Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD32: Infections/Inflammation/Cystic Disease of the Genitourinary Tract: Kidney & Bladder III
PD32-03: Tebipenem In vitro Activity Against a Collection of Pathogens Responsible for Urinary Tract Infections in the United States
Saturday, May 14, 2022
3:50 PM – 4:00 PM
Location: Room 255
SJ Ryan Arends*, North Liberty, IA, Ian Critchley, Nicole Cotroneo, Cambridge, MA, Jennifer Streit, Helio Sader, Mariana Castanheira, Rodrigo Mendes, North Liberty, IA
- SA
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Enterobacterales (ENT)—especially Escherichia coli (EC), Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPN), and Proteus mirabilis (PM)—are widely implicated in urinary tract infections (UTIs). Many oral agents are used to manage UTIs, but their usefulness has been compromised by the increased prevalence of extended-spectrum ß-lactamases (ESBL) and presence of co-resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) and quinolones. Tebipenem (TBP) is an oral carbapenem in clinical development for treating complicated UTIs and acute pyelonephritis. This study assessed the in vitro activity of TBP and comparator agents against ENT responsible for UTIs in the US during 2019-2020.
Methods: A total of 3,576 ENT recovered from urine samples during the 2019-2020 STEWARD Surveillance Program were included in the study. Isolates were collected from medical centers in all 9 US Census Regions and were centrally tested for susceptibility by reference broth microdilution method. MIC interpretation was performed based on CLSI criteria.
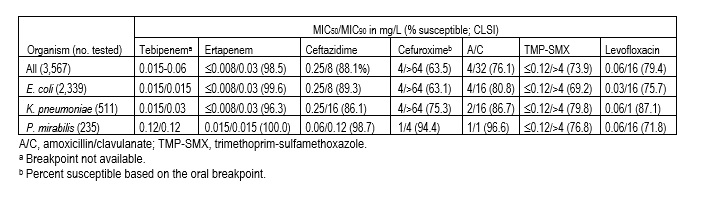
Results: EC comprised 65.6% of all ENT pathogens, followed by KPN (14.3%), PM (6.6%), and other species (13.7%). TBP (MIC90, 0.015-0.06 mg/L) and ertapenem (ERT; MIC90, 0.03 mg/L) showed similar MIC90 results against ENT, EC, and KPN (Table). Ceftazidime (CAZ; MIC90, 8-16 mg/L) had elevated MIC90 values and suboptimal susceptibility results (86.1-89.3%) against ENT, EC, and KPN. The oral agents, cefuroxime, amoxicillin-clavulanate, TMP-SMX, and levofloxacin showed susceptibility rates ranging from 63.1% to 87.1% against ENT, EC, and KPN. TBP (MIC50/90, 0.12/0.12 mg/L) inhibited all PM at £0.25 mg/L. PM isolates were susceptible to ERT (100.0%), CAZ (98.7%), cefuroxime (94.4%), and amoxicillin/clavulanate (96.6%), whereas susceptibility rates of 71.8-76.8% were noted for TMP-SMX and levofloxacin.
Conclusions: TBP displayed potent activity against ENT UTI pathogens recovered from patients in the US. TBP demonstrated in vitro activity against these UTI pathogens similar to that of ERT. In addition, these data showed compromised activity of intravenous and oral agents used for treating UTI. This data supports the development of tebipenem as an oral option for management of UTI in the US.
Source of Funding: This study was performed by JMI Laboratories and supported by Spero Therapeutics, which included funding for services related to preparing this abstract.
Methods: A total of 3,576 ENT recovered from urine samples during the 2019-2020 STEWARD Surveillance Program were included in the study. Isolates were collected from medical centers in all 9 US Census Regions and were centrally tested for susceptibility by reference broth microdilution method. MIC interpretation was performed based on CLSI criteria.
Results: EC comprised 65.6% of all ENT pathogens, followed by KPN (14.3%), PM (6.6%), and other species (13.7%). TBP (MIC90, 0.015-0.06 mg/L) and ertapenem (ERT; MIC90, 0.03 mg/L) showed similar MIC90 results against ENT, EC, and KPN (Table). Ceftazidime (CAZ; MIC90, 8-16 mg/L) had elevated MIC90 values and suboptimal susceptibility results (86.1-89.3%) against ENT, EC, and KPN. The oral agents, cefuroxime, amoxicillin-clavulanate, TMP-SMX, and levofloxacin showed susceptibility rates ranging from 63.1% to 87.1% against ENT, EC, and KPN. TBP (MIC50/90, 0.12/0.12 mg/L) inhibited all PM at £0.25 mg/L. PM isolates were susceptible to ERT (100.0%), CAZ (98.7%), cefuroxime (94.4%), and amoxicillin/clavulanate (96.6%), whereas susceptibility rates of 71.8-76.8% were noted for TMP-SMX and levofloxacin.
Conclusions: TBP displayed potent activity against ENT UTI pathogens recovered from patients in the US. TBP demonstrated in vitro activity against these UTI pathogens similar to that of ERT. In addition, these data showed compromised activity of intravenous and oral agents used for treating UTI. This data supports the development of tebipenem as an oral option for management of UTI in the US.
Source of Funding: This study was performed by JMI Laboratories and supported by Spero Therapeutics, which included funding for services related to preparing this abstract.


.jpg)
.jpg)