Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP05: Stone Disease: Basic Research & Pathophysiology
MP05-04: Discovery of drugs that promote the phagocytic ability of macrophages to calcium oxalate crystals using the FDA-approved Drug Library
Friday, May 13, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Atsushi Okada*, Hiroshi Takase, Masahiko Isogai, Tomoki Okada, Tatsuya Hattori, Ryosuke Chaya, Kengo Kawase, Yutaro Tanaka, Taiki Kato, Teruaki Sugino, Rei Unno, Kazumi Taguchi, Shuzo Hamamoto, Ryosuke Ando, Tadahiro Hashita, Keiichi Tozawa, Tamihide Matsunaga, Kenjiro Kohri, Takahiro Yasui, Nagoya, Japan

Atsushi Okada, MD,PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Nephro-urology, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: We have reported that calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal phagocytosis by anti-inflammatory macrophages is an important protective factor for urinary stones, suggesting that the factor may be less functional in patients with urinary stones. In order to search for new drugs that apply this mechanism, a crystal phagocytosis test was conducted using an FDA-approved drug library.
Methods: Of the 2,923 FDA-approved Drug Libraries, 823 drugs extracted with the keywords "Kidney stone," "Urinary stone," "Urolithiasis," and "Macrophage" were selected by PubMed search. Cultured macrophages RAW267.4 were stained with CellTracker ™ Orange CMRA Dye, adjusted to 1x104 cells / 100 µl, and the cells were dispensed 100 µl into 96-well plates. Each well was administered with 10 uM of each drug, and 15 µg / cm2 of fluorescent calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) crystals stained with Alexa Fluor 488 was added. The cell area and f-COM crystal area were measured with the IncuCyte® high-throughput live cell analysis system, and total COM remaining amount (CRA) was calculated. All drugs were tested 3-5 times under the same conditions and CRA was measured. Using DMSO as a solvent as a control, the average value of CRA at 24 hours was compared by Welch's t-test.
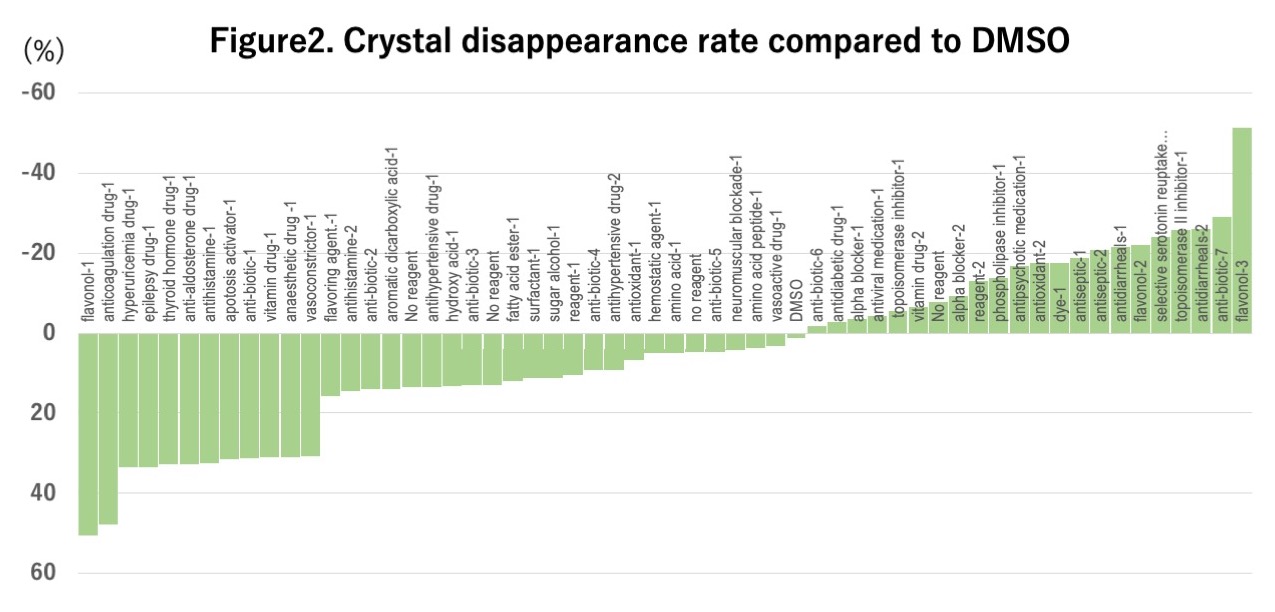
Results: Live imaging with IncuCyte confirmed the image of macrophages phagocytosing COM crystals while extending dendrites over time. Of the 823 compounds, 213 and 58 drugs showed a significant difference of p <0.05 and p <0.01, respectively. Of the 58 rugs, 36 enhanced crystal phagocytosis and 22 suppressed phagocytosis. One of the flavonols reduced CRA most, and the difference in mean CRA compared to DMSO was 50.6% (p <0.0001).
