Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP09: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening I
MP09-06: Prostate Cancer Detection and Complications of Transperineal versus Transrectal MRI-fusion Guided Prostate Biopsies
Friday, May 13, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 222
Dylan Buller*, Jessa Sahl, Ilene Staff, Joseph Tortora, Kevin Pinto, Tara McLaughlin, Laura OlivoValintin, Joseph Wagner, Hartford, CT

Dylan Buller, MD
Urology resident
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Detection rates of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in transperineal (TP) and transrectal (TR) MRI-fusion targeted prostate biopsies (MRI-bx) remains in question. We compared TP and TR approaches on rates of detection of csPCa and complications when performing MRI-bx.
Methods: We retrospectively identified men ages 18-89 who underwent TP or TR MRI-bx with concurrent systematic random biopsy from August, 2020 to August, 2021. Patients undergoing systematic-only TR biopsies were also included. Analyses primarily focused on cancer detection rates between the two MRI-bx groups; comparisons were also made to the standard random biopsy group. Data were additionally stratified by prior biopsy status. Grade Group =2 was considered csPCa. Complications within 30 days of biopsy were also compared.
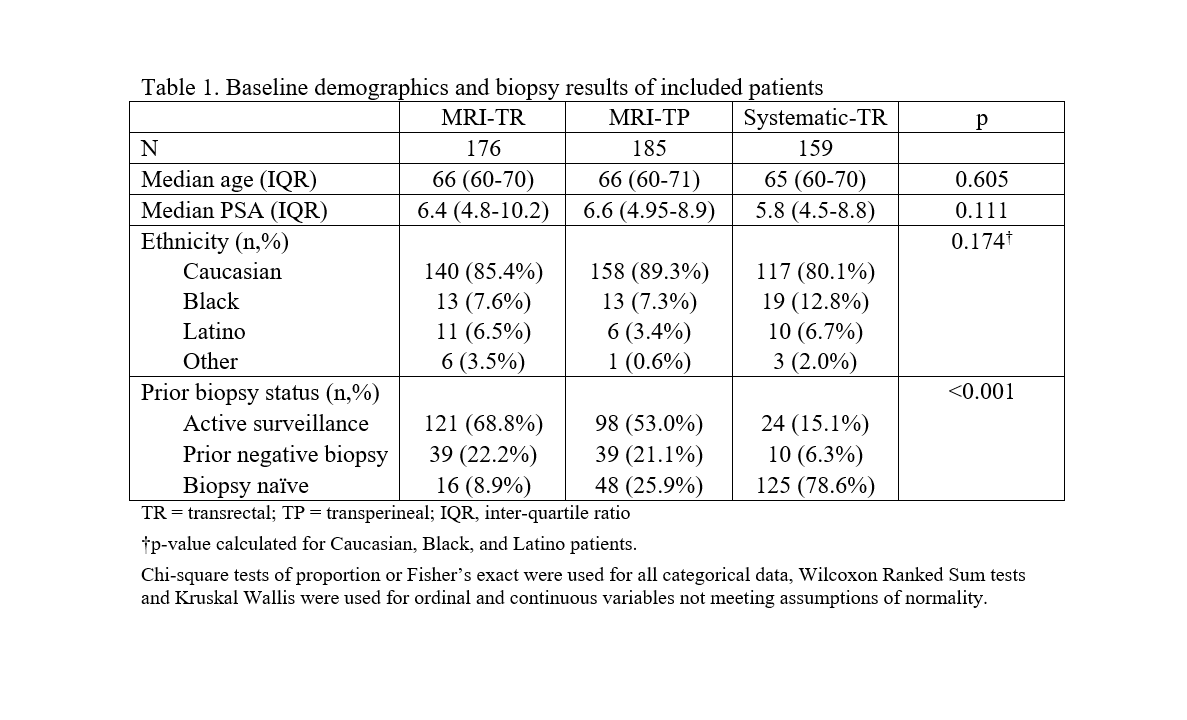
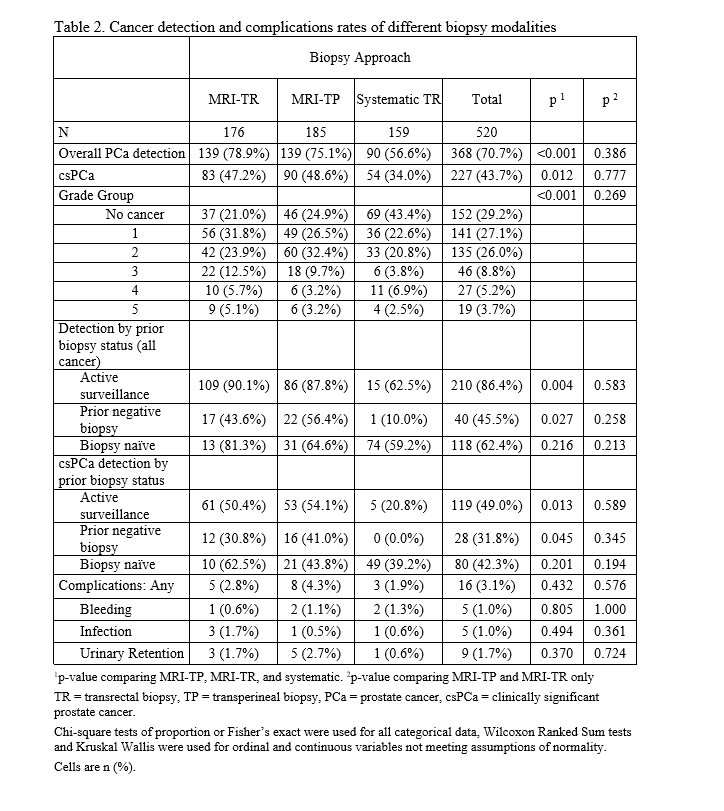
Results: 520 patients were included in the analysis. No demographic differences were observed (Table 1). When analyzing only MRI-bx approaches, no significant differences were observed between TP and TR on any of the outcomes of interest (Table 2). TR MRI-bx identified csPCA in 47.2% of patients, and TP MRI-bx identified csPCA in 48.6% of patients (p = 0.777); systematic-only TR biopsies identified csPCA in 34.0% of patients. 50.4% of TR MRI-bx and 54.1% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in patients on active surveillance (AS) (p = 0.589). 30.8% of TR MRI-bx and 41.0% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in patients with a prior negative biopsy (p = 0.345). 62.5% of TR MRI-bx and 43.8% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in biopsy-naïve patients (p = 0.194). Significant differences were observed in csPCa detection between all three approaches for AS (p = 0.013) and prior negative biopsy patients (p = 0.045), but not between MRI-TP and MRI-TR biopsies.
