Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP01: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology I
MP01-16: Functional and surgical outcomes of Aquablation in elderly men
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 228
Brendan L. Raizenne*, Montréal, Canada, David Bouhadana, Montreal, Canada, Kevin C. Zorn, Montréal, Canada, Bilal Chughtai, New York, NY, Dean Elterman, Toronto, Canada, Naeem Bhojani, Montréal, Canada

Brendan Lapointe Raizenne, MD, BS
University of Montreal
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: As benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an age-related process, growing interest in surgical management for elderly men has emerged. Recently, Aquablation was approved for treatment of BPH associated lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). This novel technology utilizes robotic ultrasound guided and surgeon-controlled waterjet resection to accurately target prostate tissue. We assessed the differences in functional and surgical outcomes between elderly and young men undergoing Aquablation for LUTS/BPH.
Methods: We retrospectively assessed prospectively collected patient data from the pivotal WATER (NCT02505919) and WATER II (NCT03123250) clinical trials reporting safety and efficacy of Aquablation in the treatment of LUTS/BPH in men 45 to 80 years old with a prostate between 30cc and 80cc, and 80cc and 150cc, respectively. Baseline demographics and clinical variables were carefully recorded in an independently monitored database. Men =65 years old were defined as elderly while men <65 years old were defined as young.
