Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP21: Sexual Function/Dysfunction: Evaluation I
MP21-08: Masturbatory Orgasm Parameters of Sexually Active Cisgender Men and Women
Saturday, May 14, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 222
Jenna Stelmar*, Michael Zaliznyak, Los Angeles, CA, Dylan Isaacson, Chicago, IL, Erin Duralde, Boston, MA, Thomas Gaither, Shannon Smith, Nance Yuan, Los Angeles, CA, Kimberly Topp, San Francisco, CA, Maurice Garcia, Los Angeles, CA

Jenna Stelmar, BS
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Sexual function has a significant effect on quality of life and is often characterized by orgasm. Anecdotally, cisgender men (CM) and cisgender women (CW) describe their experience of orgasm differently. Despite this, there is a gap in the medical literature to quantify and define these differences. The aim of this study is to address this gap by assessing orgasm parameters and sexual satisfaction amongst sexually active CM and CW.
Methods: A 15-minute survey was administered to anonymous respondents via Qualtrics®, an online survey platform. Questions queried (1) frequency of masturbation, (2) lead-time to orgasm, (3) duration of orgasm, (4) average refractory period between orgasms, (5) experience of orgasm as single or multiple peaks, and (6) satisfaction with orgasm. Orgasm parameters were assessed under the uniform condition of self-stimulation. Chi-squared and two-tailed t-tests (a=0.05) were used to compare differences that exist between CM and CW.
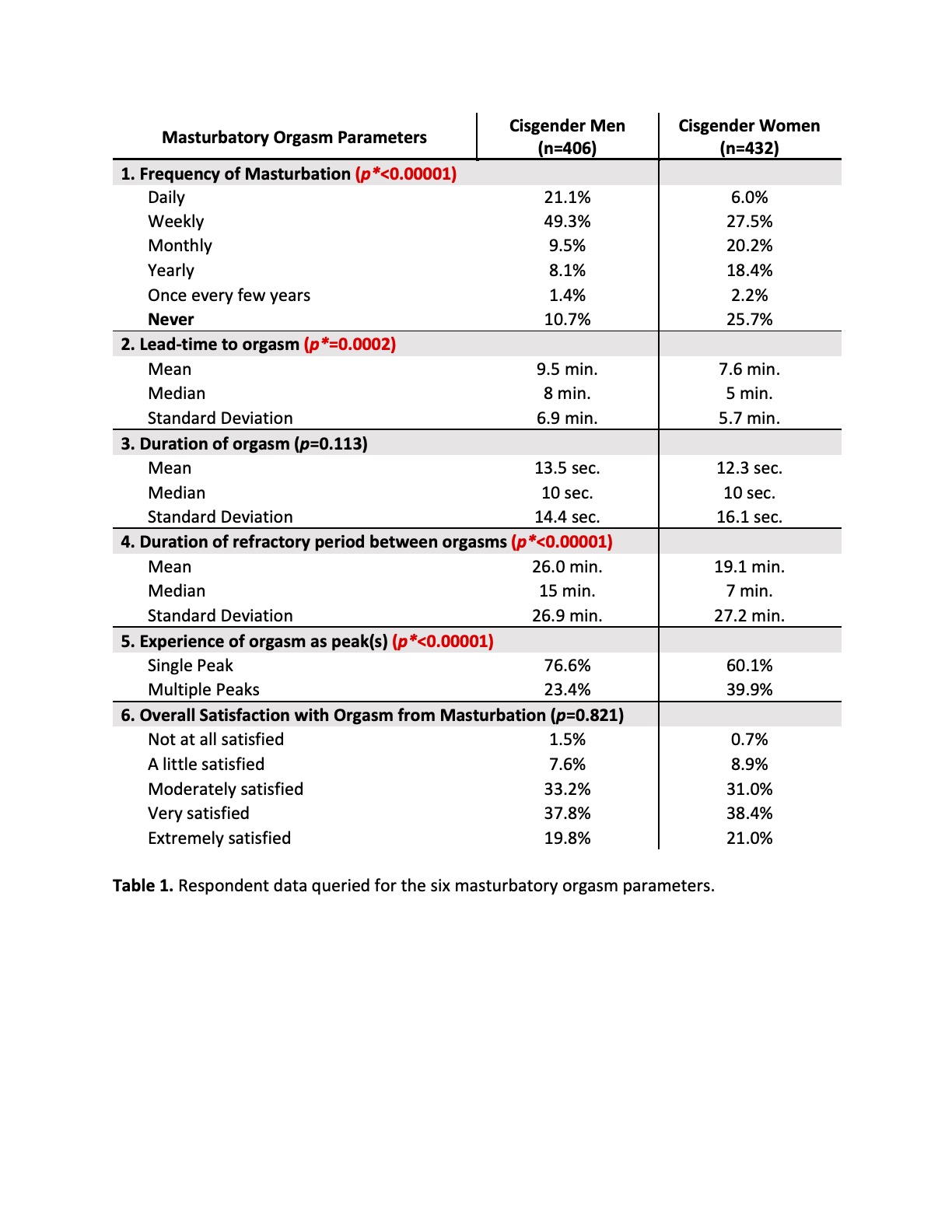
Results: A sample of 406 sexually active CM (mean age ± SD, 47.8 ± 16.9 years) and 432 sexually active CW (48.9 ± 15.5 years) completed the survey. Significantly more CM reported masturbating compared to CW (CM 89.3% vs. CW 74.3%, p<0.00001). CM also reported greater lead-time to orgasm (CM 9.5 ± 6.9 min. vs. CW 7.6 ± 5.7 min., p=0.0002) and longer refractory periods between orgasms (CM 26.0 ± 26.9 min. vs. CW 19.1 ± 27.2 min., p<0.00001). Furthermore, significantly more CW reported experiencing orgasm as multiple peaks (CW 39.9% vs. CM 23.4%, p<0.00001). There were no significant differences in the duration of orgasm sensation (CM 13.5. ± 14.4 sec. vs. CW 12.3 ± 16.1 sec., p=0.113) or satisfaction with orgasm achieved from self-stimulation (Table 1).
