Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Late-breaking Abstract II - Benign Disease
LBA02-11: Novel On-demand Treatment for Lifelong Premature Ejaculation using Transcutaneous Perineal Mini-patch Stimulator
Sunday, May 15, 2022
5:10 PM – 5:20 PM
Location: Room 243
Ariki Shechter, Nicola Mondaini, Ege Can Serefoglu, Tal Gollan, Boaz Appel, Ilan Gruenwald
- ES
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction:
Background: Premature Ejaculation (PE) is a prevalent sexual dysfunction in men. Available treatments demonstrate limited efficacy and low treatment adherence.
Objectives: To assess feasibility, safety, and efficacy of the Mini-patch, an on-demand transcutaneous perineal electrical stimulator, for the treating of PE.
Methods: Design, Setting, and Participants: Bi-center, international, prospective, randomized, double-blind, two-arm, sham-controlled, clinical study. After screening, intravaginal ejaculatory latency time (IELT) of candidates was measured. Eligibility was based on IELT values and medical/sexual history. Patients were randomized to Active and Sham device groups in a 2:1 ratio. Device safety profile was determined by incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events comparison.
Outcome Measurements and Statistical Analysis: Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGIC) scores, Premature Ejaculation Profile (PEP) questionnaire outcomes, and Mini-patch safety profile. Statistical power was calculated. Primary endpoints assessed device efficacy by mean fold change in geometric mean IELT (Mini-patch vs. sham treatment compared to baseline values). Adjusted mean difference for treatments, adjusted treatment effects (Mini-patch – sham), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and 2-sided P values were obtained.
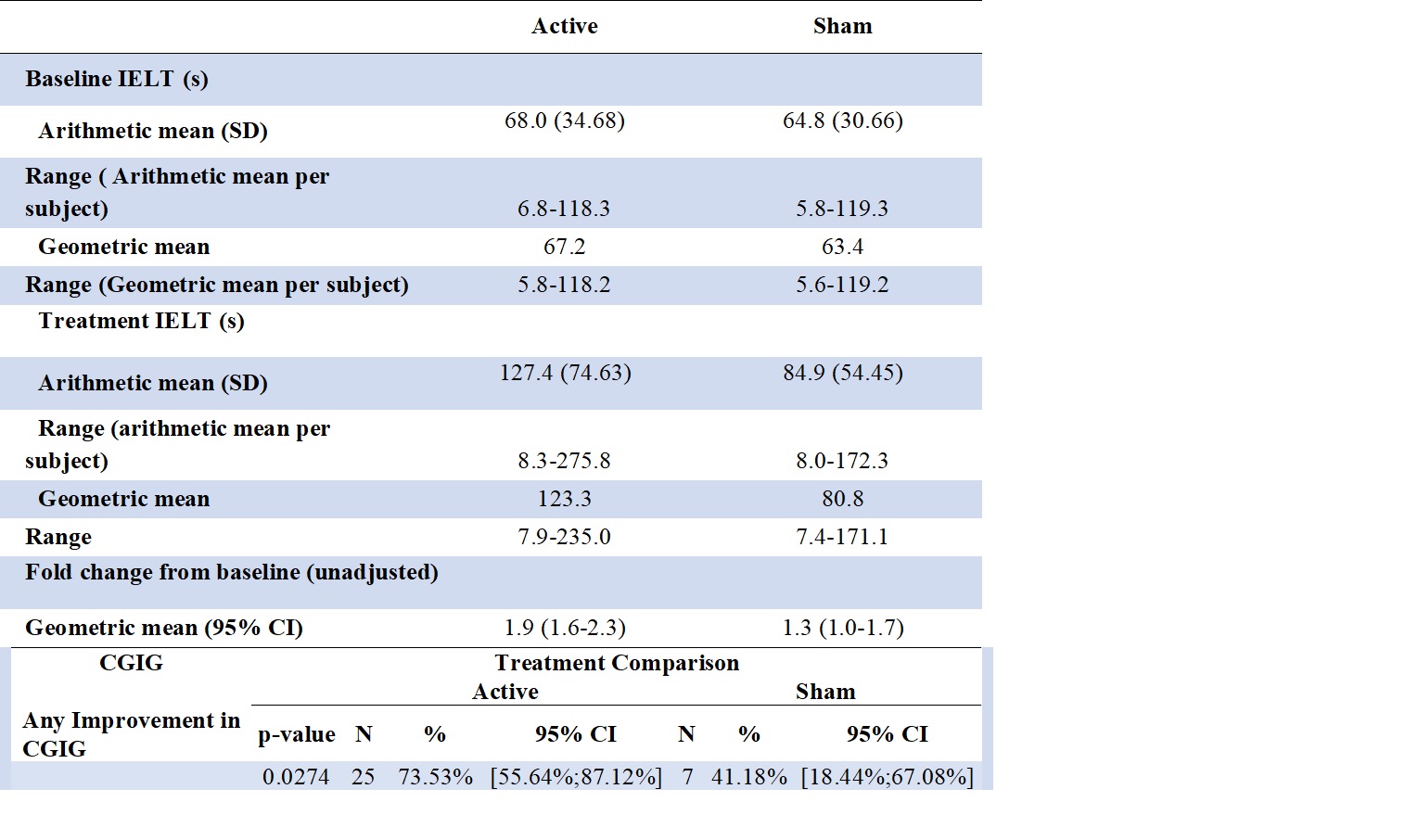
Results: Of 59 patients randomized, 51 completed the study: 34 in the Active and 17 in the Sham arm. Baseline geometric mean IELT was 67 seconds and significantly increased to 123 seconds (p < 0.0001) in the Active group, compared to 63 seconds increasing insignificantly to 81 seconds (p=0.1653) in the Sham group. The IELT significantly increased by 3.22-fold in the Active as compared to the Sham group (p=0.0047). Overall Geometric Mean Time Fold increases of IELT in the Active compared to the Sham group were 1.7 (95% CI 1.5-2.1) vs. 1.2 (95% CI 1.0-1.6), respectively. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: Mini-patch has the potential to become a leading on-demand, noninvasive, and drug-free treatments for PE.
