Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP06: Bladder Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology I
MP06-17: Alpha-2-macroglobulin in urinary extracellular vesicles is a novel protein marker for diagnosis of human bladder cancer
Friday, May 13, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 222
Jinsung Park*, Uijeongbu-si, Korea, Republic of, Jisu Lee, Yun Hee Kang, Daejeon, Korea, Republic of, Ji Young Mun, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, Hyun-Woo Oh, Daejeon, Korea, Republic of, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, Ulsan, Korea, Republic of, Myung-Shin Lee, Daejeon, Korea, Republic of

Jinsung Park, MD,PhD
Professor
Uijeongbu Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University.
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs) are considered potential biomarkers for bladder cancer (BC). However, challenges associated with the effective isolation and analyses of uEVs complicate the clinical detection of uEV-associated protein biomarkers. Herein, we sought to identify novel uEV-derived diagnostic biomarkers for BC.
Methods: Urine samples were obtained between July 2018 and October 2020. 1) To identify optimal uEV isolation methods, three different methods (differential centrifugation, ExoLutE®, ExoDisc) were compared by various methods. 2) Through comparative analysis of uEVs obtained from BC patients pre- and post-operation using an antibody array, candidate uEV biomarkers were selected. 3) Furthermore, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of uEVs isolated from 83 patients (23 control subjects and 60 BC patients) validated the clinical significance of the uEV biomarkers.
