Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP02: Infections/Inflammation/Cystic Disease of the Genitourinary Tract: Kidney & Bladder I
MP02-12: Pro and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines are Differentially Abundant during Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Postmenopausal Women
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 225
Jessica Komarovsky*, Tahmineh Ebrahimzadeh, Richardson, TX, Philippe Zimmern, Dallas, TX, Nicole De Nisco, Richardson, TX
- JK
Jessica Komarovsky
University of Texas at Dallas
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is among the most common bacterial infections in adult women. In postmenopausal women, UTI often develops into recurrent UTI (rUTI), defined as =3 symptomatic UTIs in 12 months or =2 UTIs in 6 months1,2. Because of the decreasing efficacy of available antibiotics, new therapies for rUTI must be developed. Research in mouse models suggests that host inflammation plays an important role in rUTI 3. The only inflammatory biomarker currently used for UTI diagnosis is leukocyte esterase, which has a high false-positive rate. The goal of this study is to identify urinary cytokines associated with rUTI and define their utility as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers in postmenopausal women.
Methods: After IRB approval, a cross-sectional cohort of postmenopausal women passing exclusion criteria were stratified into two groups based on rUTI status: Never (no UTI history, n=23) and Relapse (rUTI history, current symptomatic rUTI, n=23). Clean catch urine was collected and immediately stored in liquid nitrogen. Urinary concentrations of 20 cytokines were measured (Total n=46) using the LEGENDplex™ Human Inflammation Panel 1 and HU Th Cytokine Panels (BioLegend). Data was acquired using the BD Fortessa flow cytometer.
Results: Normalized and raw values of urinary cytokines IL-1ß, IL-8, IL-18, MCP-1, and IL-13 were significantly different between the two groups. We found urinary levels of IL-1ß, IL-8, IL-18, and MCP-1 to be elevated in the Relapse group, while IL-13 was higher in the Never group. Also, normalized value of IL-4, which functions similarly to IL-13, was higher in the Never group.
