Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP09: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening I
MP09-14: Stimulated Raman Histology Allows for Rapid Pathologic Examination of Unprocessed, Fresh Prostate Biopsies
Friday, May 13, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 222
Miles P. Mannas*, Derek Jones, Fang-Ming Deng, Deepthi Hoskoppal, Jonathan Melamed, Daniel Orringer, Samir S Taneja, New York, NY
- MM
Miles Mannas, MD,MSc
Assistant Professor
University of British Columbia
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Delay between prostate biopsy (PB) and pathologic diagnosis leads to a concern of inadequate sampling and repeated biopsy. Stimulated Raman Histology (SRH) is a novel microscopic technique allowing real time, label-free, high-resolution microscopic images of unprocessed, un-sectioned tissue. We evaluated the accuracy of pathologist interpretation of PB SRH as compared to traditional hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained slides.
Methods: Men undergoing prostatectomy were included in an IRB approved prospective study. 18-gauge PB cores, taken ex vivo from prostatectomy specimen, were scanned in a SRH microscope at 20 microns depth over 10-14 minutes using two Raman shifts: 2845cm-1 and 2930cm-1, to create SRH images. The cores were then processed as per normal pathologic protocols.
16 PB containing benign/prostate cancer histology were used as a SRH training cohort for 4 GU pathologists (1, 3, 2x >15 yrs experience), who were then tested on a set of 32 PB imaged by SRH and processed by traditional H&E. Sensitivity, specificity, and concordance for PCa detection on SRH relative to a consensus H&E were assessed. With a two-sided alpha level of 5%, it was calculated 32 SRH imaged biopsies would provide 90% power to detect concordance (k).
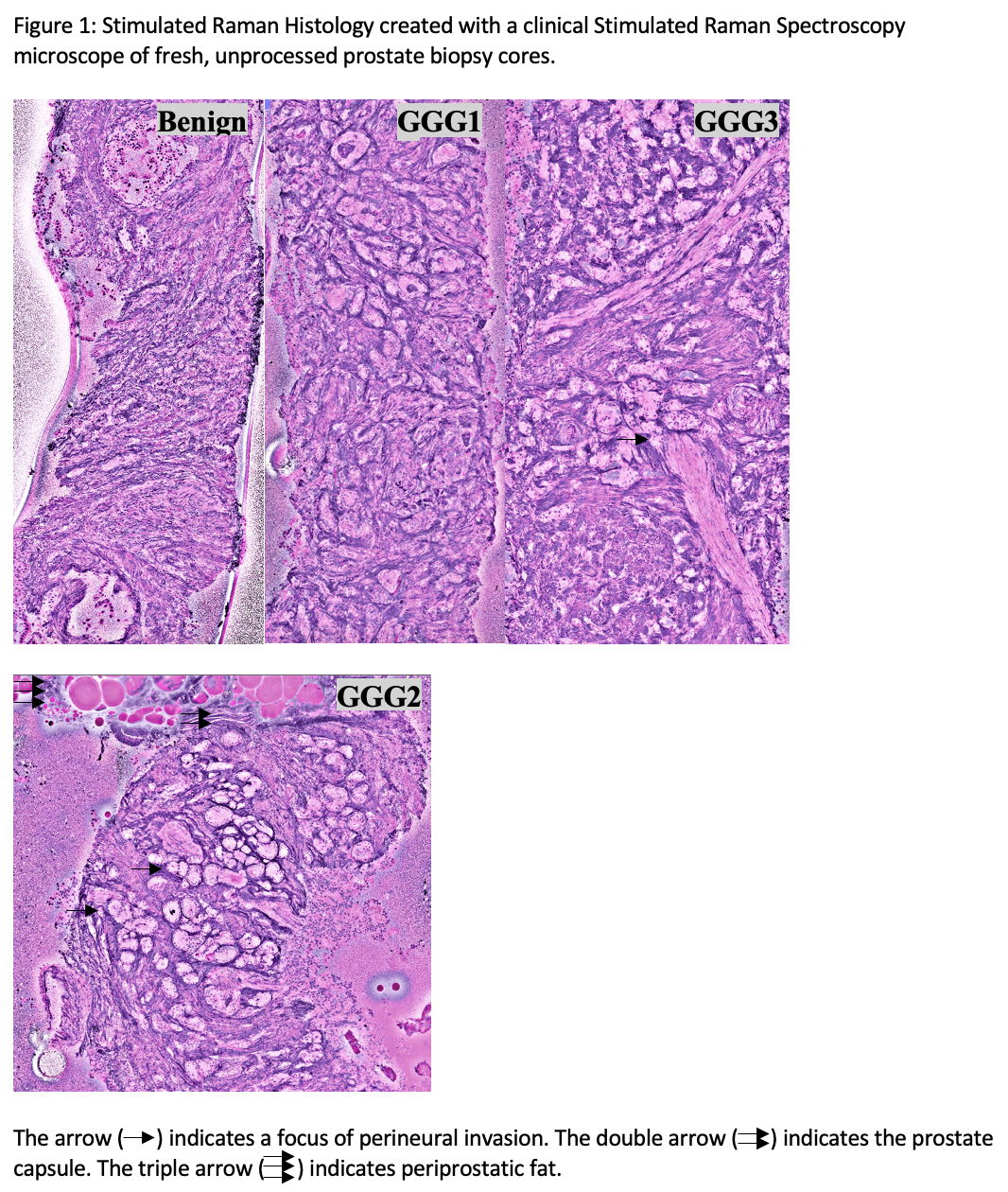
Results: PB cores were imaged in 2-3 separate strips (8-11 minutes) shown in Figure 1. In identifying any cancer, pathologists achieved moderate concordance (k=0.570; p<0.001) which improved when identifying GGG 2-5 PCa only (k=0.640, p<0001; sensitivity 96.4%; specificity 58.3%).