Results: We found that ExoDisc, a centrifugal microfluidic tangential flow filtration device, was a significantly more effective separation method than other methods (Fig 1). In the analysis of pre-and post-operative uEVs from BC patients by the ExoDisc, three proteins, namely cadherin-13, clusterin, and alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M), were identified as potential uEV biomarkers, while A2M exhibited the most significant difference. In the validation study, the A2M expression in uEVs from BC patients was significantly higher than the control group (Fig 2A) with good diagnostic performance (Fig 2B). The uEV A2M expression in the high-grade BC was significantly higher than that in low-grade BC (Fig 2C), whereas no significant difference were detected in the whole urine samples (Fig 2D). The uEV A2M expression with a cut-off of 0.035 (highest Youden index) robustly discriminated BC patients from controls, with a sensitivity of 93.3%, a specificity of 34.8%.
Conclusions: We demonstrated the potential of A2M as a novel uEV biomarker for BC diagnosis through an optimized EV isolation and analysis workflow.
Source of Funding: This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2019R1I1A3A01060913) to Dr. Jinsung Park.
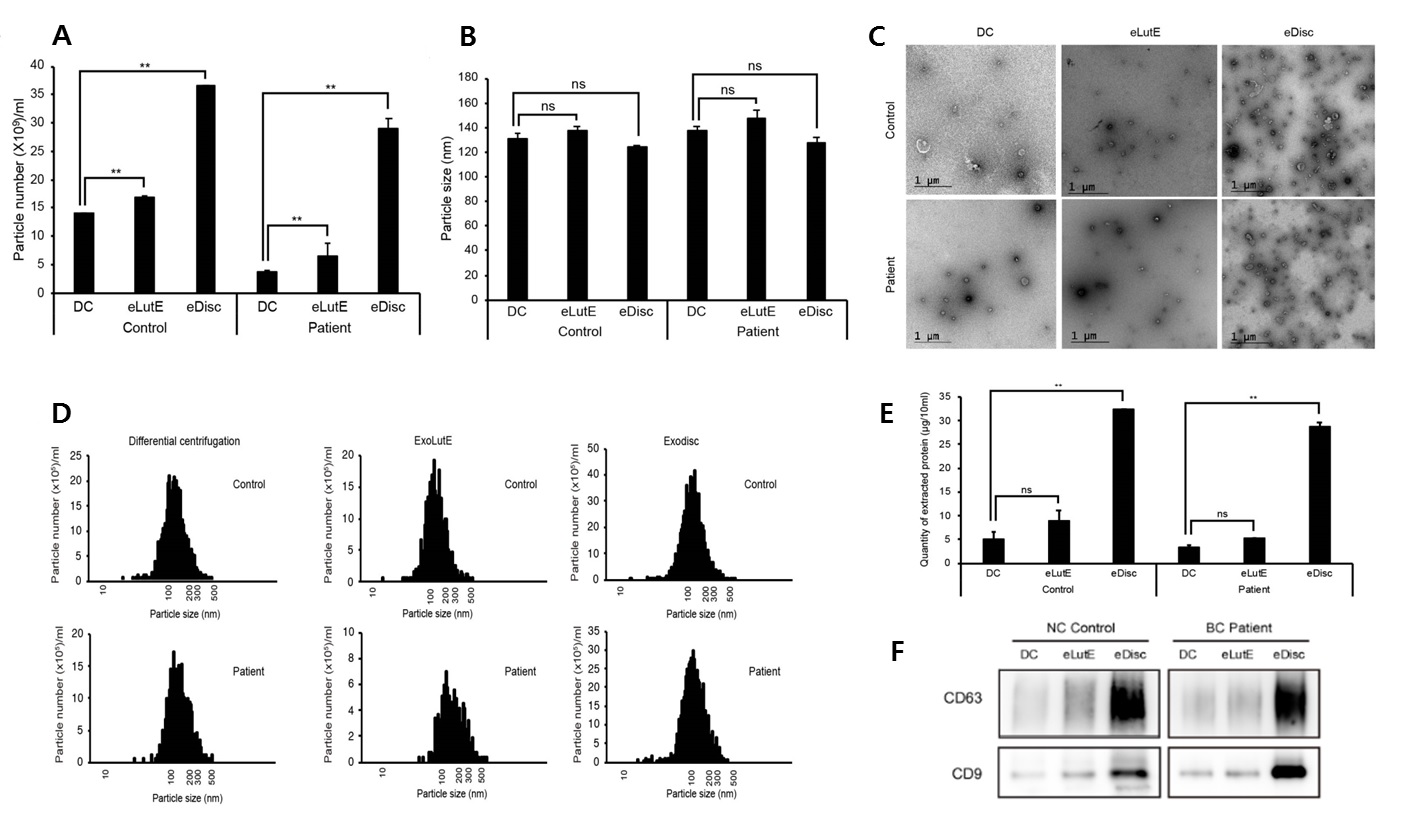
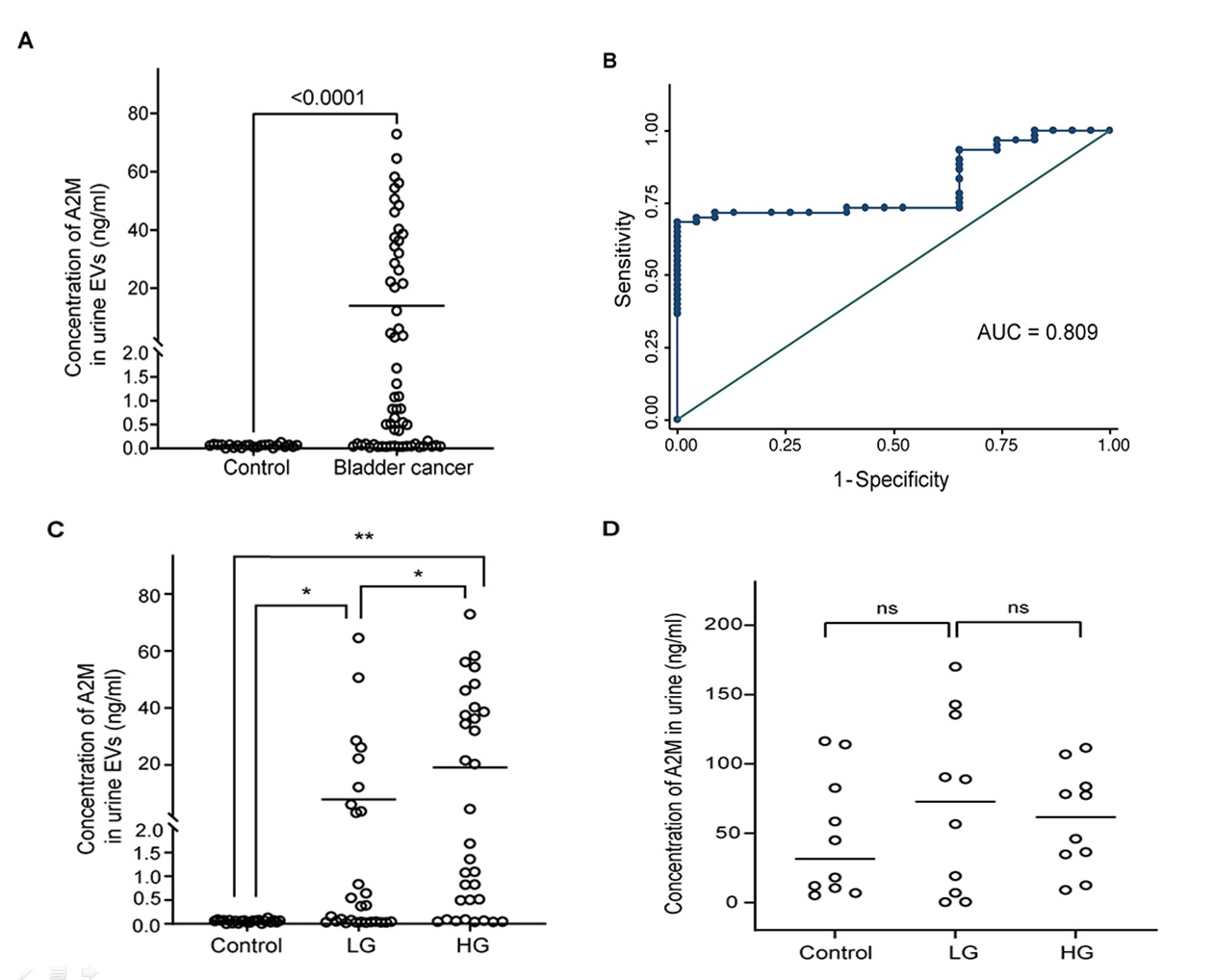
