Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP23: Bladder Cancer: Invasive III
MP23-02: Early Oncologic outcomes of Open vs Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy with totally intracorporeal Urinary Diversion: single centre prospective randomised controlled trial
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Riccardo Mastroianni*, Gabriele Tuderti, Umberto Anceschi, Alfredo Maria Bove, Aldo Brassetti, Mariaconsiglia Ferriero, Leonardo Misuraca, Salvatore Guaglianone, Michele Gallucci, Giuseppe Simone, Rome, Italy
- RM
Riccardo Mastroianni, MD
IRCCS
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Radical Cystectomy (RC) with urinary diversion (UD) is still considered a complex surgery associated with significant morbidity. Open radical cystectomy (ORC) remains the reference option of treatment, even if adoption of robot-assisted RC (RARC) is rapidly increasing. Two-yrs oncologic outcomes proved to be predictive of long term oncologic outcomes in historical series. In this study, we assessed early oncologic outcomes from a randomised controlled trial (RCT) comparing ORC and RARC with totally intracorporeal (i) urinary diversion (UD) (Clinical Trials: NCT03434132).
Methods: Institutional review board approval was obtained. Patients were eligible for randomization if they had a diagnostic TURBt with cT2-4, cN0, cM0, or recurrent HG NMIBC and no anesthesiologic contraindications to robotic surgery. Between January 2018 and September 2020, patients were enrolled with a covariate adaptive randomization process based on the following variables: BMI, ASA score, preoperative haemoglobin, UD (Padua ileal bladder or ileal conduit), neoadiuvant chemotherapy and cT-stage. Aim of this study was to evaluate oncologic outcomes: overall survival (OS), cancer specific survival (CSS), disease free survival (DFS) and metastasis free survival (MFS). Continuous and categorical variables were compared using Student t and Chi-Square tests, respectively. Kaplan-Meier (KM) method and the log-rank test were applied to assess survival outcomes.
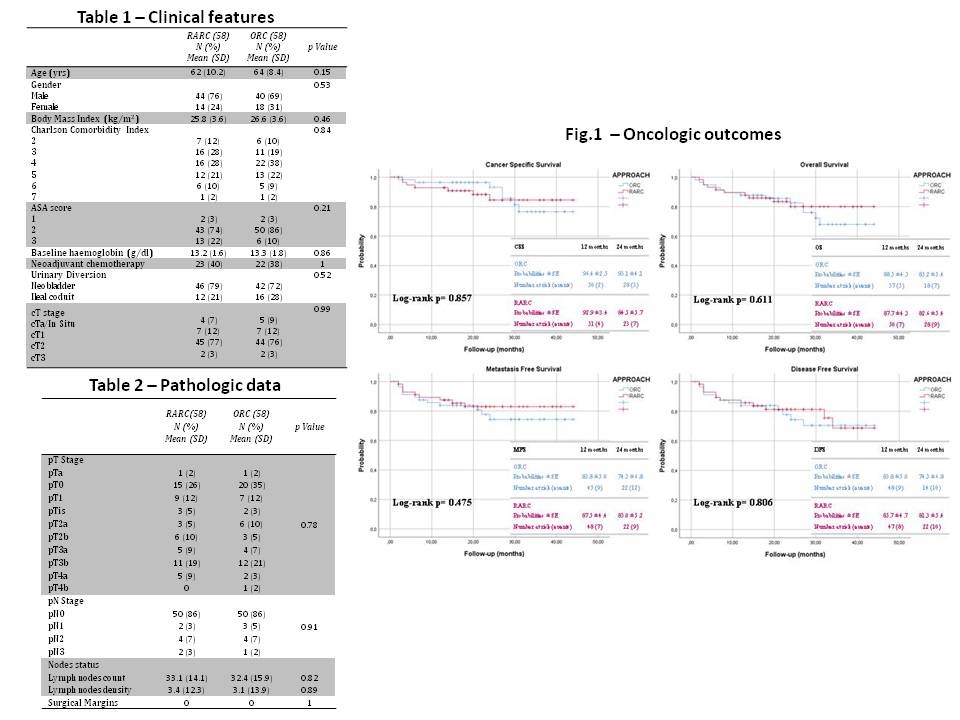
Results: Overall, 116 patients were enrolled (RARC: 58 vs ORC: 58). Both groups were homogeneous for all clinical features (all p>0.15) (Tab.1). In the robotic group, UD was performed in all cases with a totally intracorporeal approach, with no need of open conversion. Pathologic data were reported (Tab.2). Overall, 23 (19.9%) patients had a high-risk non-muscle invasive BC. Homogeneous distribution of cT stages was confirmed at final pT-stages (p=0.78) and pN-stages (p=0.91). Soft tissue surgical margins were negative in all cases. Two patients were lost to follow-up, one for each arm. At a median follow-up of 22 mo (IQR 15-31), KM analysis displayed comparable OS, CSS, DFS and MFS probabilities (Fig.1).
Conclusions: This RCT confirms comparable oncologic outcomes between ORC and RARC with totally iUD.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: Institutional review board approval was obtained. Patients were eligible for randomization if they had a diagnostic TURBt with cT2-4, cN0, cM0, or recurrent HG NMIBC and no anesthesiologic contraindications to robotic surgery. Between January 2018 and September 2020, patients were enrolled with a covariate adaptive randomization process based on the following variables: BMI, ASA score, preoperative haemoglobin, UD (Padua ileal bladder or ileal conduit), neoadiuvant chemotherapy and cT-stage. Aim of this study was to evaluate oncologic outcomes: overall survival (OS), cancer specific survival (CSS), disease free survival (DFS) and metastasis free survival (MFS). Continuous and categorical variables were compared using Student t and Chi-Square tests, respectively. Kaplan-Meier (KM) method and the log-rank test were applied to assess survival outcomes.
Results: Overall, 116 patients were enrolled (RARC: 58 vs ORC: 58). Both groups were homogeneous for all clinical features (all p>0.15) (Tab.1). In the robotic group, UD was performed in all cases with a totally intracorporeal approach, with no need of open conversion. Pathologic data were reported (Tab.2). Overall, 23 (19.9%) patients had a high-risk non-muscle invasive BC. Homogeneous distribution of cT stages was confirmed at final pT-stages (p=0.78) and pN-stages (p=0.91). Soft tissue surgical margins were negative in all cases. Two patients were lost to follow-up, one for each arm. At a median follow-up of 22 mo (IQR 15-31), KM analysis displayed comparable OS, CSS, DFS and MFS probabilities (Fig.1).
Conclusions: This RCT confirms comparable oncologic outcomes between ORC and RARC with totally iUD.
Source of Funding: none


.jpg)
.jpg)