Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD35: Prostate Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) II
PD35-10: Prognostic significance of risk stratification in CHAARTED and LATITUDE studies among Japanese men with castration-resistant prostate cancer
Sunday, May 15, 2022
8:30 AM – 8:40 AM
Location: Room 252
Masaki Shiota*, Sotaro Chikamatsu, Leandro Blas, Takashi Matsumoto, Eiji Kashiwagi, Junichi Inokuchi, Ken-ichiro Shiga, Akira Yokomizo, Masatoshi Eto, Fukuoka, Japan
- MS
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: The CHAARTED and LATITUDE trials demonstrated a survival benefit of docetaxel and abiraterone for hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. In this study, we examined the impact of the risk stratification criteria used in the CHAARTED and LATITUDE trials on the prognosis of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). We also tested whether these risk stratification criteria could help in selecting effective initial treatment for CRPC.
Methods: Japanese patients with CRPC who were treated with docetaxel or androgen receptor pathway inhibitors such as abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide between 2014 and 2018 were included in this study. Clinicopathological factors, progression-free survival, and overall survival were investigated.
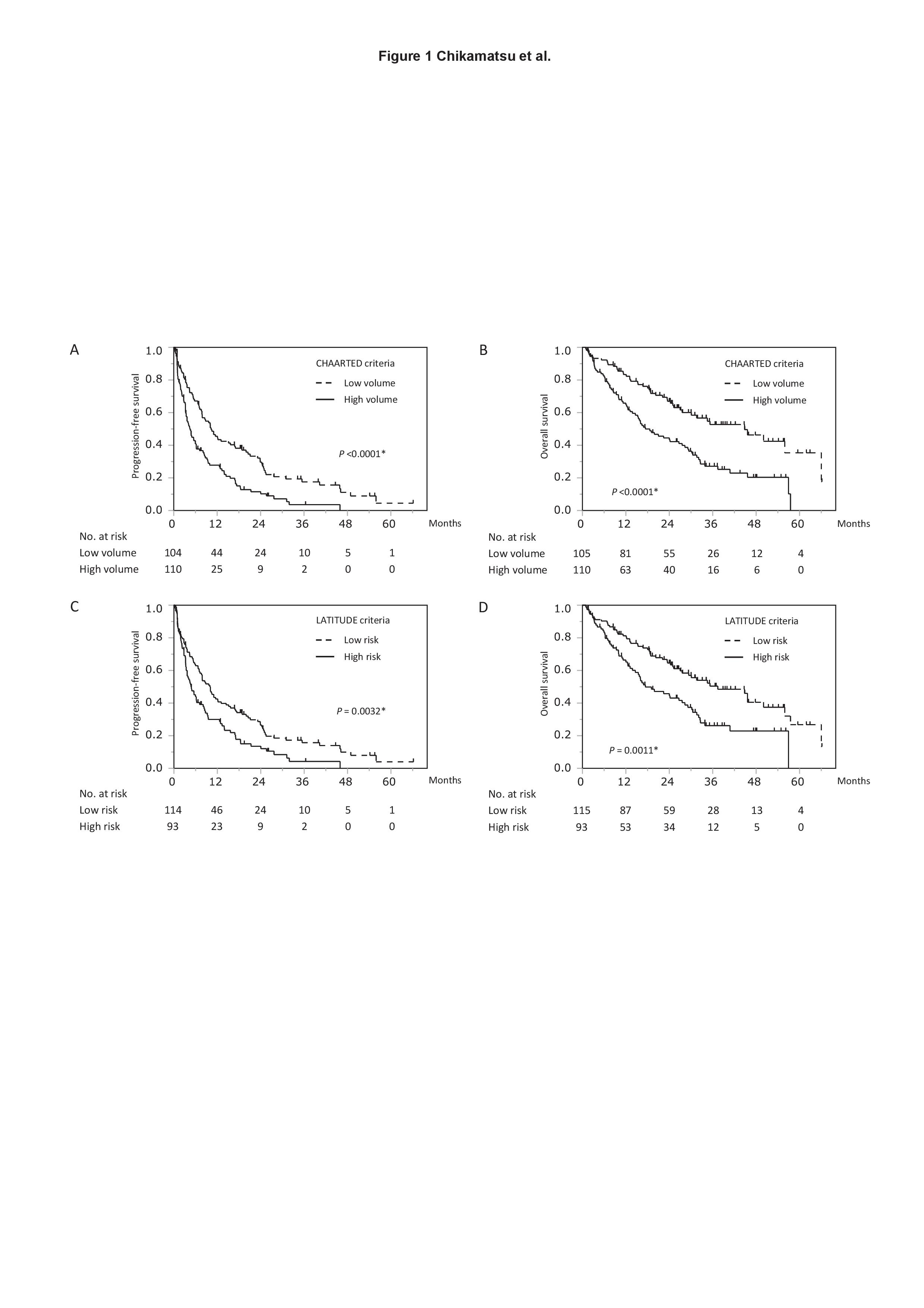
Results: Of 215 patients, 110 men (51.2%) and 93 men (43.3%) were grouped as high volume by CHAARTED criteria and high risk by LATITUDE criteria, respectively. Median progression-free survival was 10.3/4.5 months (P < 0.0001) for low/high volume (CHAARTED criteria) and 9.9/4.8 months (P = 0.0032) for low/high risk (LATITUDE criteria). The median overall survival was 44.8/17.4 months (P <0.0001) for low/high volume (CHAARTED criteria) and 37.4/17.4 months (P=0.0011) for low/high risk (LATITUDE criteria). The prognostic impact of CHAARTED and LATITUDE criteria was comparable between androgen receptor pathway inhibitors and docetaxel as first-line treatment for CRPC.
Conclusions: The CHAARTED and LATITUDE criteria were prognostic, but not predictive factors for CRPC.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Japanese patients with CRPC who were treated with docetaxel or androgen receptor pathway inhibitors such as abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide between 2014 and 2018 were included in this study. Clinicopathological factors, progression-free survival, and overall survival were investigated.
Results: Of 215 patients, 110 men (51.2%) and 93 men (43.3%) were grouped as high volume by CHAARTED criteria and high risk by LATITUDE criteria, respectively. Median progression-free survival was 10.3/4.5 months (P < 0.0001) for low/high volume (CHAARTED criteria) and 9.9/4.8 months (P = 0.0032) for low/high risk (LATITUDE criteria). The median overall survival was 44.8/17.4 months (P <0.0001) for low/high volume (CHAARTED criteria) and 37.4/17.4 months (P=0.0011) for low/high risk (LATITUDE criteria). The prognostic impact of CHAARTED and LATITUDE criteria was comparable between androgen receptor pathway inhibitors and docetaxel as first-line treatment for CRPC.
Conclusions: The CHAARTED and LATITUDE criteria were prognostic, but not predictive factors for CRPC.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)