Methods: Urine samples were obtained between July 2018 and October 2020. 1) To identify optimal uEV isolation methods, three different methods (differential centrifugation, ExoLutE®, ExoDisc) were compared by various methods. 2) Through comparative analysis of uEVs obtained from BC patients pre- and post-operation using an antibody array, candidate uEV biomarkers were selected. 3) Furthermore, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of uEVs isolated from 83 patients (23 control subjects and 60 BC patients) validated the clinical significance of the uEV biomarkers.
Results: We found that ExoDisc, a centrifugal microfluidic tangential flow filtration device, was a significantly more effective separation method than other methods (Fig 1). In the analysis of pre-and post-operative uEVs from BC patients by the ExoDisc, three proteins, namely cadherin-13, clusterin, and alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M), were identified as potential uEV biomarkers, while A2M exhibited the most significant difference. In the validation study, the A2M expression in uEVs from BC patients was significantly higher than the control group (Fig 2A) with good diagnostic performance (Fig 2B). The uEV A2M expression in the high-grade BC was significantly higher than that in low-grade BC (Fig 2C), whereas no significant difference were detected in the whole urine samples (Fig 2D). The uEV A2M expression with a cut-off of 0.035 (highest Youden index) robustly discriminated BC patients from controls, with a sensitivity of 93.3%, a specificity of 34.8%.
Conclusions: We demonstrated the potential of A2M as a novel uEV biomarker for BC diagnosis through an optimized EV isolation and analysis workflow.
Source of Funding: This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2019R1I1A3A01060913) to Dr. Jinsung Park.



.jpg)
.jpg)