Conclusions: We have identified FDA-approved drugs that significantly alter the phagocytosis of COM crystals. The therapeutic effect will be verified in animal model research and clinical research in the future.
Source of Funding: Japanese Urological Association
Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
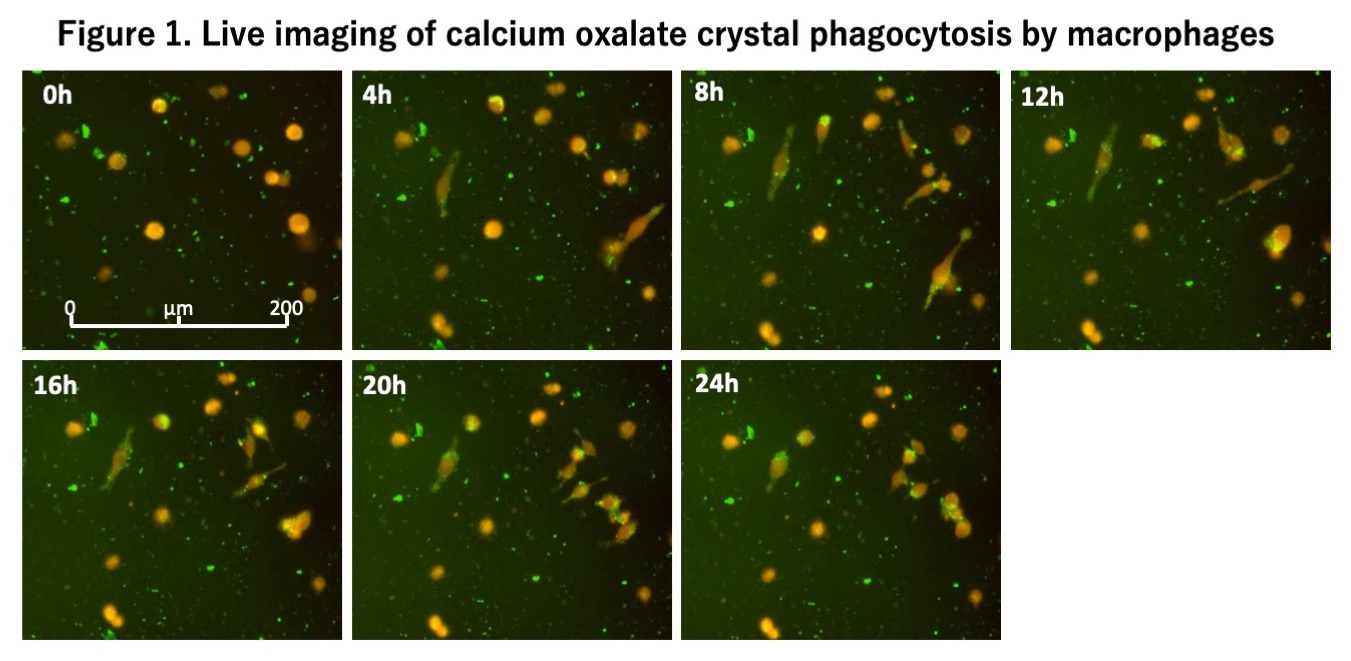
Methods: Of the 2,923 FDA-approved Drug Libraries, 823 drugs extracted with the keywords "Kidney stone," "Urinary stone," "Urolithiasis," and "Macrophage" were selected by PubMed search. Cultured macrophages RAW267.4 were stained with CellTracker ™ Orange CMRA Dye, adjusted to 1x104 cells / 100 µl, and the cells were dispensed 100 µl into 96-well plates. Each well was administered with 10 uM of each drug, and 15 µg / cm2 of fluorescent calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) crystals stained with Alexa Fluor 488 was added. The cell area and f-COM crystal area were measured with the IncuCyte® high-throughput live cell analysis system, and total COM remaining amount (CRA) was calculated. All drugs were tested 3-5 times under the same conditions and CRA was measured. Using DMSO as a solvent as a control, the average value of CRA at 24 hours was compared by Welch's t-test.
Results: Live imaging with IncuCyte confirmed the image of macrophages phagocytosing COM crystals while extending dendrites over time. Of the 823 compounds, 213 and 58 drugs showed a significant difference of p <0.05 and p <0.01, respectively. Of the 58 rugs, 36 enhanced crystal phagocytosis and 22 suppressed phagocytosis. One of the flavonols reduced CRA most, and the difference in mean CRA compared to DMSO was 50.6% (p <0.0001).
Conclusions: We have identified FDA-approved drugs that significantly alter the phagocytosis of COM crystals. The therapeutic effect will be verified in animal model research and clinical research in the future.
Source of Funding: Japanese Urological Association
Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research



.jpg)
.jpg)