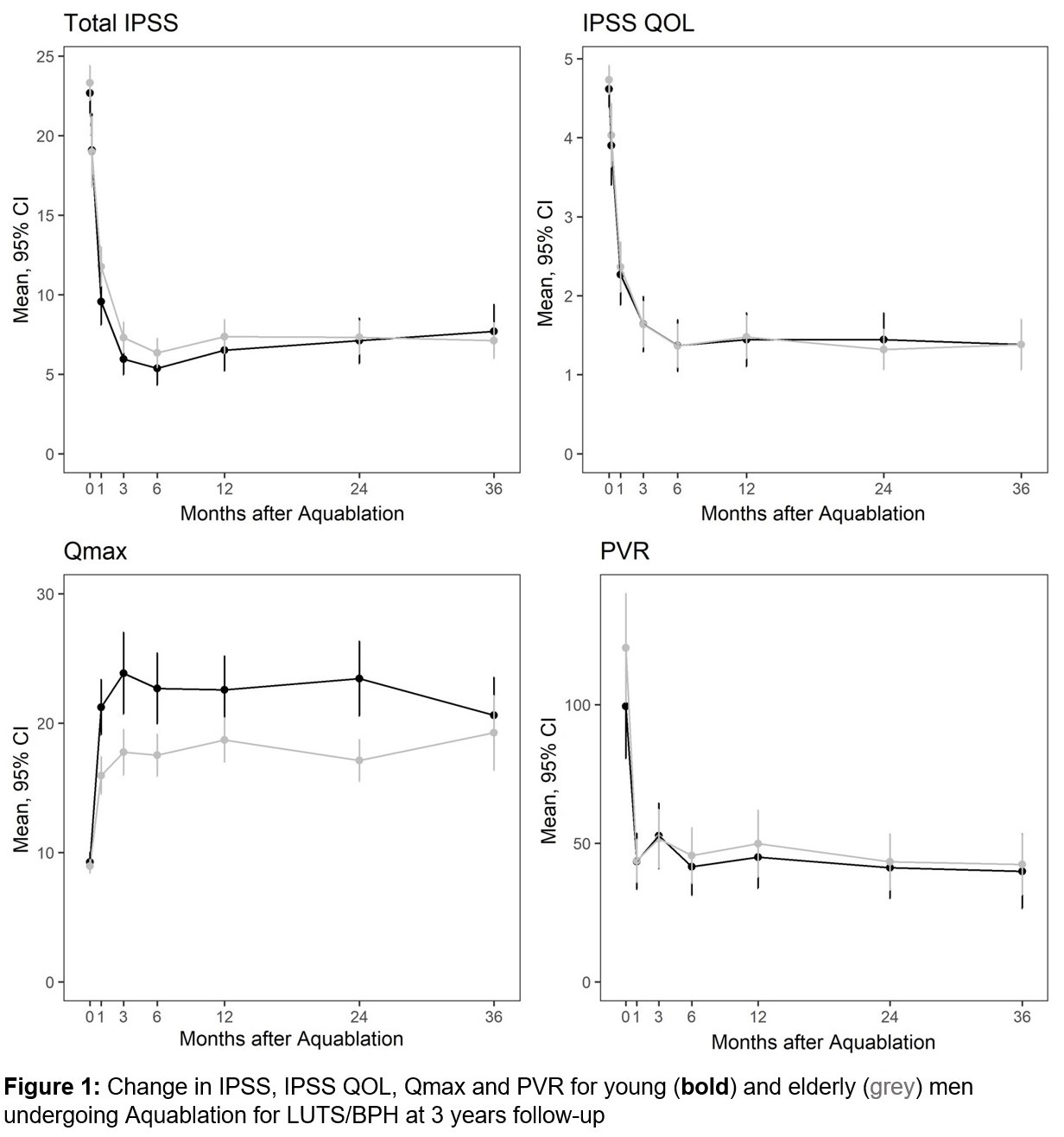
Results: Of 217 men, 83 (38.2%) were young men and 134 (61.8%) were elderly men. Mean age (±SD) was 59.3 (±3.4) years and 71.2 (±4.2) years for young and elderly men, respectively (p < 0.001). At 3 years of follow-up compared to baseline, elderly men showed similar reductions in total IPSS (7.68 points vs 7.12 points, p>0.05), IPSS QOL (1.38 points vs 1.38 points, p>0.05) and PVR (39.9 mL vs 42.3 mL, p>0.05) as well as similar increases in Qmax (20.6 mL/s vs 19.3 mL/s, p>0.05) compared to young men. The ejaculatory dysfunction rate was similar for both cohorts (12.0% vs 9.7%, p>0.05). No patients experienced new onset erectile dysfunction. Elderly men experienced similar annual retreatment rates compared to young men (1.5% vs 0.8%p>0.05).
Conclusions: Elderly men undergoing Aquablation have similar functional and surgical outcomes as young men. Elderly patient BPH surgical counseling should therefore consider Aquablation as a treatment option for LUTS/BPH.
Source of Funding: PROCEPT BioRobotics funded the clinical trials.
On behalf of the WATER I/II investigators
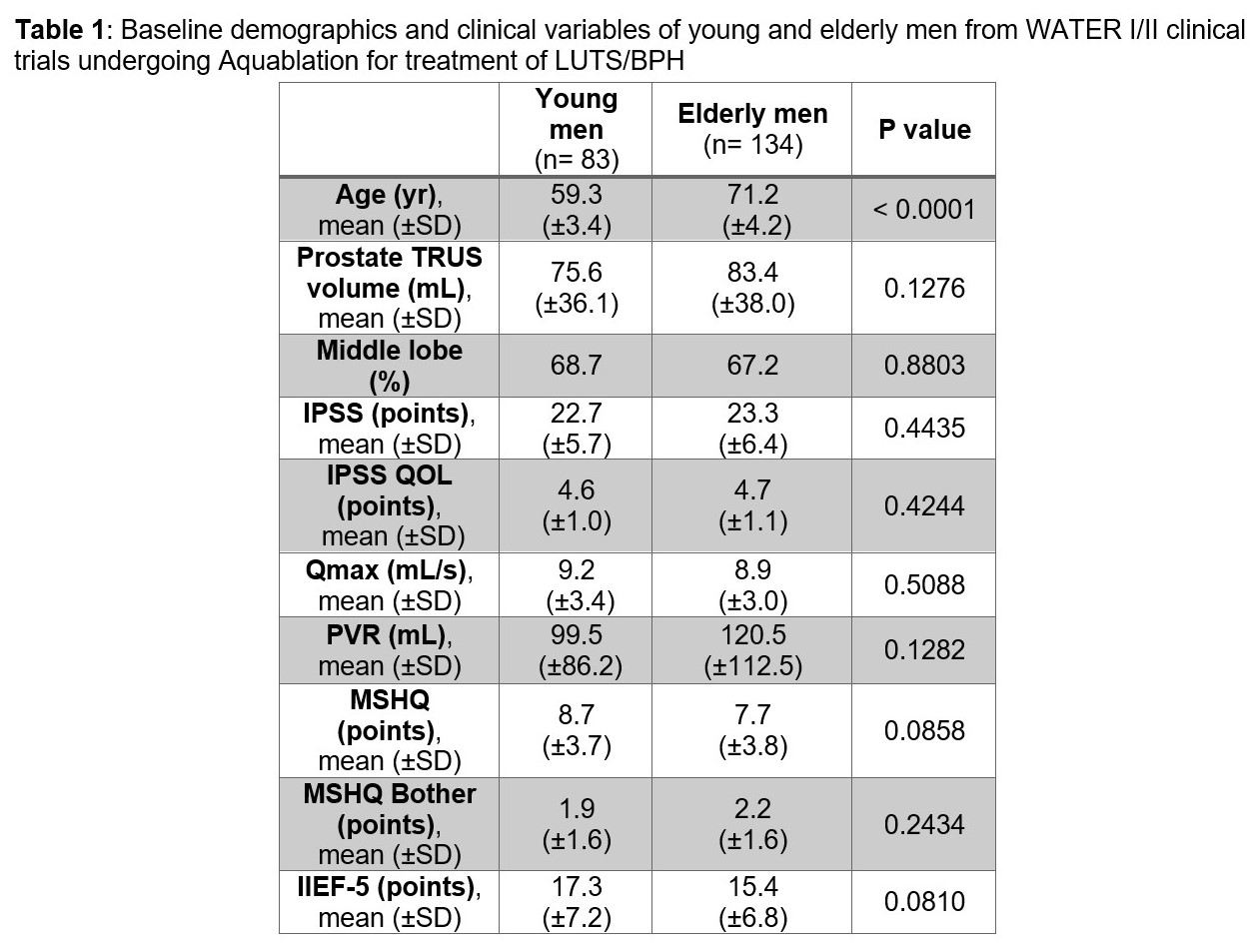