After individual assessment was completed a pathology consensus conference was held for the interpretation of the SRH PB. In identifying any prostate cancer, pathologists achieved near perfect concordance (k=0.925; p<0.001; sensitivity 95.6%; specificity 100%). When evaluating SRH in a consensus conference, the group prediction of Gleason score improved to moderate concordance (k=0.470; p<0.001).
Conclusions: SRH produces high quality microscopic images that allow for accurate identification of PCa in real-time without need for sectioning or tissue-processing. Individual pathologist performance varied highly suggesting potential for improvement with further training.
Source of Funding: NIH Grant: UL1TR001445
Methods: Men undergoing prostatectomy were included in an IRB approved prospective study. 18-gauge PB cores, taken ex vivo from prostatectomy specimen, were scanned in a SRH microscope at 20 microns depth over 10-14 minutes using two Raman shifts: 2845cm-1 and 2930cm-1, to create SRH images. The cores were then processed as per normal pathologic protocols.
16 PB containing benign/prostate cancer histology were used as a SRH training cohort for 4 GU pathologists (1, 3, 2x >15 yrs experience), who were then tested on a set of 32 PB imaged by SRH and processed by traditional H&E. Sensitivity, specificity, and concordance for PCa detection on SRH relative to a consensus H&E were assessed. With a two-sided alpha level of 5%, it was calculated 32 SRH imaged biopsies would provide 90% power to detect concordance (k).
Results: PB cores were imaged in 2-3 separate strips (8-11 minutes) shown in Figure 1. In identifying any cancer, pathologists achieved moderate concordance (k=0.570; p<0.001) which improved when identifying GGG 2-5 PCa only (k=0.640, p<0001; sensitivity 96.4%; specificity 58.3%).
After individual assessment was completed a pathology consensus conference was held for the interpretation of the SRH PB. In identifying any prostate cancer, pathologists achieved near perfect concordance (k=0.925; p<0.001; sensitivity 95.6%; specificity 100%). When evaluating SRH in a consensus conference, the group prediction of Gleason score improved to moderate concordance (k=0.470; p<0.001).
Conclusions: SRH produces high quality microscopic images that allow for accurate identification of PCa in real-time without need for sectioning or tissue-processing. Individual pathologist performance varied highly suggesting potential for improvement with further training.
Source of Funding: NIH Grant: UL1TR001445


.jpg)
.jpg)