Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP21: Sexual Function/Dysfunction: Evaluation I
MP21-11: Severity of Penile Curvature in Peyronie's Disease does not Corelate with SHIM or PDQ Scores
Saturday, May 14, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 222
Thomas Masterson*, Isaac Zucker, Pranusha Atuluru, Emad Ibrahim, Manuel Molina, Bruce Kava, Ranjith Ramasamy, Miami, FL

Thomas A. Masterson, III, MD
University of MIami
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Peyronie’s disease (PD) is heterogeneous condition that negatively affects quality of life and sexual function. Although severity of curvature is often used to characterize the disease, other objective measures to describe severity can be used, including Sexual inventory for men (SHIM), penile vascular examination, and Peyronie’s disease questionnaire (PDQ) score. We hypothesized that SHIM and PQD will be strongly negative and positively corelated, respectively
Methods: We retrospective examined a prospectively collected database that captured all men presenting with PD from November 2018 to 2020. At baseline penile doppler examination examination, men received IIEF and PDQ questionnaires. Curvature and vascular parameters were measured after injection of intracavernosal trimix. Curvature was measured by one technician using a goniometer. Results were plotted with curvature measurement as the independent variable. Microsoft excel was used to determine R2 values for SHIM, peak systolic velocity end diastolic velocity and PDQ score. to determine linear coefficients
Results: We identified 42 men with complete data. No measurement was strongly correlated to curvature (Figure 1). Of all measurements, PDQ had the strongest positive correlation with R2=0.12, the remaining were all R2 <0.05.
Conclusions:
Conclusions: In our small cohort of 42 we did not find any strong correlation between curvature, SHIM, penile vascular parameters or PDQ sore. Therefore, curvature alone is not sufficient to define disease severity or bother. Detailed history taking is critical to determine management strategy.
Source of Funding: ISR from Endo Pharmaceuticals
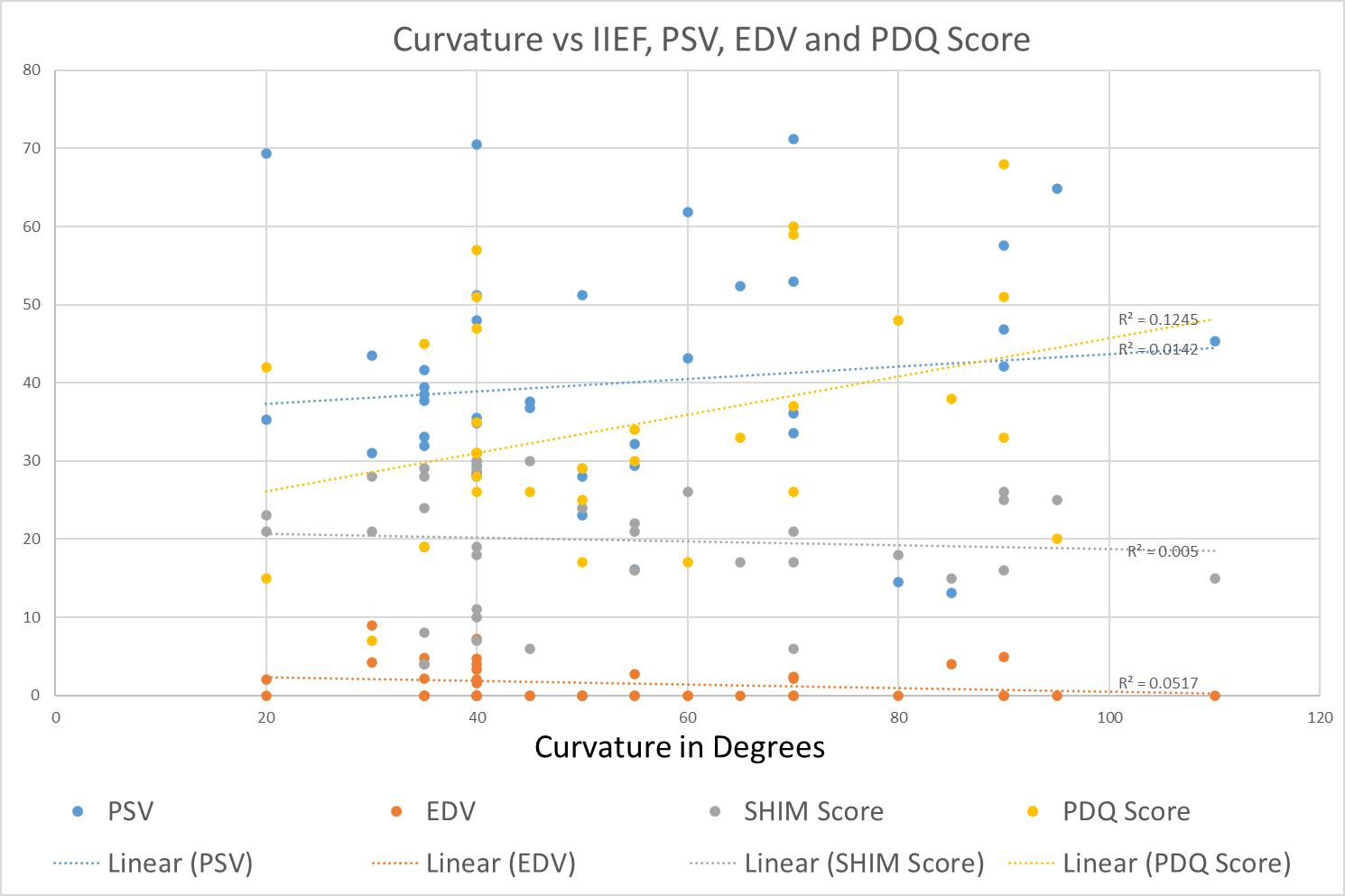
Methods: We retrospective examined a prospectively collected database that captured all men presenting with PD from November 2018 to 2020. At baseline penile doppler examination examination, men received IIEF and PDQ questionnaires. Curvature and vascular parameters were measured after injection of intracavernosal trimix. Curvature was measured by one technician using a goniometer. Results were plotted with curvature measurement as the independent variable. Microsoft excel was used to determine R2 values for SHIM, peak systolic velocity end diastolic velocity and PDQ score. to determine linear coefficients
Results: We identified 42 men with complete data. No measurement was strongly correlated to curvature (Figure 1). Of all measurements, PDQ had the strongest positive correlation with R2=0.12, the remaining were all R2 <0.05.
Conclusions:
Conclusions: In our small cohort of 42 we did not find any strong correlation between curvature, SHIM, penile vascular parameters or PDQ sore. Therefore, curvature alone is not sufficient to define disease severity or bother. Detailed history taking is critical to determine management strategy.
Source of Funding: ISR from Endo Pharmaceuticals


.jpg)
.jpg)