Methods: We retrospectively assessed prospectively collected patient data from the pivotal WATER (NCT02505919) and WATER II (NCT03123250) clinical trials reporting safety and efficacy of Aquablation in the treatment of LUTS/BPH in men 45 to 80 years old with a prostate between 30cc and 80cc, and 80cc and 150cc, respectively. Baseline demographics and clinical variables were carefully recorded in an independently monitored database. Men =65 years old were defined as elderly while men <65 years old were defined as young.
Results: Of 217 men, 83 (38.2%) were young men and 134 (61.8%) were elderly men. Mean age (±SD) was 59.3 (±3.4) years and 71.2 (±4.2) years for young and elderly men, respectively (p < 0.001). At 3 years of follow-up compared to baseline, elderly men showed similar reductions in total IPSS (7.68 points vs 7.12 points, p>0.05), IPSS QOL (1.38 points vs 1.38 points, p>0.05) and PVR (39.9 mL vs 42.3 mL, p>0.05) as well as similar increases in Qmax (20.6 mL/s vs 19.3 mL/s, p>0.05) compared to young men. The ejaculatory dysfunction rate was similar for both cohorts (12.0% vs 9.7%, p>0.05). No patients experienced new onset erectile dysfunction. Elderly men experienced similar annual retreatment rates compared to young men (1.5% vs 0.8%p>0.05).
Conclusions: Elderly men undergoing Aquablation have similar functional and surgical outcomes as young men. Elderly patient BPH surgical counseling should therefore consider Aquablation as a treatment option for LUTS/BPH.
Source of Funding: PROCEPT BioRobotics funded the clinical trials.
On behalf of the WATER I/II investigators



.jpg)
.jpg)