Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP01: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology I
MP01-19: Minimally Invasive and Endoscopic Therapies for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Head-to-Head Comparison of Short-Term Outcomes by Network Meta-Analysis
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 228
Linda Hamed, Jamaal Jackson*, Ephrem Olweny, Chicago, IL

Jamaal C. Jackson, MD
Resident Physician
Rush University Medical Center
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Surgical options for the management of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) for prostates <80 g in size include endoscopic therapies i.e. mono- or bipolar transurethral resection of the prostate (mTURP, bTURP), vaporization or laser enucleation, as well as minimally invasive surgical therapies (MISTs) i.e. transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT), prostatic urethral lift (PUL), water vapor thermotherapy (Rezum) and aquablation. We performed a head-to-head comparison of short-term outcomes for these treatment options by network meta-analysis.
Methods: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials from 1998 to 2018 in men with prostates < 100 g, moderate-severe LUTS (International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) = 8) and maximum urinary flow rates (Qmax) < 15mL/s, treated using any of the above modalities and reporting outcomes at a minimum follow up of 1 year was performed, including trials with a sham arm. Multivariable random effects network meta-analysis was used to compare the treatments with respect to IPSS, quality of life (QOL), Qmax and international index of erectile function (IIEF) scores at 1 year. For each outcome, treatments were ranked from best to worst using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) method. Referent treatment was mTURP.
Results: A total of 26 studies met inclusion criteria. 1-year IPSS and QOL scores for each treatment modality were statistically similar to those for mTURP. Qmax for PUL, Rezum and TUNA were statistically lower than for mTURP, while flow rates for all other modalities were similar. 1-year IIEF scores were not available for aquablation, TUMT or TUNA, but scores for vaporization PUL and Rezum were notably higher than for mTURP, while those for enucleation and bTURP were similar. By SUCRA, the treatment with the highest probability of best urinary function was enucleation, while Rezum had the highest probability of sexual function.
Conclusions: Compared with mTURP, Rezum and PUL achieved inferior flow rates but better IIEF scores, while vaporization achieved similar flow rates and higher IIEF scores. These findings could be invaluable in counseling patients on surgical outcomes for BPH.
Source of Funding: None.
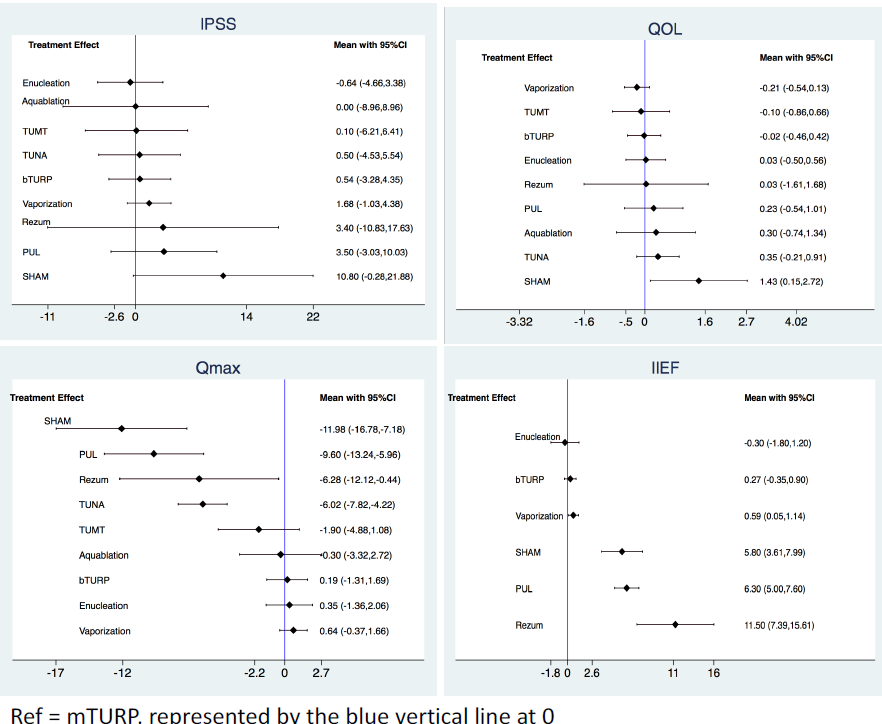
Methods: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials from 1998 to 2018 in men with prostates < 100 g, moderate-severe LUTS (International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) = 8) and maximum urinary flow rates (Qmax) < 15mL/s, treated using any of the above modalities and reporting outcomes at a minimum follow up of 1 year was performed, including trials with a sham arm. Multivariable random effects network meta-analysis was used to compare the treatments with respect to IPSS, quality of life (QOL), Qmax and international index of erectile function (IIEF) scores at 1 year. For each outcome, treatments were ranked from best to worst using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) method. Referent treatment was mTURP.
Results: A total of 26 studies met inclusion criteria. 1-year IPSS and QOL scores for each treatment modality were statistically similar to those for mTURP. Qmax for PUL, Rezum and TUNA were statistically lower than for mTURP, while flow rates for all other modalities were similar. 1-year IIEF scores were not available for aquablation, TUMT or TUNA, but scores for vaporization PUL and Rezum were notably higher than for mTURP, while those for enucleation and bTURP were similar. By SUCRA, the treatment with the highest probability of best urinary function was enucleation, while Rezum had the highest probability of sexual function.
Conclusions: Compared with mTURP, Rezum and PUL achieved inferior flow rates but better IIEF scores, while vaporization achieved similar flow rates and higher IIEF scores. These findings could be invaluable in counseling patients on surgical outcomes for BPH.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)