Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD33: Kidney Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy II
PD33-08: Comparison of Perioperative Outcomes Between Single-port and Multiport Retroperitoneal Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomies
Saturday, May 14, 2022
4:30 PM – 4:40 PM
Location: Room 245
Arnold Palacios*, Luca Morgantini, Ryan Trippel, Simone Crivellaro, Chicago, IL, Michael Abern, Durham, NC
- AP
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: In this study, we set out to compare perioperative outcomes between single port robot-assisted partial nephrectomies (SP-RAPN) and multiport robot-assisted partial nephrectomies (MP-RAPN) utilizing a retroperitoneal approach.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed of patients who underwent a SP-RAPN or MP-RAPN at out institution between 11/01/2013 and 05/30/2021. We compared the surgical platforms via univariate analysis using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and ?2 test for categorical variables.
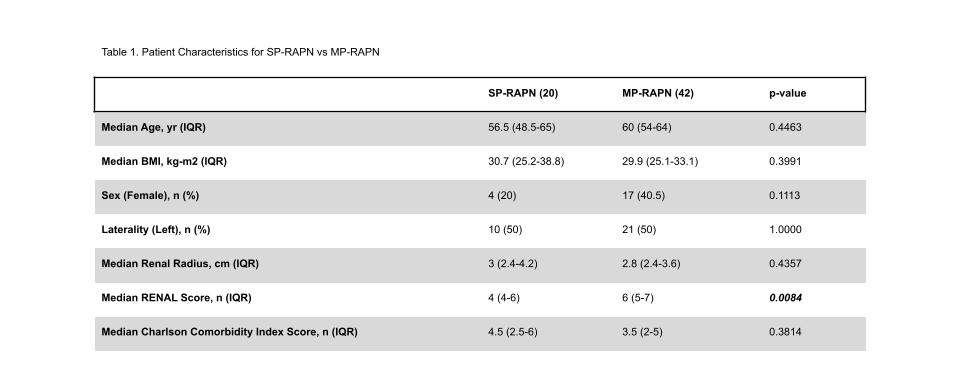
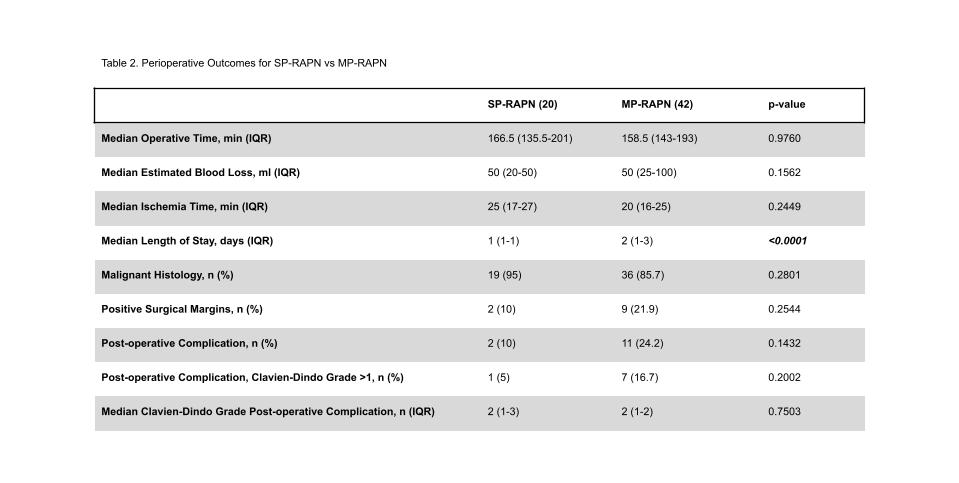
Results: 20 SP-RAPN and 42 MP-RAPN were performed utilizing a retroperitoneal approach. Patients who underwent MP were more likely to have higher RENAL scores (4 vs 6; p=0.0084), but baseline characteristics were not significantly different (Table 1). Outcome data is presented in Table 2. Patients that underwent SP-RAPN had a shorter post-operative length of hospital stay (1 vs 2 days; p<0.0001). There were no significant differences in operative time, estimated blood loss, ischemia time, positive margin rate, malignant histology, post-operative complication rate, or Clavien-Dindo complication grade.
Conclusions: Our experience with retroperitoneal SP-RAPN suggests it is safe, reproducible, and provides shorter lengths of hospital stay when compared to MP-RAPN. SP cases were associated with lower post-operative complication rate, although this was not statistically significant. The observed trend of increased ischemia time with the SP platform is likely related to operator learning curve as they adapt to a new system, although these differences were not significantly different.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed of patients who underwent a SP-RAPN or MP-RAPN at out institution between 11/01/2013 and 05/30/2021. We compared the surgical platforms via univariate analysis using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and ?2 test for categorical variables.
Results: 20 SP-RAPN and 42 MP-RAPN were performed utilizing a retroperitoneal approach. Patients who underwent MP were more likely to have higher RENAL scores (4 vs 6; p=0.0084), but baseline characteristics were not significantly different (Table 1). Outcome data is presented in Table 2. Patients that underwent SP-RAPN had a shorter post-operative length of hospital stay (1 vs 2 days; p<0.0001). There were no significant differences in operative time, estimated blood loss, ischemia time, positive margin rate, malignant histology, post-operative complication rate, or Clavien-Dindo complication grade.
Conclusions: Our experience with retroperitoneal SP-RAPN suggests it is safe, reproducible, and provides shorter lengths of hospital stay when compared to MP-RAPN. SP cases were associated with lower post-operative complication rate, although this was not statistically significant. The observed trend of increased ischemia time with the SP platform is likely related to operator learning curve as they adapt to a new system, although these differences were not significantly different.
Source of Funding: None



.jpg)
.jpg)