Source of Funding: Virility Medical Ltd; Hod-hasharon, Israel

Background: Premature Ejaculation (PE) is a prevalent sexual dysfunction in men. Available treatments demonstrate limited efficacy and low treatment adherence.
Objectives: To assess feasibility, safety, and efficacy of the Mini-patch, an on-demand transcutaneous perineal electrical stimulator, for the treating of PE.
Methods: Design, Setting, and Participants: Bi-center, international, prospective, randomized, double-blind, two-arm, sham-controlled, clinical study. After screening, intravaginal ejaculatory latency time (IELT) of candidates was measured. Eligibility was based on IELT values and medical/sexual history. Patients were randomized to Active and Sham device groups in a 2:1 ratio. Device safety profile was determined by incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events comparison.
Outcome Measurements and Statistical Analysis: Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGIC) scores, Premature Ejaculation Profile (PEP) questionnaire outcomes, and Mini-patch safety profile. Statistical power was calculated. Primary endpoints assessed device efficacy by mean fold change in geometric mean IELT (Mini-patch vs. sham treatment compared to baseline values). Adjusted mean difference for treatments, adjusted treatment effects (Mini-patch – sham), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and 2-sided P values were obtained.
Results: Of 59 patients randomized, 51 completed the study: 34 in the Active and 17 in the Sham arm. Baseline geometric mean IELT was 67 seconds and significantly increased to 123 seconds (p < 0.0001) in the Active group, compared to 63 seconds increasing insignificantly to 81 seconds (p=0.1653) in the Sham group. The IELT significantly increased by 3.22-fold in the Active as compared to the Sham group (p=0.0047). Overall Geometric Mean Time Fold increases of IELT in the Active compared to the Sham group were 1.7 (95% CI 1.5-2.1) vs. 1.2 (95% CI 1.0-1.6), respectively. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: Mini-patch has the potential to become a leading on-demand, noninvasive, and drug-free treatments for PE.
Source of Funding: Virility Medical Ltd; Hod-hasharon, Israel



.jpg)
.jpg)