Conclusions: Our large sample of sexually active CM and CW showed a statistically significant difference in four out of six masturbatory orgasm parameters: frequency of masturbation, lead-time to orgasm, duration of refractory period between orgasms, and the experience of single versus multiple peaked orgasms. Results also varied within groups, which indicates the highly variable nature of sexual function and satisfaction amongst individuals—both within and across genders.
Source of Funding: SMSNA Scholars in Sexuality Research Grants Program
Methods: A 15-minute survey was administered to anonymous respondents via Qualtrics®, an online survey platform. Questions queried (1) frequency of masturbation, (2) lead-time to orgasm, (3) duration of orgasm, (4) average refractory period between orgasms, (5) experience of orgasm as single or multiple peaks, and (6) satisfaction with orgasm. Orgasm parameters were assessed under the uniform condition of self-stimulation. Chi-squared and two-tailed t-tests (a=0.05) were used to compare differences that exist between CM and CW.
Results: A sample of 406 sexually active CM (mean age ± SD, 47.8 ± 16.9 years) and 432 sexually active CW (48.9 ± 15.5 years) completed the survey. Significantly more CM reported masturbating compared to CW (CM 89.3% vs. CW 74.3%, p<0.00001). CM also reported greater lead-time to orgasm (CM 9.5 ± 6.9 min. vs. CW 7.6 ± 5.7 min., p=0.0002) and longer refractory periods between orgasms (CM 26.0 ± 26.9 min. vs. CW 19.1 ± 27.2 min., p<0.00001). Furthermore, significantly more CW reported experiencing orgasm as multiple peaks (CW 39.9% vs. CM 23.4%, p<0.00001). There were no significant differences in the duration of orgasm sensation (CM 13.5. ± 14.4 sec. vs. CW 12.3 ± 16.1 sec., p=0.113) or satisfaction with orgasm achieved from self-stimulation (Table 1).
Conclusions: Our large sample of sexually active CM and CW showed a statistically significant difference in four out of six masturbatory orgasm parameters: frequency of masturbation, lead-time to orgasm, duration of refractory period between orgasms, and the experience of single versus multiple peaked orgasms. Results also varied within groups, which indicates the highly variable nature of sexual function and satisfaction amongst individuals—both within and across genders.
Source of Funding: SMSNA Scholars in Sexuality Research Grants Program


.jpg)
.jpg)