Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP11: Pediatric Urology: Neurogenic Bladder, Reconstruction & Urologic Emergencies
MP11-08: Restricted Access to Mirabegron in Children with Neurogenic Bladder
Friday, May 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 225
Christopher Jaeger, Andrea Balthazar*, Caleb Nelson, Tanya Logvinenko, Hsin-Hsiao Scott Wang, Boston, MA

Andrea K. Balthazar, MD
Boston Children's Hospital Department of Urology
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Mirabegron, a beta-3 agonist, is approved to treat neurogenic bladder (NB) in children =3 years in the United States. It is efficacious with a more favorable side effect profile than anticholinergics in children with NB. Yet, some patients with NB experience coverage denials or substantial delays in starting the medication that could have deleterious effects on urologic health. Our objective was to understand the factors associated with mirabegron access at our center.
Methods: Institutional data was queried identifying all pediatric patients who were prescribed mirabegron from 2012 through 2021. Covariates included patient demographics, neurologic diagnosis, number of anticholinergic medications, mirabegron prescription & start date, insurance, and insurance-related communications. A multivariate logistic regression model was fitted to investigate the impact of various factors on restricted access. Restricted access is defined as insurance denial or a delay in the mirabegron start date by =30 days from the initial prescription date.
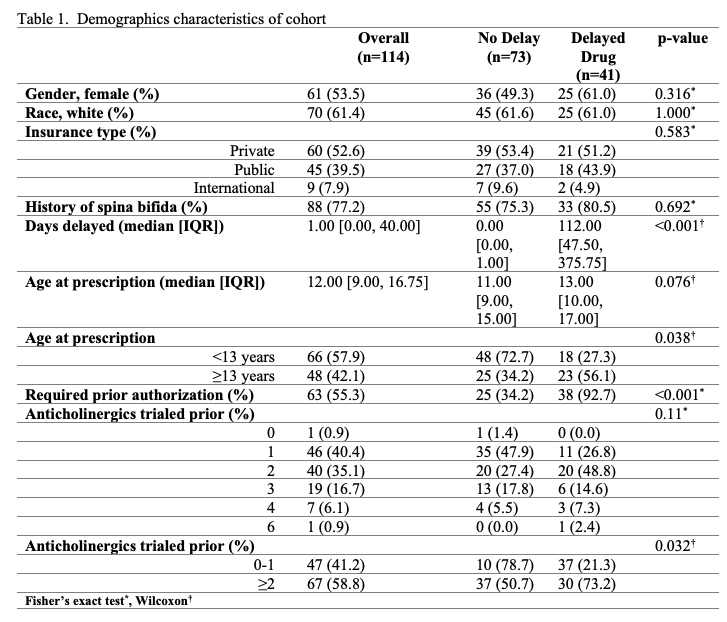
Results: 114 pediatric patients with NB, 88/114 (77%) with a spina bifida diagnosis, were prescribed mirabegron after its release in 2012. The median age at first mirabegron prescription was 12 years (IQR 9-17). 41 patients (36%) experienced restricted access to mirabegron - 29 were denied and 12 were delayed. For those whose access was restricted, the median overall delay was 112 days (IQR: 48-376) following the initial prescription vs 0 days (IQR: 0-1) for those whose access was not restricted. After adjusting for age and number of trialed anticholinergics, undergoing a prior authorization (PA) with an insurance provider (OR=24.0 (95% CI 7.5-109.0), p<0.001) was the only predictor significantly associated with restricted mirabegron access. Being 13 years or older was marginally associated with restricted access (OR= 2.5 (95% CI: 1.0-7.0), p=0.06).
Conclusions: Mirabegron is an effective medication now approved for the treatment of pediatric NB. Over one-third of our NB patients have experienced significant barriers to mirabegron access at our institution. The need for PA was identified as the most significant risk factor associated with restricted access. Payor-mandated restrictions on mirabegron require patients to fail inferior medications and ultimately risk inadequate treatment.
Source of Funding: N/A
Methods: Institutional data was queried identifying all pediatric patients who were prescribed mirabegron from 2012 through 2021. Covariates included patient demographics, neurologic diagnosis, number of anticholinergic medications, mirabegron prescription & start date, insurance, and insurance-related communications. A multivariate logistic regression model was fitted to investigate the impact of various factors on restricted access. Restricted access is defined as insurance denial or a delay in the mirabegron start date by =30 days from the initial prescription date.
Results: 114 pediatric patients with NB, 88/114 (77%) with a spina bifida diagnosis, were prescribed mirabegron after its release in 2012. The median age at first mirabegron prescription was 12 years (IQR 9-17). 41 patients (36%) experienced restricted access to mirabegron - 29 were denied and 12 were delayed. For those whose access was restricted, the median overall delay was 112 days (IQR: 48-376) following the initial prescription vs 0 days (IQR: 0-1) for those whose access was not restricted. After adjusting for age and number of trialed anticholinergics, undergoing a prior authorization (PA) with an insurance provider (OR=24.0 (95% CI 7.5-109.0), p<0.001) was the only predictor significantly associated with restricted mirabegron access. Being 13 years or older was marginally associated with restricted access (OR= 2.5 (95% CI: 1.0-7.0), p=0.06).
Conclusions: Mirabegron is an effective medication now approved for the treatment of pediatric NB. Over one-third of our NB patients have experienced significant barriers to mirabegron access at our institution. The need for PA was identified as the most significant risk factor associated with restricted access. Payor-mandated restrictions on mirabegron require patients to fail inferior medications and ultimately risk inadequate treatment.
Source of Funding: N/A


.jpg)
.jpg)