Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP03: Bladder Cancer: Invasive I
MP03-07: Impact of prior intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer on the efficacy of pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 222
Rikiya Taoka*, Kagawa, Japan, Takashi Kobayashi, Yu Hidaka, Hiroyasu Abe, Satoshi Morita, Osamu Ogawa, Kyoto, Japan, Hiroyuki Nishiyama, Tsukuba, Japan, Hiroshi Kitamura, toyama, Japan, Mikio Sugimoto, Kagawa, Japan

Rikiya Taoka, MD, PHD
Kagawa University
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: This study aimed to determine whether prior intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) affects the treatment outcomes of pembrolizumab in patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC).
Methods: In a multicenter retrospective study conducted under the Japan Urological Oncology Group framework, the clinicopathological data of 755 patients with metastatic, chemo-resistant UC who received pembrolizumab were retrospectively reviewed. The best overall response and overall survival (OS) from the initiation of pembrolizumab were analyzed concerning the BCG usage using propensity score matching (PSM). The propensity score was estimated using a logistic regression model with four covariates, namely, PS, metastatic site, pretreatment Hb level, and NLR. (Kobayashi T, et al. Cancer Sci. 2021)
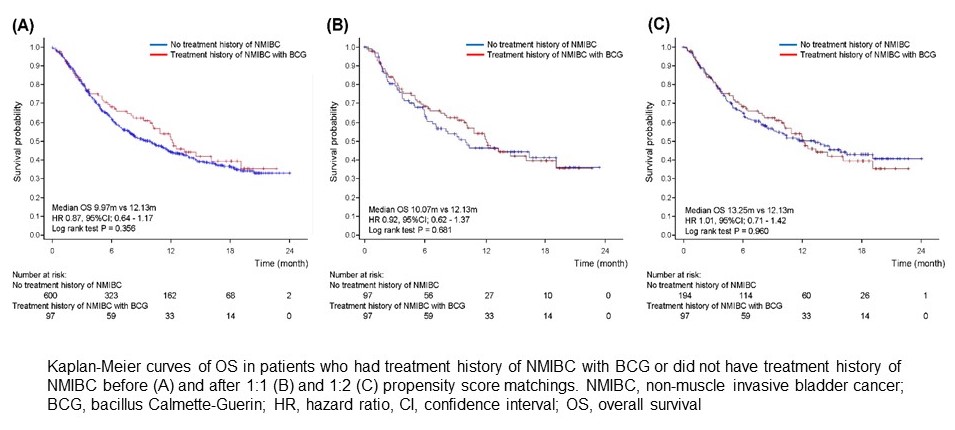
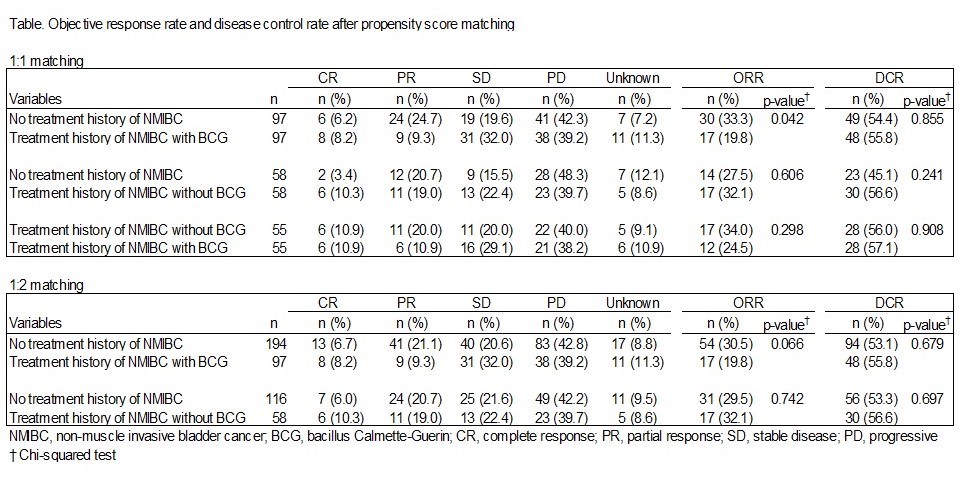
Results: A total of 155 (20.5%) patients had a history of NMIBC treatment, of which 97 (12.8%) had received intravesical BCG therapy. When compared to patients without a NMIBC history (median 9.97 months), the OS in patients with a NMIBC history but not BCG (14.49 months, HR 0.68 [0.45–1.12], P = 0.061) or those with a NMIBC history and BCG (12.13 months, HR 0.87 [0.64–1.17], P = 0.356) were not significantly different. This tendency was robust after 1:1 or 1:2 PSMs. The objective response rate (ORR, 32.1% vs. 27.5%, P = 0.606) and disease control rate (DCR, 56.6% vs. 45.1%, P = 0.241) of the 58 patients with a NMIBC history but not BCG did not differ from those of 58 matched patients without a NMIBC history. The ORR in BCG-treated patients was significantly lower than that in those without a NMIBC history (19.8% vs. 33.3%, P = 0.042), whereas DCR between the two groups did not differ significantly (55.8% vs. 54.4%, P = 0.855).
Conclusions: Our risk-adjusted analyses revealed that intravesical BCG therapy did not affect the treatment outcomes of pembrolizumab in metastatic UC patients.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: In a multicenter retrospective study conducted under the Japan Urological Oncology Group framework, the clinicopathological data of 755 patients with metastatic, chemo-resistant UC who received pembrolizumab were retrospectively reviewed. The best overall response and overall survival (OS) from the initiation of pembrolizumab were analyzed concerning the BCG usage using propensity score matching (PSM). The propensity score was estimated using a logistic regression model with four covariates, namely, PS, metastatic site, pretreatment Hb level, and NLR. (Kobayashi T, et al. Cancer Sci. 2021)
Results: A total of 155 (20.5%) patients had a history of NMIBC treatment, of which 97 (12.8%) had received intravesical BCG therapy. When compared to patients without a NMIBC history (median 9.97 months), the OS in patients with a NMIBC history but not BCG (14.49 months, HR 0.68 [0.45–1.12], P = 0.061) or those with a NMIBC history and BCG (12.13 months, HR 0.87 [0.64–1.17], P = 0.356) were not significantly different. This tendency was robust after 1:1 or 1:2 PSMs. The objective response rate (ORR, 32.1% vs. 27.5%, P = 0.606) and disease control rate (DCR, 56.6% vs. 45.1%, P = 0.241) of the 58 patients with a NMIBC history but not BCG did not differ from those of 58 matched patients without a NMIBC history. The ORR in BCG-treated patients was significantly lower than that in those without a NMIBC history (19.8% vs. 33.3%, P = 0.042), whereas DCR between the two groups did not differ significantly (55.8% vs. 54.4%, P = 0.855).
Conclusions: Our risk-adjusted analyses revealed that intravesical BCG therapy did not affect the treatment outcomes of pembrolizumab in metastatic UC patients.
Source of Funding: none



.jpg)
.jpg)