Conclusions: Our results indicate elevation of inflammatory cytokines IL-8 and MCP-1, which are responsible for neutrophil recruitment and monocyte recruitment and IL-1ß and IL-18, which are produced following inflammasome formation in women with active rUTI. On the other hand, anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, which are involved in the inhibition of IL-1ß, IL-6, and IL-8, were higher in women with no UTI history. Future work will evaluate the cytokines identified by this analysis as rUTI diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers.
Source of Funding: Nicole De Nisco, PhD: UT Dallas Startup funds, UT System Rising STARs Award; Philippe Zimmern, MD: Felicia and John Cain Chair in Women Health
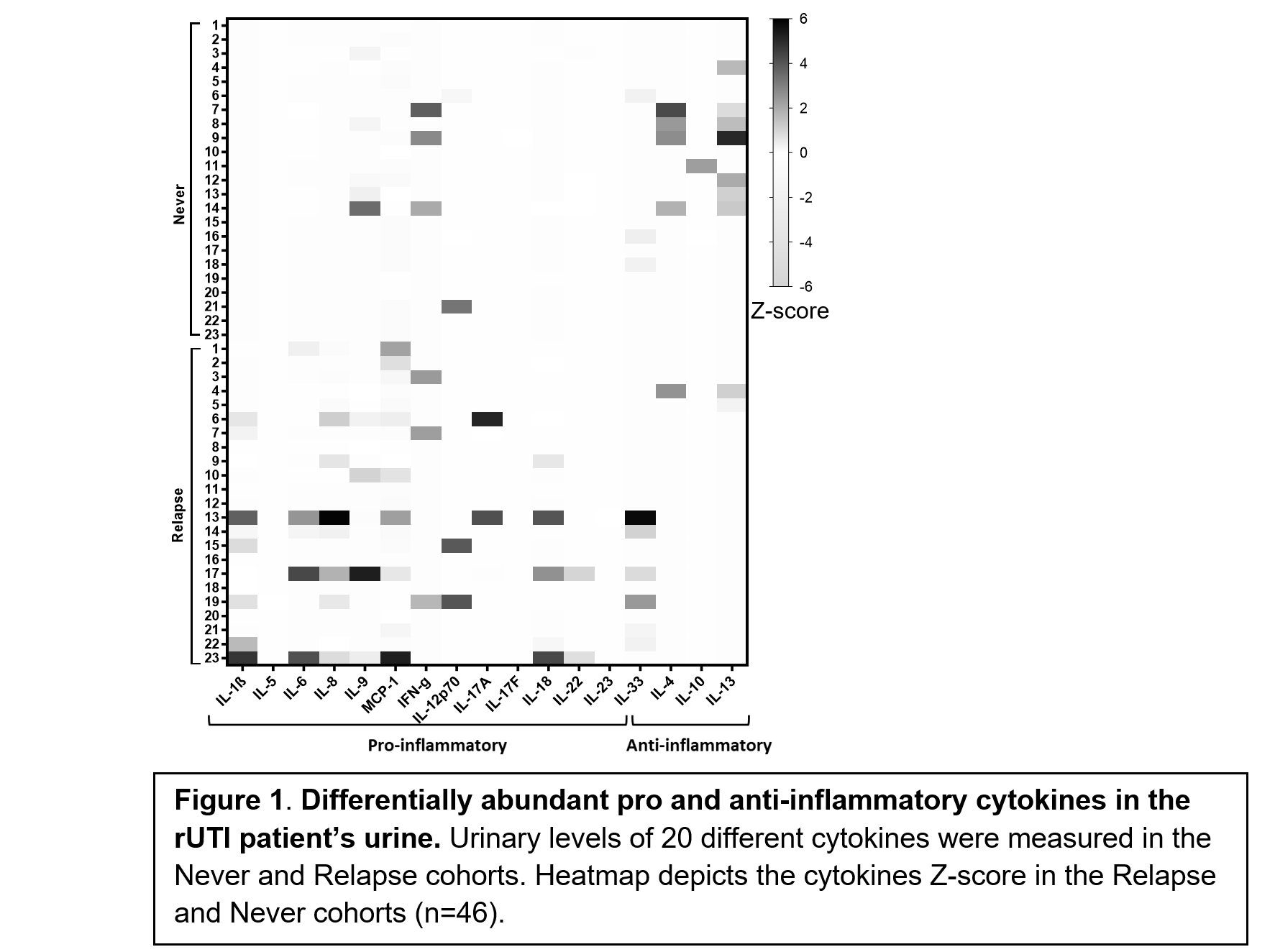
Methods: After IRB approval, a cross-sectional cohort of postmenopausal women passing exclusion criteria were stratified into two groups based on rUTI status: Never (no UTI history, n=23) and Relapse (rUTI history, current symptomatic rUTI, n=23). Clean catch urine was collected and immediately stored in liquid nitrogen. Urinary concentrations of 20 cytokines were measured (Total n=46) using the LEGENDplex™ Human Inflammation Panel 1 and HU Th Cytokine Panels (BioLegend). Data was acquired using the BD Fortessa flow cytometer.
Results: Normalized and raw values of urinary cytokines IL-1ß, IL-8, IL-18, MCP-1, and IL-13 were significantly different between the two groups. We found urinary levels of IL-1ß, IL-8, IL-18, and MCP-1 to be elevated in the Relapse group, while IL-13 was higher in the Never group. Also, normalized value of IL-4, which functions similarly to IL-13, was higher in the Never group.
Conclusions: Our results indicate elevation of inflammatory cytokines IL-8 and MCP-1, which are responsible for neutrophil recruitment and monocyte recruitment and IL-1ß and IL-18, which are produced following inflammasome formation in women with active rUTI. On the other hand, anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, which are involved in the inhibition of IL-1ß, IL-6, and IL-8, were higher in women with no UTI history. Future work will evaluate the cytokines identified by this analysis as rUTI diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers.
Source of Funding: Nicole De Nisco, PhD: UT Dallas Startup funds, UT System Rising STARs Award; Philippe Zimmern, MD: Felicia and John Cain Chair in Women Health


.jpg)
.jpg)