Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
MP04: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Therapy & New Technology II
MP04-03: Can Handheld Point of Care Ultrasound Probes Reliably Measure Transabdominal Prostate Volume? A Prospective Randomized Study
Friday, May 13, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 228
Henry Wright*, Chicago, IL, Hermen Brar, Fabrice Henry, Dillon Corrigan, Smita De, Cleveland, OH

Henry Collier Wright, MD
Northwestern Medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Prostate gland volume (PGV) helps guide management for prostatic disease. The American Urological Association (AUA) benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) guidelines recommend PGV assessment prior to BPH surgery via one of the following: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), trans rectal or trans abdominal ultrasound (TRUS/TAUS), or computed tomography (CT). Handheld ultrasound (HUS) probes show promise as point of care ultrasound (POCUS) for PGV, yet evidence is limited. Our objective was to independently evaluate the accuracy of two HUS probes (Butterfly IQ, Clarius C3) in measuring trans abdominal PGV compared to guideline imaging (MRI, TRUS, TAUS, or CT).
Methods: In this prospective clinical study, enrolled subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to undergo HUS PGV measurement with either the Clarius or Butterfly probe. Demographics, urologic history, and PGV data were collected. Reliability was quantified by estimating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) between the HUS and guideline imaging and its 95% confidence interval (R version 4.1.0). We used the following standard criteria: ICC < 0.5: poor reliability; 0.5 = ICC < 0.75: moderate reliability; ICC = 0.75: good reliability.
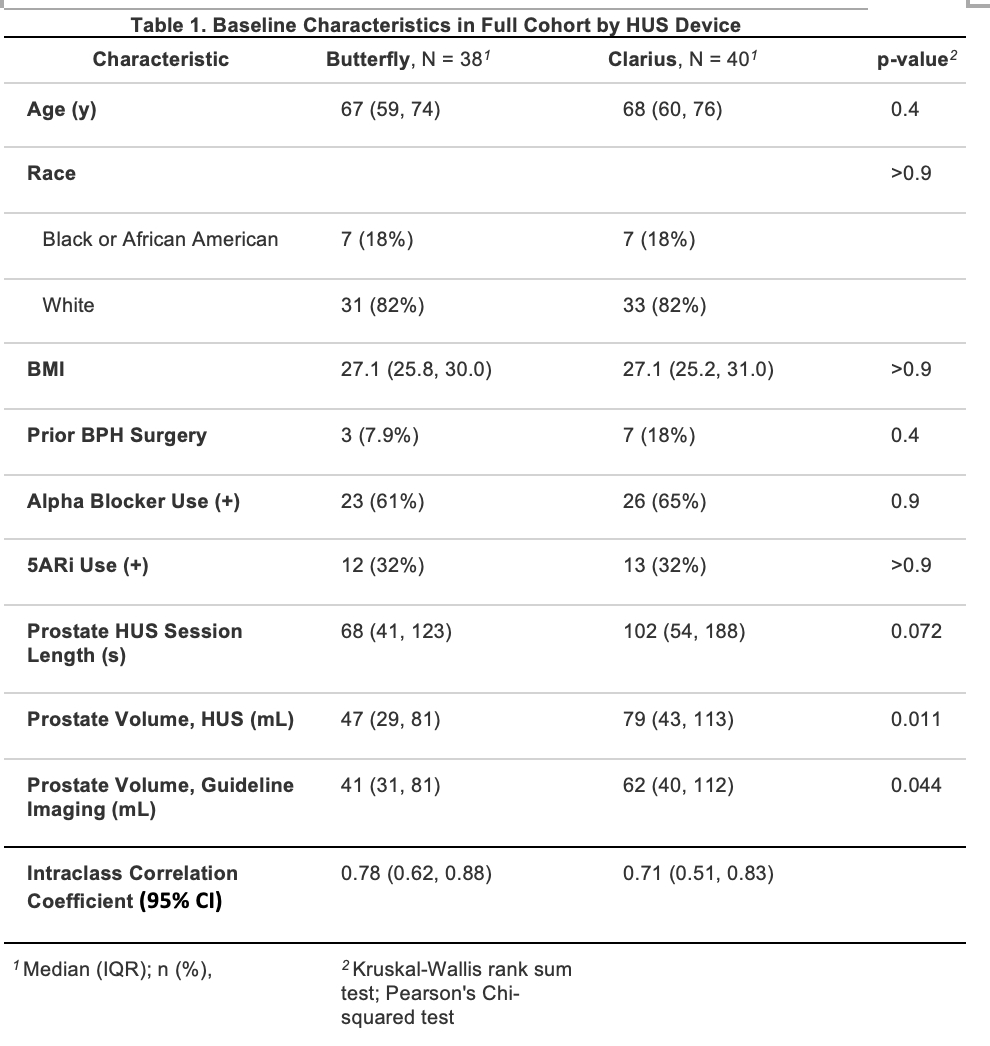
Results: 78 men were randomized (38 Butterfly, 40 Clarius). Baseline characteristics similar between groups (p>0.05). The mean PGV based on HUS and gold standard imaging was higher in the Clarius group compared to Butterfly (p=0.011 and 0.044, respectively). The ICCs were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.62, 0.88) and 0.71 (95% CI: 0.51, 0.83) for the Butterfly and Clarius probes, respectively (Table 1), indicating that the Butterfly IQ produced good reliability between HUS and reference measurements, and the Clarius C3 produced moderate reliability between HUS and reference measurements.
Conclusions: When compared to guideline imaging, the Butterfly IQ demonstrated good reliability for PGV, in comparison to moderate reliability for the Clarius C3. Further studies evaluating these probes as POCUS for urologic diseases are warranted.
Source of Funding: Cleveland Clinic Research Programs Committee Grant
Methods: In this prospective clinical study, enrolled subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to undergo HUS PGV measurement with either the Clarius or Butterfly probe. Demographics, urologic history, and PGV data were collected. Reliability was quantified by estimating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) between the HUS and guideline imaging and its 95% confidence interval (R version 4.1.0). We used the following standard criteria: ICC < 0.5: poor reliability; 0.5 = ICC < 0.75: moderate reliability; ICC = 0.75: good reliability.
Results: 78 men were randomized (38 Butterfly, 40 Clarius). Baseline characteristics similar between groups (p>0.05). The mean PGV based on HUS and gold standard imaging was higher in the Clarius group compared to Butterfly (p=0.011 and 0.044, respectively). The ICCs were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.62, 0.88) and 0.71 (95% CI: 0.51, 0.83) for the Butterfly and Clarius probes, respectively (Table 1), indicating that the Butterfly IQ produced good reliability between HUS and reference measurements, and the Clarius C3 produced moderate reliability between HUS and reference measurements.
Conclusions: When compared to guideline imaging, the Butterfly IQ demonstrated good reliability for PGV, in comparison to moderate reliability for the Clarius C3. Further studies evaluating these probes as POCUS for urologic diseases are warranted.
Source of Funding: Cleveland Clinic Research Programs Committee Grant


.jpg)
.jpg)