signs informing SIRS and qSOFA were collected no later than post-operative day one. The primary outcome was sensitivity and specificity of SIRS and qSOFA (high risk score of >/= 2 points) in predicting need for pressors and admission to the intensive care unit.
Results: A total of 133 patients at seven institutions were analyzed. The sensitivity/specificity was 100%/83.3% for SIRS and was 100%/92.4% for qSOFA.
Conclusions: Use of the qSOFA score to predict post-PCNL septic shock appears reproducible. Use of qSOFA may offer more specificity than SIRS when predicting post-PCNL septic shock.
1. Yaghoubian A, et al.. Use of the Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Prediction of Intensive Care Unit Admission Due to Septic Shock after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Multicenter Study. J Urol. 2019 Aug;202(2):314-318. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000195. Epub 2019 Jul 8. PMID: 30829131.
2. Sur RL et al.. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Preoperative Prophylactic Antibiotics for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in Moderate to High Infectious Risk Population: A Report from the EDGE Consortium. J Urol. 2021 May;205(5):1379-1386. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001582. Epub 2020 Dec 28. PMID: 33369488.
Source of Funding: None
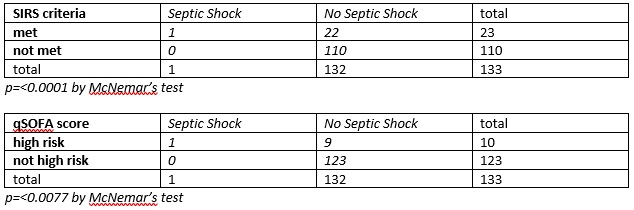
Methods: We performed a sub-analysis of a prospective multicenter study including PCNL patients across seven institutions. Clinical signs informing SIRS and qSOFA were collected no later than post-operative day one. The primary outcome was sensitivity and specificity of SIRS and qSOFA (high risk score of >/= 2 points) in predicting need for pressors and admission to the intensive care unit.
Results: A total of 133 patients at seven institutions were analyzed. The sensitivity/specificity was 100%/83.3% for SIRS and was 100%/92.4% for qSOFA.
Conclusions: Use of the qSOFA score to predict post-PCNL septic shock appears reproducible. Use of qSOFA may offer more specificity than SIRS when predicting post-PCNL septic shock.
1. Yaghoubian A, et al.. Use of the Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Prediction of Intensive Care Unit Admission Due to Septic Shock after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Multicenter Study. J Urol. 2019 Aug;202(2):314-318. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000195. Epub 2019 Jul 8. PMID: 30829131.
2. Sur RL et al.. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Preoperative Prophylactic Antibiotics for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in Moderate to High Infectious Risk Population: A Report from the EDGE Consortium. J Urol. 2021 May;205(5):1379-1386. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001582. Epub 2020 Dec 28. PMID: 33369488.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)