Conclusions: Neither the identification of csPCa by MRI-bx nor rates of complications differed significantly based on a TR or TP approach. No differences were seen between MRI-guided approaches based on prior biopsy/AS status.
Source of Funding: Unfunded
Methods: We retrospectively identified men ages 18-89 who underwent TP or TR MRI-bx with concurrent systematic random biopsy from August, 2020 to August, 2021. Patients undergoing systematic-only TR biopsies were also included. Analyses primarily focused on cancer detection rates between the two MRI-bx groups; comparisons were also made to the standard random biopsy group. Data were additionally stratified by prior biopsy status. Grade Group =2 was considered csPCa. Complications within 30 days of biopsy were also compared.
Results: 520 patients were included in the analysis. No demographic differences were observed (Table 1). When analyzing only MRI-bx approaches, no significant differences were observed between TP and TR on any of the outcomes of interest (Table 2). TR MRI-bx identified csPCA in 47.2% of patients, and TP MRI-bx identified csPCA in 48.6% of patients (p = 0.777); systematic-only TR biopsies identified csPCA in 34.0% of patients. 50.4% of TR MRI-bx and 54.1% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in patients on active surveillance (AS) (p = 0.589). 30.8% of TR MRI-bx and 41.0% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in patients with a prior negative biopsy (p = 0.345). 62.5% of TR MRI-bx and 43.8% of TP MRI-bx identified csPCa in biopsy-naïve patients (p = 0.194). Significant differences were observed in csPCa detection between all three approaches for AS (p = 0.013) and prior negative biopsy patients (p = 0.045), but not between MRI-TP and MRI-TR biopsies.
Conclusions: Neither the identification of csPCa by MRI-bx nor rates of complications differed significantly based on a TR or TP approach. No differences were seen between MRI-guided approaches based on prior biopsy/AS status.
Source of Funding: Unfunded



.jpg)
.jpg)